Network Slicing Market Report Scope & Overview:
Get More Information on Network Slicing Market - Request Sample Report
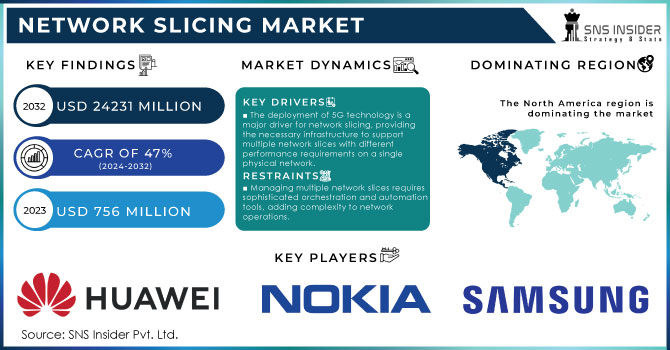
Network Slicing Market size was valued at USD 756 Million in 2023. It is expected to Reach USD 24231 Million by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 47% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
The network slicing market is growing with the increased penetration of IoT solutions and implementation of new technologies, such as AI, AR/VR (Artificial Intelligence/Virtual Reality), and M2M communication. This expansion is also supported by the usage of cloud services becoming more and more prevalent in the IT world. Demand for network slicing-enabled 5G in BFSI, healthcare & retail eCommerce is also fuelling the market growth. Such technology improves service productivity and management ROI (return on investment). It also allows businesses to customize networks to meet specific requirements efficiently and cost-effective manner and is underpinned by service-level agreements. Network slicing can increase the utilization of 5G base stations by up to 25%, optimizing the capacity and performance of the network. It supports dynamic bandwidth allocation with a minimum granularity of 1 Mbps, making it applicable in many customized network service scenarios. Efficient network slicing implementation and management can deliver up to 30% reduction in Capital Expenditure (CapEx) and up to 25% savings in operational expenditure for operators.
The widespread adoption of IoT and advancements in M2M communication networks are changing the ways products and appliances interact with systems. Some IoT applications require low-latency, high-power mobile that is ideal for video surveillance while others demand long-range, low-latency and are mostly used with network slicing in smart factories or Cities. Growth of 5G technology to drive market growth for the emergence of IoT applications, especially mission-critical and machine-type communications, network slicing solutions are expected to support these emerging types of IoT applications faster as the adoption rate grows during the forecast period more than 20 telecom operators have deployed commercial network slicing services across the globe, and more than 50 appear to trial some form of network slices around late 2024. Network slicing also enhances QoS measurements, such as packet loss and jitter by at least 60%, meaning more dependable network performance to enable critical applications.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
The deployment of 5G technology is a major driver for network slicing, providing the necessary infrastructure to support multiple network slices with different performance requirements on a single physical network.
-
The growing number of IoT devices and the need for machine-to-machine (M2M) communications require networks that can handle diverse requirements, which network slicing can efficiently provide.
-
Applications such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and ultra-high-definition (UHD) video streaming require high bandwidth and low latency, which network slicing can deliver by creating dedicated slices for these services.
-
Network slicing enables more efficient use of network resources, improving service quality and maximizing return on investment (ROI) for network operators.
The introduction of 5G networks is one of the key factors boosting the market demand for network slicing as it enables infrastructure that can accommodate different network slices with diverse performance requirements in a single physical network. With 5G technology spreading around the world, it comes with much-improved speed, latency, and capacity compared to its predecessor technologies. In 2023, the global 5G subscriptions reached 1.5 billion, representing a significant increase from 2022's 1 billion subscriptions. The increasing implementation of 5G networks across the globe is underscoring the demand for network slicing - a practice that enables network operators to deliver virtualized and isolated parts within the same networking architecture, customizing them to distinct use cases and applications. Healthcare is a major use case for 5G network slicing. Ericsson, BT Group, and Qualcomm Technologies have completed a 5G end-to-end network slicing demonstration in the UK in 2024. The first part of the demonstration showed that network slicing can support critical healthcare applications like remote surgery and telemedicine, which depend on ultra-reliable communication (URLLC). Also, T-Mobile rolled out a 5G network slicing beta for developers in August 2023. The beta program allows developers to hone their video calling apps using improved network conditions including steady uplink and downlink speeds, reduced latency, and enhanced reliability over T-Mobile's 5G standalone (SA) network. These initiatives underline the prospects of network slicing in improving user experience across various use cases, which is expected to facilitate market growth. The rising utilization of 5G networks not only improves existing applications but opens new opportunities across sectors and underpins the significance of network slicing in an evolving telecommunications ecosystem.
Restraints
-
The initial investment required for the deployment of network slicing infrastructure, including 5G technology and related equipment, can be substantial, and create a barrier for some operators.
-
Managing multiple network slices simultaneously requires sophisticated orchestration and automation tools, adding complexity to network operations.
-
While network slicing can enhance security by isolating slices, it also introduces new security challenges, such as ensuring each slice is adequately protected and preventing cross-slice interference.
The cost of deploying network-slicing infrastructure is one the most important problems preventing its significant barrier to its widespread adoption. Deploying a network-slicing framework entails significant investments - from converting existing networks to 5G technology and rolling out new hardware to the use of advanced software for NFV (Network Functions Virtualization) & SDN. The European Telecommunications Network Operators' Association (ETNO), projected Europe's telecom operators into as much as €500 billion of investment in 5G and Fiber networks by the end of 2025. These costs are not limited to hardware but also encompass significant expenditures on software upgrades, staff training, and maintenance.
Earlier adopters like SK Telecom and Deutsche Telekom have also highlighted significant investments they conduct network slicing trials. For example, SK Telecom invested over $100 million in 2022 to upgrade its network infrastructure for QoS-enabled slice delivery. While these investments are necessary steps, the return on investment (ROI) is uncertain given how nascent network slicing is as a technology and in terms of its adoption curve. The initial capital expenditure to build network slicing may deter many of the smaller telecom operators and enterprises from adopting it and hindering overall market growth. The financial burden, coupled with the need for continuous updates and maintenance, underscores the economic challenges associated with network slicing deployment.
Segment Analysis
By Enterprise type
Based on enterprise type, the large enterprise segment has dominated the market with 65% in 2023 and is expected to maintain this dominance during the forecast period. As such, the availability of 5G networks and IoT technologies in large enterprises to improve uninterrupted customer service is creating demand for these platforms. On the other hand, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are expected to grow at a CAGR of 51%, over the forecast period. The SMEs had been slow to adopt network slicing solutions which promise improved productivity and cost efficiencies. This slow integration by smaller companies indicates a constant rise, as they still become acquainted with the advantages and benefits of these new technologies.
By End-user
The healthcare segment was the dominant revenue contributor with a more than 21.6% market share in 2023 and is poised to grow with a significant CAGR over the forecast period. The growth is due to the growing usage of 5G technologies as well as network-slicing solutions in the healthcare sector. With technological advancements such as robotic surgeries, IoT and AI redefining healthcare delivery, 5G services along with network slicing the entire value chain of healthcare revolutionized. We anticipate that these innovations will differentially affect various key stakeholders, such as providers, health plan providers, and pharmaceutical companies. 70% of organizations across manufacturing, healthcare and automotive aiming to adopt network slicing by 2025 in their unique connectivity & performance. The above network slicing solutions transformations lead to the potential for far greater benefits in the areas of hospital inventory management (real-time tracking), real-time occupancy tracking within hospitals, and movement monitoring all leading to enhanced patient experience, care quality improvement, and a cost reduction. 5G networks can also transmit these insights to the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems ensuring optimal monitoring and assessment of hospital procedures.
On the other hand, the manufacturing segment is projected to witness the highest CAGR with 52.3% over the forecast period. Factory Automation is a Type of Manufacturing Process That Results to Requiring No Human Interaction and Work Automatically. This changes the traditional way of the decision-making process by having interconnected devices from one place to another which helps increase efficiency and innovation in manufacturing processes. Network slicing can reduce latency by up to 50% compared to traditional networks, making it highly suitable for applications requiring real-time communication such as autonomous driving and industrial automation.
Regional analysis
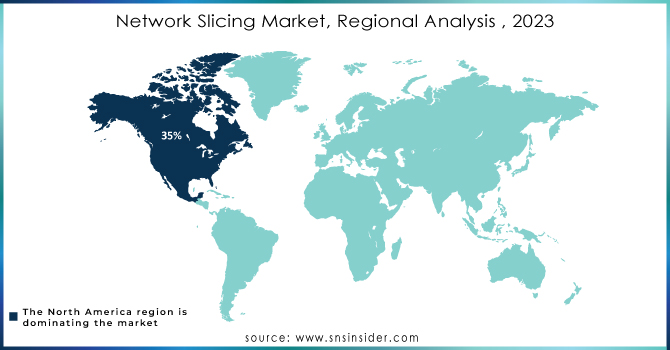
The North America region dominated the market with a 34.5% revenue share in 2023, the growth driven by greater smartphone adoption and the proliferation of internet services that kept adding new internet subscribers. Market growth has been significantly increased in the region due to the presence of major industry players like Cisco Systems Inc., Mavenir Systems, Inc., and Intel Corporation. Additionally, companies in North America are advancing innovative solutions for the risk-free utilization and control of network services, further proliferating market growth. Moreover, the public 5G deployment promotion and increased investment as well as early adoption of advanced technologies on account of high digital engagement are some factors contributing to growth. The increasing adoption of IoT and the explosion in the growth of smart cities across North America region anticipated to offer several opportunities for market expansion over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Asia Pacific is likely to emerge as one of the key regions boasting a CAGR of over 50% during the forecast period. The large and distributed consumer bases in both India & China are driving demand for more services, making network-slicing solutions very valuable. This growth can be attributed to the advancements in IoT technology and infrastructure, along with the rapid adoption of these solutions across multiple major sectors such as healthcare, government, manufacturing & financial services. This makes the area a great investment opportunity for communication service providers, to exploit this untapped potential. Apart from this, companies expanding their presence in the APAC region are increasingly focusing on gaining a wider customer base and growing internet subscribers through solid growth prospects created lucrative opportunities for the regional market.
Region Coverage:
North America
-
USA
-
Canada
-
Mexico
Europe
-
Eastern Europe
-
Poland
-
Romania
-
Hungary
-
Turkey
-
Rest of Eastern Europe
-
-
Western Europe
-
Germany
-
France
-
UK
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Netherlands
-
Switzerland
-
Austria
-
Rest of Western Europe
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Vietnam
-
Singapore
-
Australia
-
Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East & Africa
-
Middle East
-
UAE
-
Egypt
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Qatar
-
Rest of the Middle East
-
-
Africa
-
Nigeria
-
South Africa
-
Rest of Africa
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
Colombia
-
Rest of Latin America
KEY PLAYERS
The major key players in the Network Slicing Market are Ericsson, Samsung, Nokia Corporation, Huawei Technologies, ZTE Corporation, Cisco Systems Inc., HPE, Mavenir Systems Inc., VMware, Affirmed Networks, Samsung, Amdocs, Inc., Intel Corporation, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Tambora Systems Ltd., and other players.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
Ericsson, BT Group, and Qualcomm Technologies completed the first end-to-end testing of UK enterprise and consumer applications all connected across a commercial grade 5G standalone network in February 2024. Ericsson enabled the UK to become an innovation hub with their 5G Core and Radio Access Network.
-
T-Mobile 5G network slicing beta - August 2023 Also, the beta program allows developers to improve video calling applications with better network conditions by providing higher uplink and downlink speeds, lower latency, and increased reliability using T-Mobile's 5G standalone (SA) network.
-
In June 2023, Nokia announced a successful trial of an innovative solution allowing Android smartphone users to purchase and activate network slices on-demand from their service provider. Available to Android 14 users, this feature will enhance user experiences across various applications, including gaming, broadcasting, streaming, and social media.
-
In February 14, 2023, The second development in an announcement in the network slicing market was made by Ericsson. Ericsson announced that it had launched a new network-slicing platform called Ericsson Network Slicing Manager. This platform is designed to help mobile operators deploy and manage network-slicing services more efficiently.
| Report Attributes | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 756 Mn |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 24231 Mn |
| CAGR | CAGR of 51.7 % From 2023 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Component (Solution, Services) • By Enterprise Type (Large Enterprises, Small & Medium Enterprises) • By End-User (Communication Service Providers, Enterprises) • By Industry Vertical (Manufacturing, Healthcare, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods, Retail, E-commerce, Automotive, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]). Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Ericsson, Samsung, Nokia Corporation, Huawei Technologies, ZTE Corporation, Cisco Systems Inc., HPE, Mavenir Systems Inc., VMware, Affirmed Networks, Samsung, Amdocs, Inc., Intel Corporation, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Tambora Systems Ltd. |
| Key Drivers | • The deployment of 5G technology is a major driver for network slicing, providing the necessary infrastructure to support multiple network slices with different performance requirements on a single physical network. |
| Market Restraints | • The initial investment required for the deployment of network slicing infrastructure, including 5G technology and related equipment, can be substantial, and create a barrier for some operators. |

