Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling Market Size & Growth:
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling Market size was valued at USD 699.43 Million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1371.12 Million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.78% during 2025-2032.
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) e-scrap recycling market is experiencing significant growth due to the rapid rise in electronic waste and increasing demand for sustainable solutions. This growth is led by the robust electronics manufacturing and recycling facilities in particularly the APAC region. Innovations in recycling technologies, such as hydrometallurgy and biotechnology, enhance the recovery of metals and facilitate circular economy concepts. Although this business market is promising, some problems remain to be solved, such as the high cost of the facilities required and the difficulty of recycling valuable materials in a diverse range of PCB components and the lack of standard recycling methods. Conquering these barriers is a key factor in enhancing efficiency, raising profitability, and truly harnessing the potential of PCB e-scrap recycling in the years ahead.

To Get more information on Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling Market - Request Free Sample Report
TU Dresden scientists developed “Leaftronics” biodegradable circuit boards from magnolia leaves to tackle rising e-waste, with support from Germany’s EXIST program. With PCBs forming up to 60% of 62M tons of global e-waste (2022), these boards degrade within a month in compost.
The U.S. holds the largest share in the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market market, due to high e-waste generation and strong recycling infrastructure.
PCB E-scrap Recycling Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
-
Rising E-Waste and Metal Scarcity Driving Growth in PCB E-Scrap Recycling Market
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) e-scrap recycling market is driven by the rising volume of electronic waste and the high concentration of valuable metals such as gold, silver, and copper in PCBs. Growing environmental regulations and social pressures are driving companies towards sustainable recycling practices that avoid landfill dumps and recycle precious materials. Increased focus on resource scarcity, as well as the advantages of a circular economy, will also drive demand for efficient recycling technologies. Furthermore the requirement of a consistent supply of strategic metal for electronic fabrication also drives the market, lowering the dependence on conventional mining process and reducing the environmental impact. All of these phenomena contribute to invest and develop PCB e-scrap treatment approaches.
MTM Critical Metals achieved ultra-high-grade gold recovery at 551 g/t, silver at 2,804 g/t, and copper at 42%, with over 95% recovery rates for gold and titanium, and over 90% for silver, tin, and zinc. They secured a five-year e-waste supply agreement with a minimum of 700 tonnes per annum, targeting around 800 tonnes yearly.
Restraints:
-
Impact of Inconsistent Regulatory Frameworks Leading to Operational Challenges in PCB E-Scrap Recycling
Inconsistent regulatory frameworks across different regions create significant challenges for PCB e-scrap recycling operations. The absence of uniform global guidelines has recyclers processing different environmental rules and regulatory baselines that can be quite complex. This patchwork of regulations adds unnecessary complexity to operations, compelling companies to continuously adjust operations to meet local requirements, which leads to higher costs and impedes scaling. Furthermore, inconsistent laws bring legal uncertainties as well as higher penalties for non-compliance. Such an environment is counterproductive to investments and innovating recycling technologies and undermines the efficiency of and wide dissemination of environmentally sound PCB e-waste handling. In order to address these problems, harmonized regulations and clear guidance is required in order to help create a stable and growth encouraging market.
Opportunities:
-
Increasing E-Waste Generation and Regulatory Pressure Expanding PCB E-Scrap Recycling Markets
The increasing volume of electronic waste worldwide offers significant growth opportunities for the PCB e-scrap recycling market. Efficient recycling technology is in greater demand as implementation of waste rules and sustainability targets becomes more rigorous on global markets. Now, fast-growing economies with a rapidly expanding digital adoption have churned out more and more e-waste, creating new markets for recycling. Besides, the development of processes aiming to enhance both the recovery of metals and recycling can also fall into the economic dimension. Circular economy will be led so that manufacturers and recyclers have to work more closely to facilitate the return of materials – that will mean we will see investment and innovation. Furthermore, companies specialised in green certifications and low carbon footprints generate competitive advantages. All these factors combined provided a suitable base for the development of PCB e-scrap recycling plants around the world.
SGS certification Korea Zinc’s Onsan Smelter was certified by SGS for the production of copper products made from 100% Zn, lead byproducts and PCBs instead of new copper concentrate. The firm, aiming to enlarge its production of copper by mid-2025, stands by its green, low-carbon manufacturing.
Challenges:
-
Complex Regulatory Variations Lead to Higher Costs and Operational Difficulties in PCB E-Scrap Recycling
Regulatory compliance complexity poses a significant challenge for Printed Circuit Board (PCB) e-scrap recycling due to the inconsistent and often fragmented environmental laws across different regions and countries. These decentralized local and international rules create a patchwork that makes it hard for recyclers comply. This heterogeneity raises the burden of making business at European level, because companies have to tailor their procedures to comply with different legal requirements and therefore incur additional administrative and compliance costs. In addition, the absence of common guidelines prevents the implementation of more cost-effective and homogeneous recycling activities. As such recyclers have increased exposure to penalties from non-compliance, operations downtime and decreased margins. Clearing these regulatory roadblocks is important to simplify recycling and support sound e-waste management worldwide.
Printed Circuit Board E-scrap Recycling Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
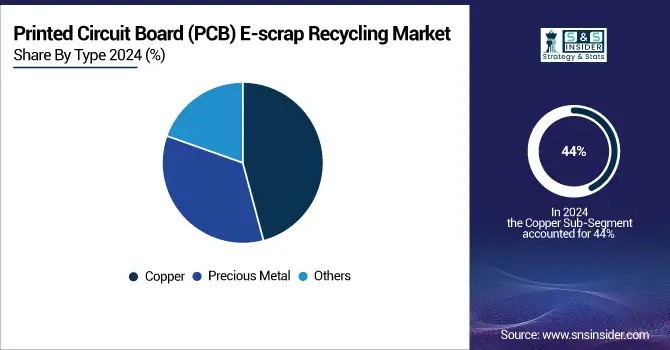
The Copper segment held a dominant Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market share of around 44% in 2024, owing to the fact that it is an indispensable part of electronic components and has high recycle value. Increase in the price of virgin copper, concern for environment and the progression in the process technology to recover copper economically from e- waste has led to an increase in the reclamation of copper from e-waste. This growing demand supports sustainable management of resources and also minimizes reliance on conventional mining operations, thereby benefitting market growth.
The Precious Metal segment is expected to experience the fastest growth in the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market over 2025-2032 with CAGR 10.85%, due to high requirement for expensive metals such as gold, silver and palladium in electronics production. The recovery and re-use of precious metals from PCB e-scrap are also fueled by growing metal scarcity, increasing metal prices, and emphasis on sustainable recycling.
By Application
Smartphones segment held a dominant Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market share of around 36% in 2024 and is projected to experience fastest growth in the market during 2025-2032, at a CAGR of 9.88%. This growth is fueled by the fast-paced smartphone replacement cycle, driven by technological advancements, consumer preferences for upgraded models, and the surge in mobile connectivity. Additionally, the high concentration of precious and rare metals in smartphone PCBs enhances recycling profitability, encouraging both manufacturers and recyclers to expand sustainable e-waste processing practices.
By Source Types
IT and Telecommunication Products segment held a dominant Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market share of around 52% in 2024 and is projected to experience fastest growth in the market during 2025-2032, at a CAGR of 9.44%. This strong growth is fueled by the rapid digitization of economies, the proliferation of connected devices, and rising investments in cloud computing and 5G infrastructure. As organizations upgrade legacy systems and replace obsolete IT hardware, a growing volume of discarded PCBs becomes available for recycling, presenting opportunities to recover valuable metals and support sustainability efforts.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling Market Regional Overview:
In 2024, the Asia Pacific dominated the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market and accounted for 44% of revenue share, due to its rapidly growing electronics manufacturing sector, rising volume of e-waste production, and supportive government programs encouraging the development of e-waste recycling infrastructure and environmentally responsible behaviors.

Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
In Asia Pacific, China leads the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market, owing to presence of large electronics manufacturing bodies and high e-waste generation.
North America is projected to register the fastest CAGR of 8.25% during 2025-2032, driven by stringent environmental regulations, rising e-waste volumes, and increasing awareness about sustainable recycling. The region's robust technological infrastructure and growing adoption of advanced recycling methods further fuel market expansion and investment in PCB e-scrap recycling facilities.
In 2024, Europe emerged as a promising region in the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market , driven by rigorous environmental regulations, strong governmental support for circular economy practices and growing consumer and industrial awareness regarding sustainable e-waste disposal, which accelerated the investment into the advanced recycling technologies and complementing infrastructure in the region.
LATAM and MEA is experiencing steady growth in the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling market, is also growing steadily due to growing e-waste generation, burgeoning urbanization and rising electronic devices penetration. Efforts from governments to manage waste sustainably and growth in recycling infrastructure are contributing further the expansion of the market in these regions.
Key Players:
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling Companies are Umicore, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Aurubis AG, Glencore, DOWA Holdings Co., Ltd., Boliden Group, JX Nippon Mining & Metals Corporation, Elemental Holding S.A., Interco Trading, Inc., Kuusakoski Group and Others.
Recent Developments:
-
In June 2024, Aurubis AG installed a fully automated scrap sampling system at its Lünen, Germany plant, cutting sample preparation from five days to one hour. The USD 6 million investment enhances process security, transparency, and sustainability, with plans to expand the technology to other global sites.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 699.43 Million |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 1371.12 Million |
| CAGR | CAGR of 8.78% From 2025 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2021-2023 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Type (Precious Metal, Copper and Others) • By Application (Smartphones,PC & Laptop, Telecommunications, TV & Monitor and Others) • By Source Type (Household Appliances, IT and Telecommunication Products and Entertainment Devices) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Poland, Turkey, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Australia, Taiwan, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-scrap Recycling companies are Umicore, Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Aurubis AG, Glencore, DOWA Holdings Co., Ltd., Boliden Group, JX Nippon Mining & Metals Corporation, Elemental Holding S.A., Interco Trading, Inc., Kuusakoski Group and Others. |

