Deep Space Exploration Market Report Scope & Overview:
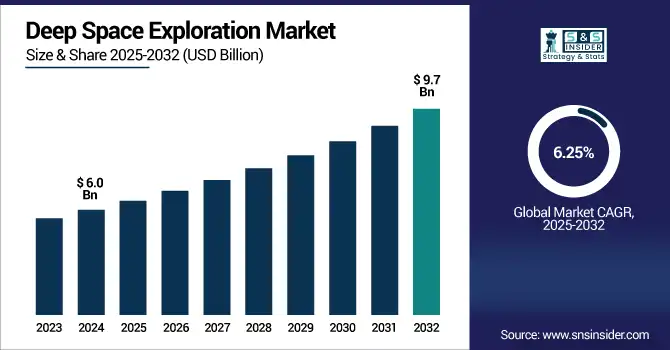
The deep space exploration market size was valued at USD 6.0 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 9.7 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.25% during 2025-2032.
To Get more information on Deep Space Exploration Market - Request Free Sample Report
The deep space exploration market growth is driven by the government and private firm investments in interplanetary missions, technological advancements in propulsion systems, and growing interest in lunar and Mars exploration. Increased number of missions and technology innovations by key players, such as NASA and ESA, and a new trend of private firms stepping up, are speeding things along. Market dynamics are also fostered with favorable policies and collaborations including NASA's Artemis program. The deep space exploration market trends highlight a pivot to reusable space vehicles, AI-driven navigation, and commercial lunar payload services. According to recent deep space exploration market analysis, the market is projected to grow significantly through 2032, backed by satellite miniaturization & deeper international collaboration.
The U.S. deep space exploration market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increased investments by the government in missions such as NASA's Artemis program, ongoing advances in propulsion and AI systems, and an influx of private space companies playing a significant role in deep space exploration, the U.S. deep space exploration market is steadily gaining traction as it moves from the design phase into building rockets and eventually launching missions. In 2024, the U.S. market size is estimated at approximately USD 2.01 billion. By 2032, the market is projected to reach around USD 3.20 billion, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 6.02% during the forecast period.
Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
-
Rising Public and Private Investments are Accelerating R&D, Leading to Advanced and Frequent Deep Space Missions
Another factor being promoted by the escalating spending of national space agencies, such as NASA, ESA, ISRO, CNSA, and investment by private players, including SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Lockheed Martin. Investments by the governments in things, such as the Artemis program and Mars sample return missions are driving new capabilities in deep-space systems, including advanced spacecraft, launch systems, and deep-space technologies. Significantly, public-private partnerships are meeting the demand for accelerating innovation cycles while cutting costs and enabling large-scale deep space missions. This joined-up momentum is both unlocking more ambitious destinations for exploration and accelerating international cooperation, and is driving continued demand for high-performance space exploration infrastructure to sustain future Earth-independent, long-duration interplanetary missions.
For instance, in FY 2024, NASA received a USD 8.1 billion allocation specifically for lunar exploration (Artemis program), along with USD 1.39 billion for R&D in new space technologies.
Restraints:
-
High Financial and Technical Demands of Deep Space Missions Restrict Entry to Well-Funded Entities Only
These systems measure several kilometers in size and are needed for deep space missions, and are thus extremely expensive and require advanced engineering, all of which inhibit market scalability. Such elements as launch systems, propulsion technology, life-support systems, and deep-space comm infrastructure require an enormous investment of R&D costs, manufacturing time, and testing. The financial risk of mission failures or delays makes smaller private firms and emerging countries reluctant to venture into the sector. This is in addition to the challenge of designing missions with a high probability of success when missions may take decades (or centuries) in a hostile environment featuring extreme radiation, microgravity, and large distances from each other. Such high entry barriers prevent the market from opening up fully to the rest of the world, slowing growth and forcing opportunities into only the most well-funded agencies or organizations.
Opportunities:
-
Shift Toward Lunar and Martian Commercialization Is Creating Profitable Opportunities for Private Sector Players
Deep space missions are also being made more commercially viable, largely due to so many spaceships can go to the Moon and Mars. From payload delivery, satellite deployment, to infrastructure development for extraterrestrial habitats, governments are gradually opening up to private players to sign contracts with them to conduct the process on a commercial level. The exploration has moved away from pure research into revenue-generating activities, such as lunar mining, Mars colonization, and interplanetary cargo transport. Reusable launch vehicles, robotic systems, and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technologies are all getting investment from commercial entities. It is opening the door to commercial deep space logistics, tourism, and data monetization, where startups, defense contractors, and space-tech firms are all helped by an enabling environment, providing customized support in pursuit of mission success.
For instance, after landing its Odysseus lander, Intuitive Machines’ stock surged 335.1% in 2024, propelled by multiple NASA contracts (USD 4.82 billion Near Space Network, USD 116.9 million CLPS), showcasing investor confidence and commercial expansion
Challenges:
-
Survival Risks in Deep Space Environments Hinder Continuous Human Presence and Mission Scalability
Deep space exploration market comes with a major challenge to sustain and the survival of the human body in a long-duration mission. Space around the Deep black sea means Astronauts are not free from harmful cosmic radiation, psychological isolation, and limited life-support resources. Autonomous health state monitoring, radiation protection, and sealed loop life support systems. Establishing environmentally friendly sources of energy, habitat, and food production for pentasts in space will not only be technically challenging, but it will also require sophisticated materials that may have to involve some level of AI in the integration process. If these fundamental survival hurdles are not solved, our long-term presence on either the Moon or Mars will be limited, which could put an upper cap on plans for a deeper space enterprise.
Segmentation Analysis:
By Subsystem:
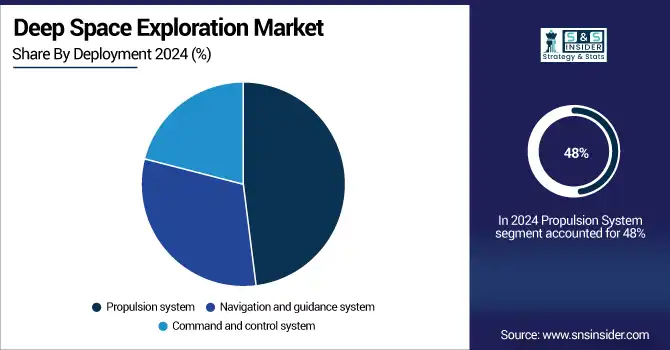
The Propulsion System segment dominated the market in 2024 and accounted for 48% of the deep space exploration market share, due to the increasing mission range and the need for thrust efficiency. The advancements in ion and electric propulsion technologies are allowing longer missions with larger payloads. Through 2032, the dominance of this segment is projected to remain due to government-backed deep space projects and increasing private research & development in advanced propulsion.
For Instance, on February 18, 2025, NASA installed the first new-production RS‑25 engine (E20001) onto Stennis’s Fred Haise Stand, marking the beginning of a new testing series ahead of Artemis V
The command and control system segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR owing to a surge in autonomous operations and secure space communications. Mission complexity requires real-time data management and decision-making capabilities. AI-based control modules, along with integrated satellite communication technologies, are quickly being adopted in this segment, hence accelerating the growth of global missions.
By Application:
The moon exploration segment dominated the deep space exploration market in 2024 and accounted for a significant revenue share, owing to the presence of publicly funded missions, such as NASA's Artemis program, and increasing commercial lunar payload contracts. In this way, the Moon has become a sort of giant proving ground for extended missions. Tipping continued over the period to 2032 due to heightened investments in lunar landers, resource mapping, and surface infrastructure, but enhanced private and international participation will uphold dominance as well.
The Mars exploration segment is projected to register the fastest CAGR, due to increasing interplanetary aspirations and technology demonstrations to support eventual human settlement. Ambitious Missions, such as NASA's Mars Sample Return and SpaceX's Starship program are ramping up R&D. Increased capabilities in the fields of robotics, autonomous systems, and entry-descent-landing technologies is allowing for more complex Mars missions to be conducted more often, resulting in this segment expanding rapidly through 2032.
By Mission Type:
The Unmanned Mission segment dominated the deep space exploration market in 2024 and accounted for 69% of revenue share, driven by the low-risk, low-cost nature of the process and its implementation in early-stage exploration activities. There are so many robotic probes, orbiters, and landers taking these human measurements in inhospitable places. Improvements in AI, remote sensing, and autonomous navigation will keep unmanned missions as the preferred option for deep space exploration until 2032.
The manned mission segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR, given the renewed global interest in manned spaceflight and long-term colonization goals. Crew spacecraft development is in the works, due to programs, such as NASA's Artemis and SpaceX's Mars plans. Growing investment in life support systems, space habitats, and astronaut safety technologies will propel a significant increase in crewed missions over the forecast horizon.
By End-Use:
The Government Space Agencies segment dominated the deep space exploration market in 2024 and accounted for a significant revenue share, owing to the large funding, technological framework, and mandates of the missions. Deep space exploration is driven by a few top agencies, such as NASA, ESA, CNSA, and ISRO, which create elaborate, strategic, and international long-term programs. This segment will remain a key driver of market leadership to 2032 due to its ongoing investments in planetary science, lunar missions, and human exploration.
The Commercial segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR, as private investments, satellite launching deployment, and lunar delivery services ramp up. Space companies are rewriting the rules of mission economics thanks to the reuse of vehicles and payload contracts, such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Intuitive Machines. Commercial participation in deep space missions through 2032 is being accelerated by supportive government programs and emerging business models in space tourism, infrastructure, and mining.
Regional Analysis:
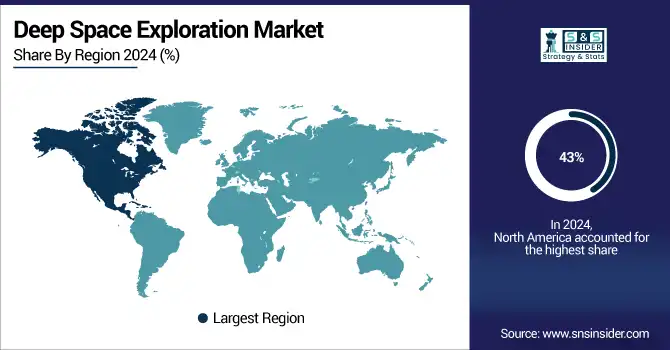
North America dominated the deep space exploration market in 2024 and accounted for 43% of revenue share, due to strong government support and significant space programs such as NASA's Artemis and the high number of private players in the field led by SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Lockheed Martin, North America held the largest share of revenue share in deep space exploration market, at 43% in 2024. The region will remain the leader in deep space missions, lunar explorations, and spacecraft innovations by 2032 due to its high R&D spending, advanced infrastructure, and established aerospace ecosystems.
USD 27.2 Billion Proposed for NASA in FY 2024, marking a 7% increase over FY 2023 and allocating USD 8.1 Billion to the Artemis lunar program, reinforcing its deep space leadership.
Asia Pacific is expected to register the fastest CAGR, driven by ambitious national space programs from China, India, and Japan. Chinese Chang’e missions and Indian Gaganyaan and lunar programs have been progressing quickly. But with greater investment from governments, more private space startups, and a number of regional partnerships taking place, deep space capabilities are gaining ground in the Asia Pacific, where a bevy of countries is set to become a giant of global space exploration in the years ahead.
Europe is witnessing steady growth driven by ESA-led lunar and Mars collaboration programs are continuing to expand across a steady growth Europe with new advanced satellite systems and growing investment in deep space R&D. By 2032, Europe can develop continued partnerships with NASA and commercial partners to further establish its position in planetary missions, robotics, and long-duration technologies for operating into space.
Germany leads the European deep space exploration market due to a strong aerospace industry, contributions to the ESA, and innovations in propulsion and robotic systems, and naturally claims a leading role in the European deep space exploration market. Germany is likely to continue being the linchpin of European deep space technological prowess through 2032 with active support for its Moon and Mars programs at DLR.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Key Players:
The major key deep space exploration market companies are NASA, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Roscosmos, European Space Agency (ESA), ISRO, Airbus Defence, and others.
Recent Developments:
-
15 January 2025, Firefly Aerospace successfully launched Blue Ghost Mission 1 under NASA’s CLPS program, which achieved a soft landing on the lunar Mare Crisium by 2 March 2025.
-
27 February 2025, Intuitive Machines launched the IM‑2 Athena mission, which landed sideways on the Moon on 6 March 2025, still managing to collect valuable surface data.
-
14 October 2024, NASA launched the Europa Clipper aboard SpaceX Falcon Heavy, marking a key milestone in Jupiter system exploration and future deep space science missions.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
|
Market Size in 2024 |
US$ 6.0 Billion |
|
Market Size by 2032 |
US$ 9.7 Billion |
|
CAGR |
CAGR of 6.25% From 2025 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
|
Historical Data |
2021-2023 |
|
Report Scope & Coverage |
Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
|
Key Segments |
• By Subsystem (Propulsion system, Command and control system, Navigation and guidance system) |
|
Regional Analysis/Coverage |
North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Poland, Turkey, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of Latin America) |
|
Company Profiles |
NASA, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Roscosmos, European Space Agency (ESA), ISRO, Airbus Defence and Space and others in the report |

