Logistics Robots Market Report Scope and Overview:
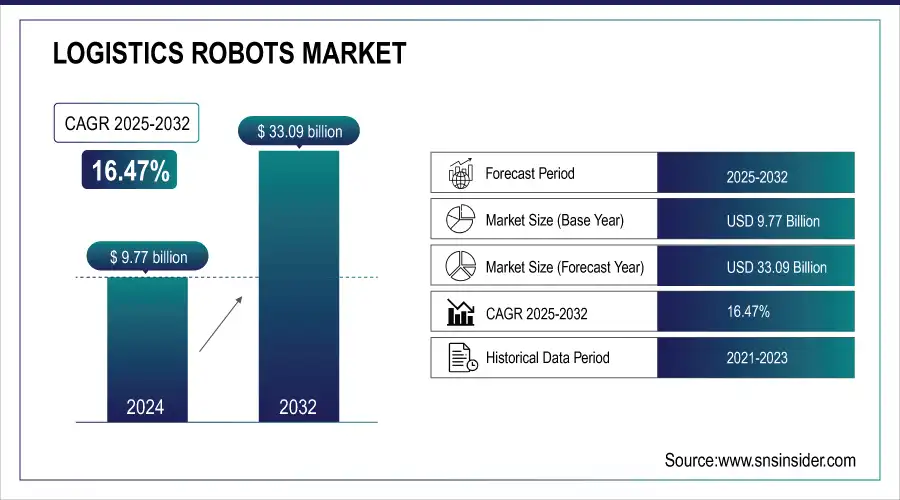
The Logistics Robots Market size was valued at USD 9.77 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 33.09 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 16.47% over the forecast period 2025-2032.
To Get more information on Aviation Crew Management Systems Market - Request Free Sample Report
The logistics robots market has experienced substantial growth due to rapid advancements in automation technologies and a growing need for effective supply chain operations. These robots are created to increase efficiency, cut down on expenses, and boost precision in duties like choosing, organizing, and moving items in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants. For instance, there has been substantial growth in the U.S. e-commerce sector in the past few years. E-commerce sales make up a significant share of this industry, comprising about 22% of all retail sales in the U.S. in 2023. The average order value for online shopping purchases was around USD 90 in the year 2023. Due to the rise in e-commerce, businesses are facing great demands to fulfill customer desires for quicker shipping, sometimes even on the same day. In order to fulfill these requirements, companies have been making significant investments in automation solutions, such as logistics robots.
Logistics Robots Market Size and Forecast:
-
Market Size in 2024: USD 9.77 Billion
-
Market Size by 2032: USD 33.09 Billion
-
CAGR: 16.47% from 2024 to 2032
-
Base Year: 2024
-
Forecast Period: 2025–2032
-
Historical Data: 2021–2023
Logistics Robots Market Highlights:
-
Logistics robots ensure timely delivery of components to production lines, improving efficiency, handling bulky or hazardous items, and reducing risks to human workers
-
Enhanced sensors, AI, and machine learning enable robots to navigate warehouses autonomously, detect obstacles, and optimize operations over time
-
Automation of tasks such as inventory management, sorting, packing, and transport reduces human error, increases accuracy, and allows 24/7 operations
-
AI and machine learning help robots learn from past tasks, refine strategies, and adapt to dynamic environments, enhancing overall logistics performance
-
Incorporating robots into existing supply chain and warehouse systems can be complex, requiring custom software, operational reconfiguration, and staff training
-
Initial robot costs, system upgrades, and potential operational disruptions can be significant, particularly for companies with outdated infrastructure or limited technical expertise
Logistics robots are essential in just-in-time inventory systems within the manufacturing industry. Government funding in the manufacturing industry in the United States has been strong and diverse in the past few years, indicating a deliberate effort to rejuvenate and progress the sector. The Manufacturing USA institutes received more than USD 1 billion in funding from the federal government. The CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 is a notable recent investment, providing USD 52 billion for the development and research of semiconductors. This legislation seeks to enhance local semiconductor manufacturing and reinforce supply chains, demonstrating a commitment to advanced manufacturing industries. These systems depend on accurate timing and coordination to guarantee the delivery of components and materials to the production line at the exact moment required. Logistics robots streamline the transportation of items from warehouses to assembly lines, promoting efficient processes and reducing delays. Furthermore, these robots can manage dangerous substances or bulky objects, minimizing the potential for harm to human employees.
Logistics Robots Market Drivers:
-
Technological advancements in robotics technology, such as enhanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
The logistics robot market is growing due to factors such as technological upgradation in robotics technology, especially enhanced sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. Robots can now move more effectively within warehouses and distribution centers, working autonomously with greater flexibility thanks to also improved sensors. With these sensors, the creations can detect obstacles and, in some cases, get feedback on their surroundings at runtime to adapt accordingly, thus reducing human oversight while minimizing error.
Logistics robots now come equipped with AI and machine learning tools, enhancing their ability to remember past events and adjust over time. Using AI-driven algorithms, robots can perform logical decisions related to dynamic environments like sorting or picking and mobility of goods faster and more accurately. These robots learn from every completed task, in areas Machine Learning comes into play to optimize performance by using data extracted from previous work executed and thus refine strategies for operations that are yet scheduled. This makes the processes of logistics robots more adjustable to different requirements and operational aspects.
-
Logistics robots boost operational efficiency and cost savings by automating processes.
Logistics robots can automate a large number of processes, which were previously handled by human labor directly to provide benefits in terms of operational efficiency and cost savings for the logistics industry. These robots optimise a set of workflows including inventory management, sorting, packing and transport, allowing for faster and more accurate operations. Because logistics robots eliminate the human factor, they are less prone to mistakes that might happen due to tiredness or simply missing something and increase precision when it comes down to issues like picking orders fast enough and keeping inventories in line.
Moreover, the installation of logistics robots for automation helps to work 24 hours a day as these is not associated with human job timings, and hence productivity will be improved. This is something important in a high-demand environment like e-commerce where both speed and accuracy are critical to customer satisfaction.
Logistics Robots Market Restraints:
-
Integrating logistics robots into current supply chain and warehouse management systems can be difficult and time-consuming.
Incorporating logistics robots into current supply chain and warehouse management systems is a major hurdle for companies wanting to implement automation. One of the primary challenges is the intricate process of coordinating robots with existing workflows and infrastructure. Numerous warehouses and distribution centers function with a range of outdated systems, each having distinct software and hardware setups. Custom software development, reconfiguration of operations, and staff training are often necessary for logistics robots to function efficiently due to requiring precise coordination with these systems. This procedure may require a significant amount of time and resources, particularly for companies that lack technical knowledge or the ability to handle the change.
Moreover, the expense of incorporating these robots into existing processes may be too high. Aside from the initial cost of the robots, businesses need to consider the costs linked with installing them, upgrading the system, and any possible disruptions during the integration process. Additionally, it can be challenging to achieve smooth communication between robots and other supply chain components, especially when current systems are old or don't work well with robotic software.
Logistics Robots Market Segment Analysis:
By Type
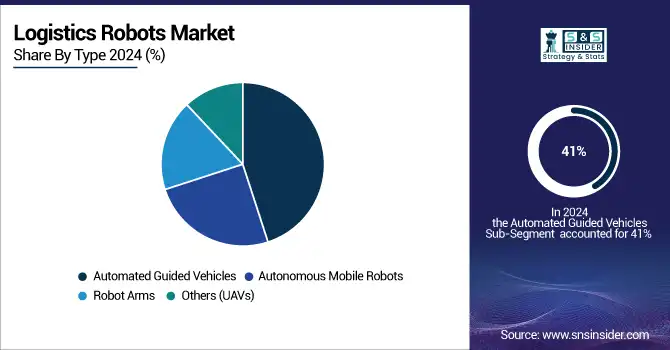
In 2024, Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) dominated the market with a share of more than 41% due to their dependable and consistent performance. AGVs are confined to set routes, whereas AMRs are adaptable, causing the rise and fast growth of AMRs. AMRs' strong market position and projected growth are driven by their ability to be agile and scalable in a variety of logistics applications.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are forecasted to experience a fast growth rate over the period 2025-2032. AMRs are greatly preferred for their versatility and capacity to navigate intricate environments independently, making them well-suited for warehouse automation and material transportation. The rapid increase in online shopping and the need for fast shipping options has driven the expansion of this industry. AMRs provide great efficiency, cutting operational expenses and enhancing productivity, making them an essential choice for businesses aiming to streamline their logistics.
By Application
Palletizing & De-palletizing dominated the market with a market share exceeding 40% in 2024. This automates the process of stacking and unstacking products on pallets to increase efficiency in warehouses and distribution centers. The growth of online shopping and increased shipping demands have made this sector essential for cutting labor expenses, guaranteeing precision, and enhancing efficiency in goods management.
Pick & Place is forecasted to experience the highest rate of growth during 2025-2032. This app includes robots picking and placing items in warehouses, a key job in sectors such as retail and production. The increasing need for quicker order fulfillment, driven by customers' desire for speedy delivery, has sped up the integration of pick-and-place robots.
By Industry
The E-commerce industry dominated the market in 2024 with a market share of around 39%, due to the rapid expansion of online shopping and the increasing demand for efficient order fulfillment. Logistics robots are widely used in warehouses to automate tasks such as picking, sorting, and packaging, which helps to speed up delivery times and reduce operational costs. As e-commerce giants like Amazon and Alibaba scale their operations, the demand for logistics robots continues to surge.
The Healthcare sector is considered to be the fastest-growing segment in the logistics robots market during the forecast period. With the rise in demand for efficient handling of medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment, hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting robots to ensure timely delivery and inventory management. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this growth by highlighting the importance of automation in healthcare logistics to minimize human contact and ensure safety, fueling investments in robotic solutions within this industry.
Logistics Robots Market Regional Analysis:
North America Logistics Robots Market Trends:
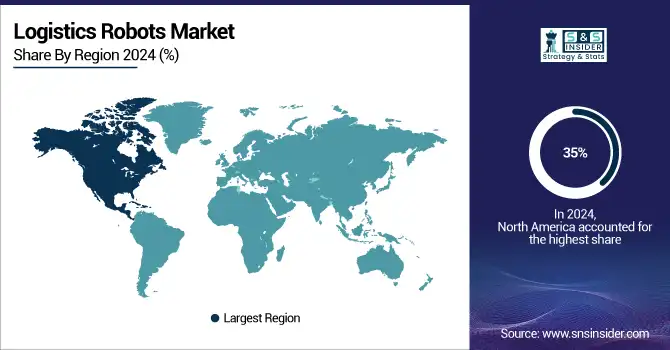
North America gained a significant market share, exceeding 35% in 2024, due to its embrace of advanced technology, significant investment in automation, and highly developed infrastructure. The United States and Canada both have many advanced warehouses and distribution centers that use robotics to improve how they operate. Leading companies such as Amazon and Walmart are making significant investments in robotic technology for logistics to improve the efficiency of their supply chains. The technological skills, thriving economy, and expensive labor in the region also drive the need for automation.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Asia-Pacific Logistics Robots Market Trends:
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is accounted to grow at a faster CAGR during the forecast period 2025-2032, driven by fast-paced industrialization, urbanization, and the expansion of e-commerce. Nations such as China, Japan, and South Korea are making significant investments in robotics to update their logistics and supply chain activities. The area enjoys cost savings on labor, an expanding tech-savvy labor force, and government efforts backing automation. The implementation of logistics robots is being driven by China's Belt and Road Initiative and Japan's emphasis on Industry 4.0.
Europe Logistics Robots Market Trends:
Europe holds a notable market share, driven by advanced manufacturing, well-established supply chains, and strong adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are investing heavily in warehouse and factory automation. Government incentives for digitalization, a skilled workforce, and high labor costs further support the deployment of logistics robots across the region.
Latin America Logistics Robots Market Trends:
Latin America is witnessing moderate growth in logistics robot adoption, led by countries such as Brazil and Mexico. The growth is supported by increasing e-commerce, modernizing distribution centers, and foreign investments in supply chain infrastructure. Rising labor costs, urbanization, and the need for faster order fulfillment are driving companies to implement robotic automation solutions in logistics and warehousing operations.
Middle East & Africa (MEA) Logistics Robots Market Trends:
The MEA region is gradually adopting logistics robots, with growth fueled by modernization of warehousing, retail expansion, and the rise of e-commerce in countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia. Investments in smart ports, free zones, and industrial hubs, along with government initiatives supporting technology-driven logistics, are boosting robot deployment. The region benefits from labor cost optimization and improved operational efficiency through automation.
Logistics Robots Market Key Players:
-
KUKA AG
-
Fanuc Corporation
-
Kion Group AG
-
Toshiba Corporation
-
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
-
Omron Corporation
-
Locus Robotics
-
GreyOrange
-
Vecna Robotics
-
Exotec
-
Berkshire Grey
-
SSI Schaefer
-
Dematic
-
Honeywell Intelligrated
-
Swisslog Holding AG
-
Siasun Robot Automation
Logistics Robots Market Competitive Landscape:
Anyware Robotics is a U.S.-based robotics company specializing in AI-powered mobile robots designed to autonomously unload boxes from trucks and containers. Their flagship product, Pixmo, utilizes a collaborative arm and vacuum-based end effector to handle boxes up to 65 lbs, achieving throughput rates of up to 1,000 boxes per hour. Founded in 2022 and headquartered in Fremont, California, Anyware Robotics raised $12 million in seed funding in early 2025 to accelerate product development and market deployment.
-
In March 2024, Anyware Robotics introduced an add-on for its Pixmo robot, designed to aid in truck and container unloading. The accessory features a vertical lift and conveyor belt for enhanced efficiency.
Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR), established in 2013, is a Danish company headquartered in Odense, specializing in autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) designed to automate internal logistics and material handling. MiR offers a versatile range of robots, including the MiR100, MiR250, MiR600, and MiR1350, capable of transporting payloads from 100 kg to 1,350 kg. In 2018, MiR was acquired by Teradyne, a global leader in automation, and in 2022, Teradyne integrated AutoGuide Mobile Robots into MiR, expanding its product line to cater to various industrial needs. With a presence in over 60 countries and a workforce of approximately 450 employees, MiR serves industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, providing scalable and flexible automation solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
-
In March 2024, Mobile Industrial Robots unveiled the MiR1200, an autonomous pallet jack using 3D vision and AI for precise pallet handling. It was showcased at LogiMAT 2024.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.77 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 33.09 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 16.47% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2021-2023 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Type (Automated Guided Vehicles, Autonomous Mobile Robots, Robot Arms, Others (UAVs)) • By Application (Palletizing & De-palletizing, Pick & Place, Transportation, Others (Shipment & Delivery)) • By Industry (E-commerce, Healthcare, Retail, Food & Beverages, Automotive, Others (Consumer Electronics)) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Poland, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, ASEAN Countries, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Colombia, Rest of Latin America). |
| Company Profiles |
ABB Ltd, KUKA AG, Toyota Industries Corporation, Fanuc Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Kion Group AG, Toshiba Corporation, Krones AG, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., Omron Corporation, Locus Robotics, GreyOrange, Vecna Robotics, Exotec, Berkshire Grey, SSI Schaefer, Dematic, Honeywell Intelligrated, Swisslog Holding AG, Siasun Robot Automation |

