Organ on a chip Market Size:
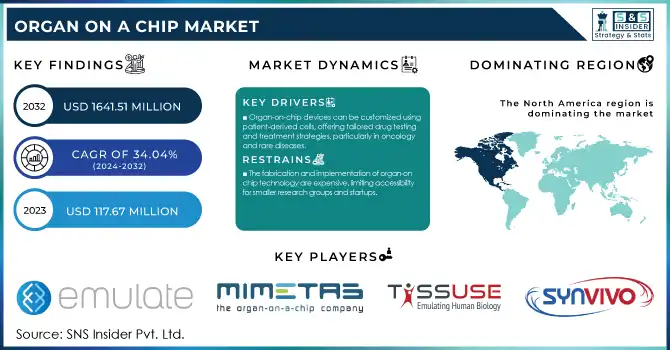
The Organ on a Chip Market size was valued at USD 117.67 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1,641.51 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 34.04% from 2024 to 2032.
To get more information on Organ on a chip Market - Request Free Sample Report
The organ on chip market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for more accurate and efficient drug development tools. It is a speculative alternative to animal testing, offering greater predictability of human reactions to potential drugs. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for faster, more cost-effective drug discovery processes are key factors propelling market expansion. One of the factors that has been instrumental in the development of this organ-on-chip technology is the support it receives from the government. Today, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) has committed over $100 million in funding for organ-on-chip research because they believe it could transform the process of drug discovery and toxicity testing by avoiding the need for animal models. The FDA has also shown strong support, collaborating with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to advance organ-on-chip models for assessing medical countermeasures against COVID-19.
In 2023 alone, the European Union has spent over €250 million in grants for collaborative organ-on-chip projects on neurodegenerative diseases. Such efforts are indicative of the increasing global realization of pending organ-on-chip as a revolutionary asset in international healthcare research and pharmaceutical development. The emerging trend is towards building a multi-organ-on-chip system that more accurately mimics physiological interaction. There is also a growing focus on the combination of organ-on-chip technology with artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve data analysis and prediction.
Organ on a chip Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
The demand for human-mimetic models in drug development is increasing due to their ability to replicate human physiology more accurately than traditional animal models, reducing reliance on animal testing.
-
Innovations in microfluidic technologies and materials, such as biocompatible hydrogels, are enabling the creation of more complex and functional organ-on-chip systems.
-
Organ-on-chip devices can be customized using patient-derived cells, offering tailored drug testing and treatment strategies, particularly in oncology and rare diseases.
The increasing demand for predictive drug tests with advanced technologies along with high-throughput drugs and emulsions is the primary driver toward the growing organ-on-a-chip market. Such drivers are based in part on the realization that animal models and more conventional cell cultures often fail to accurately predict human responses to drugs. Organ-on-a-chip technologies allow for more accurate simulation of human physiology and can be a compelling platform for testing drug efficacy and toxicity. As an example, a proximal tubular organ-on-chip confirmed the nephrotoxicity of a compound SPC-5001 that demonstrated nephrotoxicity in phase 1 clinical trials but not in preclinical testing performed on mice and non-human primates. This demonstrates the potential of organ-on-chip systems to identify drug-related issues that may be missed by traditional methods. For example, an analysis of 870 Liver–Chips on the same set of 27 known hepatotoxic and non-hepatotoxic drugs shows that the sensitivity of these systems is 87% while the specificity is 100%. Predicting drug toxicity with this level of accuracy could greatly minimize the likelihood of late-phase drug failures in clinical trials.
Additionally, organ-on-chip technology is also compliant with the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 which was approved in 2022, and supports the use of "alternative methods" or "non-animal testing methods". The availability of regulatory support will probably help drive the adoption of organ-on-chip platforms in drug development, which will reduce the timelines and costs associated with bringing new drugs to market, and combat the ethical issues related to animal testing.
Restraints
-
The fabrication and implementation of organ-on-chip technology are expensive, limiting accessibility for smaller research groups and startups.
-
A lack of universally accepted protocols and standardization across platforms hinders reproducibility and comparability of results, slowing adoption.
-
Current organ-on-chip technologies struggle with scalability and low throughput, restricting their application in large-scale drug screening studies.
The organ-on-a-chip market faces a major restraint in the form of a lack of standardization and scalability. The origin of this problem is the high complexity of organ-on-chip technologies, such as very complex microfluidic systems and still complex, cell cultures with a fragile balance formed to imitate, as closely as possible, human organ functions. The lack of universally accepted protocols and standards across different platforms hinders the reproducibility and comparability of results, making it difficult for researchers to validate findings across different systems. In addition, the need for standardization is aggravated by the currently limited possibilities to upscale organ-on-chip technologies for application in high-throughput testing. Consequently, existing systems are often small-scale, bespoke research tools making it difficult to transition towards larger-scale drug screening or toxicity tests. The inability to easily scale up these technologies restricts their potential applications in pharmaceutical research and development, where high-volume testing is often required.
In addition, the lack of standardization for data collection, analysis, and interpretation between organ-on-chip platforms is problematic for their applicability in current pharmaceutical development workflows. As a result of this heterogeneity in their devices, discrepancies in outcomes are introduced, which ultimately prevents organ-on-chip technologies from being fully adopted by the pharmaceutical industry.
Organ on a chip Market Segmentation Analysis
By Products & Service
In 2023, the services segment held the largest revenue share of 53%. The growing need for tailored proficiency in developing and implicating organ-on-chip technologies is attributed to this supremacy. Likewise, government statistics evidence this trend; according to the NIH, organ-on-chip devices have found their way into over 500 research institutions and biotech companies. The organ-on-chip is a highly complex system for which design, fabrication, and operation are performed at the microscale, requiring professional personnel, and therefore driving demand for organ-on-chip services. This is further anticipated to fuel the organ-on-chip segment, as the U.S. Department of Defence has also invested in organ-on-chip services for toxicity testing of chemical and biological agents. The services sector additionally benefits from the often substantial demand for customizing and optimizing organ-on-chip platforms for specific research applications, which frequently takes the form of continued support and consulting. As this technology improves, the segment is poised to continue to lead the way as services provide essential support to researchers and pharmaceutical companies in utilizing organ-on-chip technology for drug discovery and development.
By Application
In 2023, drug discovery accounted for the highest revenue share of 61% in the market. The reason behind this substantial market share is the pressing demand for cost-effective and accelerated drug development processes in the pharmaceutical industry. The FDA has stated it costs on average more than $2.6 billion to bring a new drug to market, a high proportion of which is due to late-stage failures. Organ-on-chip technology addresses this issue by enabling more rapid and more predictive human responses to drugs earlier in the development pipeline. NIH says that organ-on-chip types of research were utilized in more than 200 clinical trials assessing patient-specific responses to drugs in 2023 alone, especially in oncology and rare diseases. There is also growing attention by the FDA on including organ-on-chip data in regulatory decision-making for drug approvals, further embedding this trend. Not even the U.S. government has failed to see the promise this kind of technology offers, as the Department of Health and Human Services set aside $20 million in 2023 for organ-on-chip research to speed drug discovery for rare diseases. Together, these efforts highlight the importance of organ-on-chip technology in transforming the drug discovery process and optimizing pharmaceutical R&D.
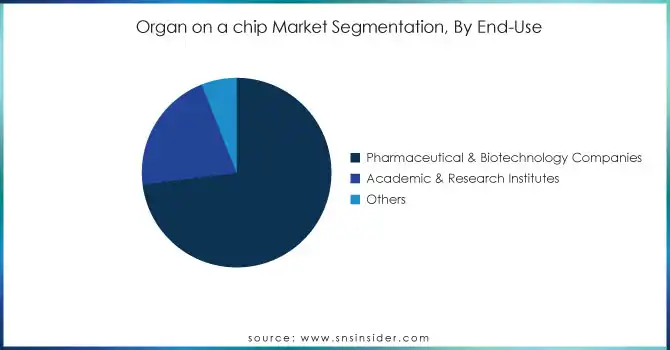
By End-use
In 2023, the pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies segment led the market and held 73% of the revenue share. Such dominance can be due to the growing availability of organ-on-chip technology among leading pharmaceutical companies for improving their drug discovery and development process. Historical data from the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) reports that the U.S. biopharmaceutical industry invested roughly $102 billion in R&D in 2022, a large proportion of which goes to generating more efficient preclinical testing methods. This segment has also fair well due to past government initiatives. As an example, in 2020 the NIH initiated a funding opportunity with an expansive goal of spending $20 million in promoting partnerships between academic researchers and pharmaceutical companies to facilitate scale-up development of organ-on-chip models for drug screening. This initiative has increased the adoption of the technology by large pharmaceutical players. Additionally, the efforts of the FDA towards the inclusion of organ-on-chip data in regulatory submissions have led to a high level of interest from biotech companies investing in this technology, which is expected to account for a high share of this segment.
Organ on a chip Market Regional Insights
The North American region held the largest share of the organ-on-chip market in 2023, at 51% of the total revenue. This leadership position is attributed to the presence of major market players, substantial government funding, and a robust research infrastructure. The region's dominance is further solidified by initiatives such as the NIH's $1 billion investment in organ-on-chip research and development. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth, with China emerging as a key player. Even the Chinese government has poured hundreds of millions of dollars of domestic organ-on-chip research on this technology. The rapid uptake in the Asia-Pacific region can be attributed to research and development (R&D) initiatives, increasing healthcare spending, and rising awareness of the potential of technology. A ¥10 billion ($90 million) Japanese government initiative has been announced to support research on organ-on-chip to the clinic. Although not the fastest growing, Europe is still sizable, and Germany & the Netherlands lead in Steve. In 2023, more than €250 million has flowed from the European Union into organ-on-chip projects required by legislation that needs to be addressed through collective efforts, which shows how serious this region has become about translational technology. These regional trends showcase the worldwide growth of the organ-on-chip market and the different strategies adopted by countries across the globe to retrieve the potential gain from the market.

Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Key Organ on a chip Companies:
-
Emulate, Inc.
-
Nortis, Inc.
-
BICO
-
CN Bio Innovations Ltd
-
The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory, Inc.
-
SynVivo, Inc.
-
AlveoliX AG
Recent Developments
-
In March 2024, Emulate Inc., a leading organ-on-chip company, announced a collaboration with the FDA to develop liver-on-chip models for improved drug toxicity testing. The goal of the partnership is to develop consensus protocols for the use of organ-on-chip technology in regulatory decisions.
-
In April 2024, CN Bio raised $21 million in Series B funding from Bayland Capital, and CN Innovations Holdings Ltd to support product development and expansion to meet rapidly increasing demand for organ-on-a-chip solutions, powered by developments in drug R&D and legislative transformations like the US FDA Modernization Act 2.0.
-
In March 2024, MIMETAS became a member of the Centre for Animal-Free Biomedical Translation, which aims to help drive forward innovations in animal-free biomedical research with financial support of €124 million [US$134.78 million] from the Dutch National Growth Fund.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 117.67 Million |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 1641.51 Million |
| CAGR | CAGR of 34.04% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Products & Service (Products {Instrument, Devices [Liver-on-a-Chip, Lung-on-a-Chip, Intestine-on-a-Chip, Kidney-on-a-Chip, Heart-on-a-Chip, Others]}, Services) • By Application (Drug Discovery, Toxicology Research, Others) • By Model Type (Organ-based model, Disease-based model) • By Purpose (Therapeutic purpose, Research purpose) • By End Use (Academic & Research Institutes, Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Emulate, Inc., MIMETAS B.V., TissUse GmbH, Nortis Inc., AxoSim, CN Bio Innovations Ltd., InSphero, Altis Biosystems, SynVivo, Valo Health. |
| Key Drivers | • The demand for human-mimetic models in drug development is increasing due to their ability to replicate human physiology more accurately than traditional animal models, reducing reliance on animal testing. • Innovations in microfluidic technologies and materials, such as biocompatible hydrogels, are enabling the creation of more complex and functional organ-on-chip systems. |
| Restraints | • The fabrication and implementation of organ-on-chip technology are expensive, limiting accessibility for smaller research groups and startups. • A lack of universally accepted protocols and standardization across platforms hinders reproducibility and comparability of results, slowing adoption. |

