District Heating Market Report Scope & Overview:

Get More Information on District Heating Market - Request Sample Report
The District Heating Market Size was valued at USD 182.06 Billion in 2023 and is now anticipated to grow USD 263.19 Billion by 2032, displaying a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.18% during the forecast Period 2024-2032.
The growing district heating market is having a big impact on the equipment market as cities and communities aim to improve energy efficiency and lower carbon emissions, leading to increased popularity of district heating systems. The demand for particular equipment components is being fueled by this change. There is a strong demand for boilers, heat exchangers, and heat pumps to help with effective heat production and distribution. District heating production stayed comparable to 2022 levels, fulfilling approximately 9% of the worldwide heating demand in buildings and industry. The top-performing networks have shown that district heating has significant potential for effectively, affordably, and flexibly incorporating low-emission energy sources into the heating energy mix on a large scale. Nevertheless, the potential for reducing carbon emissions in district heating systems has not been fully realized, with fossil fuels accounting for around 90% of heat production in district networks worldwide, particularly in China and Russia, the two leading markets.
The power consumption in the U.S. saw a 2.6% increase in 2022 however, projections indicate a 0.6% decline in demand for 2023, followed by an average rise of 1.2% in 2024 and 2025. Throughout this forecasted period, the escalating power demand in the U.S. is expected to drive heat meter. As energy consumption rises, accurate measurement and management of heat usage become increasingly vital, especially in applications like residential and commercial heating systems. The district heating allows customers to precisely control over heating and providing flexibility and customization to adapt to consumer needs. Individual heating systems suffer from inconsistencies related to heat loss. Furthermore, district heating has a centralized heat generation and uses a mix of renewable energy sources, waste heat recovery there by is very flexible in implementation making a key factor in highly adopting the heater.
In April 2023: the European Union provided EUR 401 million in support for the Czech green district heating scheme.
In March 2023: the Energy Security Bill in the UK implemented a heat networks regulation to allow for heat zoning. The Climate Change Committee predicts that by 2050, heat networks could provide approximately 18% of the United Kingdom's heat consumption.
MARKET DYNAMICS
DRIVER
The increasing focus on decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change is a major motivator, since district heating systems have the ability to significantly decrease carbon footprints by utilizing renewable energy sources and waste heat.
The increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change is a major factor driving the uptake of district heating systems. These systems can greatly decrease carbon footprints by using sources of renewable energy like biomass, geothermal, and solar energy, in addition to utilizing waste heat from industrial processes and power generation. District heating reduces dependence on fossil fuels and significantly lowers carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions by incorporating clean energy sources. This change not just aids in achieving worldwide climate aims but also improves energy efficiency and sustainability in cities. Governments and policymakers are showing more support for district heating by offering incentives and regulations, understanding its ability to help achieve a low-carbon future. As a result, the district heating sector is seeing strong expansion, in line with broader environmental goals and the critical need to address the impacts of climate change.
District heating systems generally offer better energy efficiency compared to individual heating systems, leading to cost savings for consumers and lower overall energy usage.
District heating systems are more energy efficient than individual heating systems because they use centralized heat production and distribution. This method enables the incorporation of very effective combined heat and power (CHP) facilities and the utilization of renewable energy sources like biomass and geothermal. District heating reduces energy loss by generating heat in one place and distributing it through an insulated network of pipes instead of using multiple individual systems. Moreover, the cost savings for consumers are substantial due to the operational and maintenance costs being reduced through the economies of scale achieved in district heating. Efficient use of energy helps to decrease overall energy consumption, aiding sustainability efforts and reducing carbon footprints. District heating offers economic and environmental advantages, making it an appealing solution for urban areas.
RESTRAIN
The substantial initial expenses linked to setting up district heating systems may serve as a major hindrance for certain areas or local authorities.
The significant obstacle for numerous regions and municipalities is the considerable initial expenses associated with setting up district heating infrastructure. The financial challenge arises from the significant investment needed to build the network of pipes, centralized heating plants, and related systems. The costs at the beginning cover more than just the physical structure; they also include the planning, permits, and possible disturbances to current city landscapes during setup. Smaller towns or areas with restricted finances may struggle to allocate the required funds. Moreover, obtaining funding for these extensive initiatives can pose challenges, with potential investors showing reluctance because of the extended repayment schedules and uncertainties surrounding future energy needs. As a result, even though district heating offers long-term environmental and economic advantages, the large upfront cost can discourage communities from using this sustainable heating option, impeding the wider adoption and incorporation of district heating systems.
The efficiency of district heating systems is reduced by heat loss through the pipe network, as thermal energy escapes before reaching end-users.
Heat escaping through the pipes reduces the effectiveness of district heating systems by letting thermal energy leak before reaching the final users. This loss of heat leads to greater energy usage because additional fuel is needed to make up for the lost heat, causing higher operating expenses and a greater impact on the environment. The insulation of pipes reduces some heat loss but may not fully prevent it, especially over long distances or in old infrastructure. As a result, users experience temperatures lower than what was expected, which decreases the efficiency of the heating system and may cause discomfort or require additional heating sources. Improving insulation, consistently servicing the network, and incorporating modern materials and technologies may decrease these losses, but fully eliminating them is difficult. Hence, reducing heat loss is essential for optimizing energy efficiency, cutting expenses, and maintaining the dependability of district heating systems.
KEY SEGMENTATION ANALYSIS
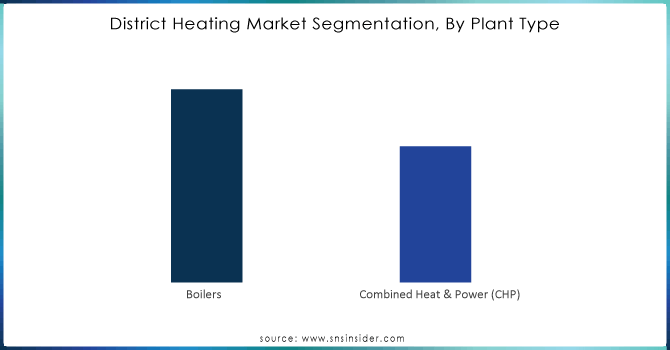
By Plant Type
The Combined Heat & Power (CHP) are leading the market with a 61% market share in 2023, because they can produce both electricity and heat from one fuel source simultaneously, such as biomass, natural gas, or waste heat. The generated electricity is either utilized locally or sent to the grid, and the extra heat is distributed through district heating to supply space heating and hot water to consumers.
Get Customized Report as per your Business Requirement - Request For Customized Report
By Heat Source
In 2023, the market is mostly controlled by Natural Gas as a heat source, making up 30.40% of the market share. In regions with established gas infrastructure, natural gas is frequently utilized as a primary source of heat for district heating systems. Boilers or combined heat and power (CHP) plants use natural gas to generate heat that is distributed to different buildings through pipelines. Natural gas heating offers the benefits of reduced carbon emissions, increased efficiency, and versatility. However, it also comes with drawbacks such as expensive prices, dependency on gas availability, and the release of methane.
By Application
The industrial segment held the largest market share of more than 38% in 2023, the district heating market by application, driven by the substantial demand for reliable and cost-effective heat in various industrial processes. District heating systems provide an efficient means of supplying thermal energy to industrial zones, contributing to enhanced energy efficiency and reduced operational costs. The centralized nature of district heating aligns well with the concentrated heating needs of industrial facilities, offering a practical solution for large-scale heat requirements.
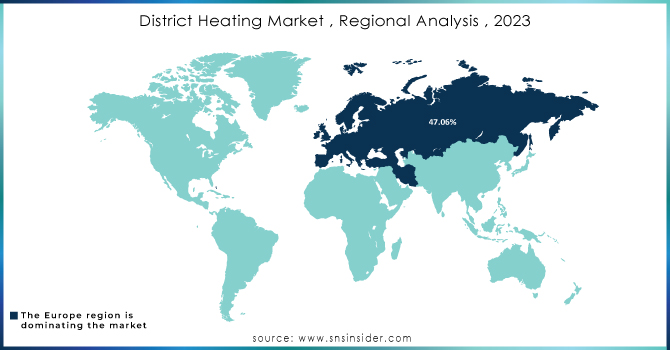
KEY REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The Europe Region is dominating the market with a share of 47.06% of the total market because the region has low temperature for most of the year. Europe has a huge and established network throughout the region creating a robust foundation for its adoption of district heaters. The growth of this market is based on de-carbonization (removal or reduction of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere) and the transition to renewable energy sources.
Key Players
The major key players are Vattenfall, Statkraft, Fortum, STEAG, Goteborg Energi, Shinryo Corporation, RWE, NRG Energy, Korea District Heating Corporation, Ørsted and others.
RECENT DEVELOPMENT
In February 2024: Evonik and Uniper formally launched the Technical Options for Thermal Energy Recovery (TORTE) project in Gelsenkirchen. The TORTE project will deliver industrial waste heat from isophorone generation into the district heating network. Over 1,000 homes in the Ruhr region will be delivered by the end of 2024.
In April 2023: Danfoss Group announced the new options for OEMs as it expands the Z-design range of Micro Plate Heat Exchangers; where the latest addition to the range C262L-EZD is a dual-circuit evaporator that's ideal for scroll chillers. These robust and reliable units extend the range's capability with cooling capacities now covering up to 300 kW in single circuits and up to 800 kW in dual circuits.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 182.06 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 263.19 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 4.18% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Plant Type (Boilers, Combined Heat & Power) • By Heat Source (Coal, Natural Gas, Renewables, Oil & Petroleum Products, Geothermal) • By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Vattenfall, Statkraft, Fortum, STEAG, Goteborg Energi, Shinryo Corporation, RWE, NRG Energy, Korea District Heating Corporation, Ørsted |
| Key Drivers | • The increasing focus on decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change is a major motivator, since district heating systems have the ability to significantly decrease carbon footprints by utilizing renewable energy sources and waste heat.
• District heating systems generally offer better energy efficiency compared to individual heating systems, leading to cost savings for consumers and lower overall energy usage. |
| Restrain | • The substantial initial expenses linked to setting up district heating systems may serve as a major hindrance for certain areas or local authorities.
• The efficiency of district heating systems is reduced by heat loss through the pipe network, as thermal energy escapes before reaching end-users. |

