Solid Waste Management Market Report Scope & Overview:
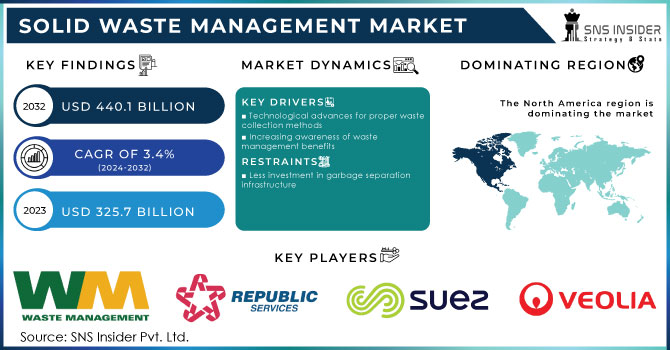
The Solid Waste Management Market Size was valued at USD 325.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 440.1 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 3.4% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Get E-PDF Sample Report on Solid Waste Management Market - Request Sample Report
The solid waste management market is considering that increased awareness globally about waste management, constantly changing regulatory frameworks, and increased environmental sensitivity. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, solid waste management incorporates core activities, important among them being waste materials collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and waste disposal. Activities like these are strictly regulated to ensure environmental protection along with public health. According to EPA guidelines, effective solid waste management systems are supposed to have measures for waste reduction, including source separation and recycling to reduce impacts on the environment.
Solid waste management legislation in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia is extremely strict. The provincial government, through the Nova Scotia Solid Waste-Resource Management Regulations, demands the implementation of almost all-inclusive solid waste management practices. Its key focus areas are waste generation reduction, promotion of recycling, and composting. Success has been fantastic regarding the diversion of a big percentage of the stream, and it acts as an example to other jurisdictions. It underlines the impacts that regulatory frameworks have on setting up sustainable waste management practices.
Solid waste management is one of the areas of current research recently published within the ASCE Library. It discusses generally emerging trends and how, bit by bit, there is a preference for waste-to-resource technologies. Indeed, the study shows a tendency towards more sustainability with regard to making waste into something other than garbage. Driving this paradigm shift is an increasing realization that there is value in waste, on one hand, and the need to reduce the environmental footprint, on the other hand, created by existing waste management practices. Central to this transition are innovations, including anaerobic digestion, waste-to-energy technologies, and advanced recycling methods.
Among recent reports, the United Nations Environment Programme, for example, calls for a global shift beyond the traditional ways of managing waste towards seeing waste as a resource. It sought to emphasize the urgency of moving towards circular economy principles, which focus on the reuse, recycling, and recovery of materials. UNEP called for systemic changes that couple waste management into broad sustainability aspirations and urged countries into more holistic and innovative directions with investments in waste management. There is a need for this shift to deal with the spiraling global waste crisis and in the quest for future long-term environmental sustainability.
The growth in the Solid Waste Management Market is coupled with increasing regulatory demands, improving with every advance in technology. Courses of action that reduce waste, imposed regulations related to these, and innovative technologies converting waste into resources account for the significant changes toward sustainable waste management. Giving priority to waste as a resource and applying the principles of the Circular Economy gives momentum to a worldwide commitment in search of less intrusive processes into the environment, moving toward sustainability.
Solid Waste Management Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
-
Growing urbanization increases solid waste generation, driving demand for efficient waste management solutions and infrastructure expansion
Increased urbanization involves growing population densities that heavily contribute to the increase in the generation of solid wastes and, thus demands better approaches towards waste management and expansion of such infrastructure. This means that the rapid growth of metropolitan centers like Bangalore and Jakarta results in growing populations and a rapid expansion of urban activities that increase the production of waste. This growing quantum of waste requires the simultaneous development and management of waste that must be capable of treating varied waste streams efficiently. For this, cities like San Francisco and Tokyo have adopted different kinds of waste segregation at source initiatives, coupled with highly advanced waste processing and recycling facilities that can manage the various streams of waste generated. Besides, infrastructure expansion is required: cities build landfills, waste treatment facilities, and recycling centers to serve the constantly growing volumes of waste. More and more urban areas introduce smart technologies of waste management, such as sensor-equipped bins and data analytics, which enhance the efficiency of waste collection and treatment processes. Besides demands driven by this growing urban population, it is important to remind ourselves that such innovations make necessary the ingraining of sustainable practices for minimal impact on the environment and better urban livability.
-
Advancements in recycling technologies enhance waste diversion rates and resource recovery, boosting market growth and sustainability efforts
Waste diversion rates and resource recovery have improved greatly due to improvements in the technologies employed for recycling, therefore giving much significance to the market growth and supporting sustainable development. Advanced sensors and artificial intelligence use automation sorting systems that sort recyclable materials from combined waste streams more proficiently, hence boosting the purity and quality of resultant recycled materials. Advanced optical sorting at recycling plants sorts plastics by type far more accurately, hence increasing the rate of recycling while reducing contamination. In addition, major chemical recycling breakthroughs - techniques that degrade plastics into their basic monomers for re-polymerization - promise ways to handle complex, mixed plastic items that conventional mechanical recycling methods cannot cope with. Examples include companies like Loop Industries, which have adopted the technology to reprocess waste plastics into high-quality resin suitable for manufacturing new products. Second, there are efficient composting technologies, such as in-vessel composting systems, designed to hasten the decomposition of organic wastes into valuable compost available for agricultural uses. Both these factors help to improve the efficiency of recycling processes and the volume of waste that is sent for landfill disposal, therefore reinforcing the principles of a circular economy in broader environmental sustainability. With technological growth comes increased investment in newer infrastructure as well as operational practices that are instrumental in developing market expansion through embedding commitment to waste reduction and resource conservation.
Restraint:
-
High costs associated with waste management infrastructure and technology may limit adoption, especially in developing regions with constrained budgets
The costs regarding infrastructures and technologies for waste management may be so high to the extent that they become a major restraint to the growth of the solid waste management market, particularly in developing regions with limited financial resources. Advanced waste treatment plants alone require huge capital investment in terms of construction, equipment, and maintenance for establishing modern facilities such as those generating energy from waste or sophisticated recycling systems. These high capital costs could be very discouraging for governments and the private sector, especially in regions with tight budgets, such as most areas of sub-Saharan Africa or rural parts of South Asia. Because of this, waste management practices in such places continue to be very rudimentary or obsolete; open dumping or unsanitary landfills are some of the most common practices that have negative impacts on the environment and public health. This financial limitation also restrains the implementation of full-fledged waste management programs that can be expected to improve waste diversion rates and recover valuable resources, thereby impeding progress toward sustainable waste management solutions.
Opportunity:
-
Emerging innovations in waste-to-energy technologies present opportunities for converting waste into valuable energy sources, reducing landfill dependency
The emerging waste-to-energy technologies provide a large pathway to convert wastes into useful energy resources, reducing landfills, while answering energy demands sustainably. Improved anaerobic digestion and gasification technologies can take organic waste, among other feedstocks, into biogas or syngas for power generation and heat. These technologies not only help in handling waste better by diverting waste from landfills but also provide a renewable energy source that can go into the local grids. Facilities implemented by companies like Covanta in the United States and Enerkem in Canada represent an efficient way of waste-to-energy systems that convert municipal solid wastes into clean energy, reducing the environmental consequence of waste while providing an alternative to fossil fuels. The valuation of waste is, therefore, in good accord with the circular economy principle as a practical solution that could work for both developed and developing regions in managing those challenges more effectively.
Challenge:
-
Managing the increasing complexity of waste streams, including hazardous and electronic waste, poses significant logistical and environmental challenges for the industry
Management of increasing complexity in the composition of these streams-particularly hazardous and electronic wastes-presents significant logistical and environmental hurdles to the industry of solid waste management. For instance, hazardous waste produced through chemical or pharmaceutical products entails specialized handling and disposal practices that avoid land and water contamination with associated risks to human life using often costly and highly regulated processes. There is a lot of electronic waste that includes many types of materials, from metals to plastics and circuit boards, which are made of toxic components like lead and mercury that can leach into the environment if there is no appropriate management. Advanced technology and expertise in safely dismantling, recycling, or disposing of these materials make it more expensive and involve complex logistics. Facilities have to therefore employ efficient sorting, treatment, and processing for various types of wastes that burden infrastructure and other resources. This has been exacerbated by the speed at which technology is still evolving, where new electronic device types and materials keep emerging, demanding updates in the solution for their waste management.
Solid Waste Management Market Segments
By Waste
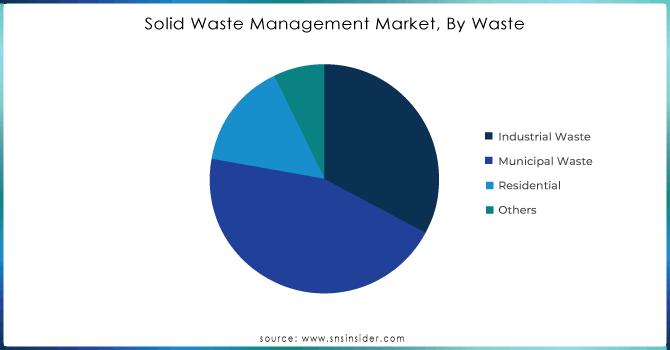
Municipal Waste dominated the market in 2023, with an approximate revenue share of 45%. It includes household wastes generated through domestic activities or households, commercial wastes generated through commercial activities or commercial establishments, and institutional wastes coming from institutional sources. The increasing urbanization and higher population densities in urban agglomerations contribute to the high-volume share of municipal waste, generating large volumes of waste in cities and towns. For instance, large cities like New York and Tokyo face serious problems in managing waste disposal processes due to the huge amounts produced every day. Besides, municipal solid waste management systems involve complex efforts in both waste collection and recycling procedures as well as appropriate disposal practices that ensure urban cleanliness and environmental hygiene. This commanding position signifies the normality of the demand for effective waste management activities on behalf of the highly concentrated human population.
Get Customized Report as Per Your Business Requirement - Request For Customized Report
By Material
In 2023, the Plastics segment dominated the Solid Waste Management Market, which is estimated to capture approximately 35% market share. The largest category of waste materials is plastics, which come from their wide usage in households and are unable to decompose quickly; hence, they further build up in landfills and within the environment. For instance, in cities like Los Angeles and Mumbai, a substantial fraction of municipal streams consists of plastic waste emanating from packaging, bottles, and carry bags. Different types, with complicating factors in single-use plastics and mixed materials, further raise the challenge in plastics management. The dominance underlines the urgent need for better management strategies and technologies to handle the environmental impact of plastic waste with greater efficiency in recycling.
By Treatment Method
The Disposal segment dominated the Solid Waste Management Market in 2023, with a share of about 40%. Among these, open dumping and landfilling are very common due to their uses and relative simplicity compared to other methods. For example, in growing cities like Manila and Lagos, landfills are going to be a key strategy for dealing with waste due to the limited infrastructure and high costs associated with advanced processing technologies. Even though such methods of landfilling raise serious environmental and health concerns, such as soil and water contamination, they are common because they tend to offer a fairly practical solution for managing large volumes of waste. The dominant segment has been observed to be disposal, underlining the very real need for further improving waste management practices and technologies that could contribute to the reduction of negative impacts from landfills and increasing efficiency in general.
Regional Analysis
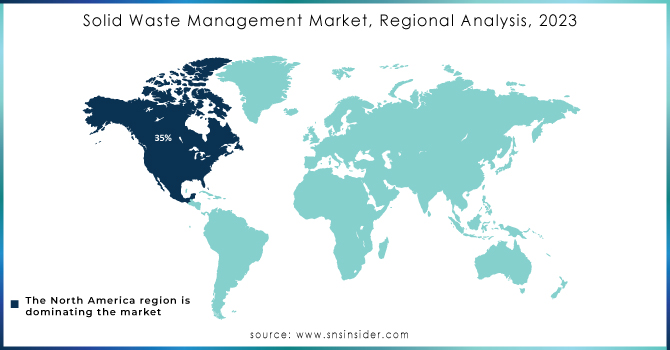
North America dominated and accounted for the largest share in the Solid Waste Management Market in 2023 at about 35%. Advanced infrastructure and strong waste management infrastructures within the region have been highly influenced by high waste generation rates and equally stringent regulatory frameworks. For instance, overall waste management practices, such as comprehensive recycling programs and modern landfill technologies that achieve very low environmental impacts, have so far been developed in the United States and Canada. Discarding the trash and recycling, thereby keeping it away from passing on into landfills, has been boosted across cities like New York and Toronto, making North America the leading hub. The region's emphasis on all things sustainable and the level of tech innovation in the waste management industry make dominance within the global market greatly possible for the region.
Key Players
Waste Management Inc, Republic Services, SUEZ, Veolia, Biffa PLC, Clean Harbors, Covanta Holding, Daiseki, Hitachi Zosen, Stericycle Inc. and other key players are mentioned in the final report.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
August 2024: The committee of the Seneca County Board of Supervisors moved an updated solid waste management plan to be put to a public hearing to address local waste management concerns and improve waste disposal and recycling methods.
-
June 2024: Waste Management Inc. completed the acquisition of Stericycle's medical waste services for $7.2 billion aimed at enhancing the company's medical waste handling to further consolidate its leading position in the market.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 325.7 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 440.1 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 3.4% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | •By Waste (Industrial Waste, Municipal Waste, Residential, Others) •By Material (Organic Matters, Plastics, Paper & Paperboard, Glass & Metal, Others) •By Treatment Method (Collection, Processing {Recycling, Compositing}, Disposal {Open Dump & Landfilling, Incineration, Others}) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Waste Management Inc, Republic Services, SUEZ, Veolia, Biffa PLC, Clean Harbors, Covanta Holding, Daiseki, Hitachi Zosen, Stericycle Inc. and other key players |
| Key Drivers | • Growing urbanization increases solid waste generation, driving demand for efficient waste management solutions and infrastructure expansion • Advancements in recycling technologies enhance waste diversion rates and resource recovery, boosting market growth and sustainability efforts |
| RESTRAINTS | • High costs associated with waste management infrastructure and technology may limit adoption, especially in developing regions with constrained budgets |

