Offshore Decommissioning Market Report Scope & Overview:
The Offshore Decommissioning Market size was valued at USD 5.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow to USD 9.8 billion by 2030 with an emerging CAGR of 7.5% over the forecast period of 2023-2030.
Decommissioning is the process of promptly, safely, and satisfactorily removing or otherwise dealing with offshore infrastructure that was once utilised to support oil and gas activities. An offshore petroleum project will eventually need to decommission, which should be planned for from the beginning and matured during the course of operations. The potential and difficulties of decommissioning offshore oil and gas infrastructure when it is no longer necessary can be handled in a variety of ways. However, the Australian government and NOPSEMA are completely committed to making sure decommissioning is carried out in a timely, safe, and ecologically friendly manner regardless of the procedure a responsible manner.
.png)
To Get More Information on Offshore Decommissioning Market - Request Sample Report
Many operators decide to utilise parts of their offshore facilities due to the expense of decommissioning a platform. Operators must consider variables such the purpose of usage, a parameter, and wear and tear. Choose between reusing a platform as a whole or specific components. These components include, for instance, wellheads and production manifolds. Whether or not the structure has experienced corrosion is a key factor in this choice. In "Decommissioning Offshore Structures," Gorman and Neilson researched and reported on this potential for reuse as well as the other proposals listed.
MARKET DYNAMICS
KEY DRIVERS:
-
The price of crude oil is falling, and there are more and more oil and gas fields that are getting older.
-
Increasing abandoned wells and huge, mature offshore oilfields.
When a well's useful life is up, it needs to be fully sealed up and abandoned. A number of cement plugs are inserted into the wellbore during such plug and abandoned (P&A) operations to separate the reservoir and other fluid-bearing formations. The quantity of wells that must be permanently sealed up and abandoned, particularly in developed, offshore regions.
RESTRAIN:
-
High Cost
-
Risk Involved
OPPORTUNITY:
-
Obsolete offshore infrastructure
CHALLENGES:
-
Recent downturn in price of oil
-
Increasing technology use to boost output from established fields
An oilfield produces crude oil or gas during its primary lifespan under the pressure of a natural reservoir. EOR can boost production and stop older fields from deteriorating.
IMPACT OF RUSSIA-UKRAINE WAR
The EU's top supplier of oil, natural gas, and solid fossil fuels essential elements of the continent's energy mix prior to its invasion of Ukraine was Russia. Russian economy grew at a second-largest exporter of crude oil, bringing in $123 billion for the country's economy. In spite of this, several European nations levied further sanctions against Russia in response to the invasion of Ukraine has endangered these people. The goal of the sanctions imposed by the West was to obstruct Russian industrial production and economic influence in a variety of industries. Economic sanctions were put in place to punish Russia harshly for its behaviour and to make it more difficult for it to carry out future hostilities. Individuals who supported, funded, or carried out acts were the object of punishment.
KEY MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Service Type
-
Project Management, Engineering & Planning
-
Permitting & Regulatory Compliance
-
Platform Preparation
-
Well Plugging & Abandonment
-
Conductor Removal
-
Mobilization & Demobilization of Derrick Barges
-
Platform Removal
-
Pipeline & Power Cable Decommissioning
-
Materials Disposal
-
Site Clearance
By Removal
-
Leave in place
-
Partial
-
Complete
By Depth
-
Shallow water
-
Deepwater
By Structure
-
Topside
-
Substructure
-
Subsea Infrastructure
.png)
Do You Need any Customization Research on Offshore Decommissioning Market - Enquire Now
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Europe held the greatest market share for offshore decommissioning globally in 2021. The existence of mature oil and gas fields is a primary driver of the Europe offshore decommissioning sector. Furthermore, strict government regulations in European countries enabled market participants to conduct decommissioning operations safely and effectively, which has fuelled the offshore decommissioning market in this area. To effectively complete the decommissioning of their oil fields, a number of market participants have taken actions including launching new products and negotiating contracts.
REGIONAL COVERAGE:
North America
-
US
-
Canada
-
Mexico
Europe
-
Eastern Europe
-
Poland
-
Romania
-
Hungary
-
Turkey
-
Rest of Eastern Europe
-
-
Western Europe
-
Germany
-
France
-
UK
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Netherlands
-
Switzerland
-
Austria
-
Rest of Western Europe
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Vietnam
-
Singapore
-
Australia
-
Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East & Africa
-
Middle East
-
UAE
-
Egypt
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Qatar
-
Rest of Middle East
-
-
Africa
-
Nigeria
-
South Africa
-
Rest of Africa
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
Colombia
-
Rest of Latin America
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
One of the largest topside removal projects has been underway since May 2021 thanks to Heerema Marine Contractors and AF Offshore Decom. initiatives of this nature on behalf of TAQA in the North Sea. As a late-life asset operator in the UK, TAA and its partners' Brae Bravo removal campaign is the company's first significant asset removal operation. Safety and environmental impact standards are central to the project.
-
Aker Solutions and Heerema Marine Contractors inked a contract in March 2021 for the decommissioning of the offshore Norwegian fields of Heimdal and Vesleffikk. Three offshore facilities from the Heimdal and Veslefrikk fields are included in the scope, along with their receiving, deconstruction, and recycling.
-
A contract for the offshore development of the North Field Production sustainability project was given to Saipem by Qatargas in February 2021. The engineering, procurement, building, and installation of numerous offshore facilities are all included in the scope.
KEY PLAYERS
The Major Players are Heerema Marine Contractors (The Netherlands), Royal Boskalis Westminster N.V. (The Netherlands), Petrofac (Jersey), Oceaneering International (US), Baker Hughes Company (US), Halliburton (US), Schlumberger (US), Saipem (Italy), DNV GL (Norway), DeepOcean Group (Norway), and other players are listed in a final report.
Royal Boskalis Westminster N.V.-Company Financial Analysis
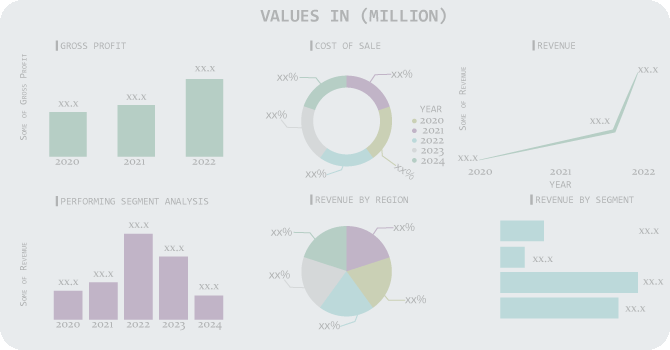
| Report Attributes | Details |
| Market Size in 2022 | US$ 5.5 Bn |
| Market Size by 2030 | US$ 9.8 Bn |
| CAGR | CAGR of 7.5 % From 2023 to 2030 |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2023-2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2021 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Service Type (Project management, engineering & planning, Permitting & regulatory compliance, Platform preparation, Well plugging & abandonment, Conductor removal, Mobilization & demobilization of derrick barges, Platform removal, Pipeline & power cable decommissioning, Materials disposal, Site clearance) • By Removal (Leave in place, Partial, Complete) • By Depth (Shallow water, Deepwater) • By Structure (Topside, Substructure, Subsea infrastructure) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]). Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Heerema Marine Contractors (The Netherlands), Royal Boskalis Westminster N.V. (The Netherlands), Petrofac (Jersey), Oceaneering International (US), Baker Hughes Company (US), Halliburton (US), and Schlumberger (US), Saipem (Italy), DNV GL (Norway), DeepOcean Group (Norway) |
| Key Drivers | • The price of crude oil is falling, and there are more and more oil and gas fields that are getting older. • Increasing abandoned wells and huge, mature offshore oilfields. |
| Market Restraints | • High Cost • Risk Involved |

