Automatic Lubrication System Market Scope & Overview:
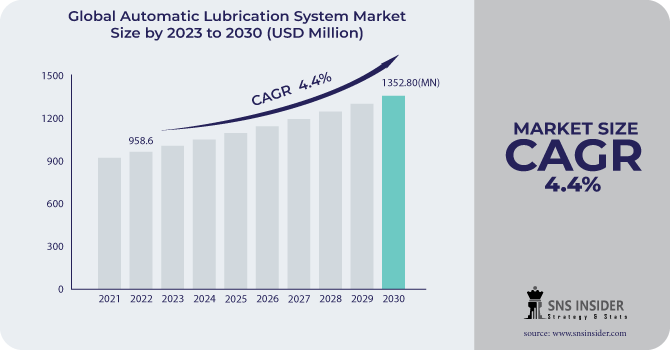
The Automatic Lubrication System Market size was estimated at USD 1001.71 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 1424.55 million by 2031 at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period of 2024-2031.
The market is expanding as a result of rising consumer knowledge of the benefits of employing automatic lubrication systems. Manufacturing businesses all over the world are gradually switching from inefficient manual lubrication techniques to more effective automatic lubrication procedures. This switch from manual to automatic lubrication is propelling market expansion. Some of the world's largest and fastest-growing economies, including China, Japan, and India, are found in the Asia-Pacific region. Cement, steel, and energy Lubrication facilities have been established in the area as a result of the enormous domestic demand for goods and services and the numerous chances for corporate expansion. This is a compelling prospect for market expansion in APAC.
To get more information on Automatic Lubrication System Market - Request Free Sample Report
MARKET DYNAMICS
DRIVER
-
Equipment Longevity and Maintenance automatic lubrication systems ensure consistent and precise lubrication, which can extend the lifespan of machinery and reduce maintenance downtime.
-
Efficiency and Lubrication Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
-
Worker Safety automatic lubrication systems can enhance worker safety by reducing the need for manual lubrication in potentially hazardous environments.
RESTRAIN
-
Purchasing and installing automatic lubrication systems may require a significant initial investment, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses.
-
Automatic lubrication systems may face slower adoption due to a lack of awareness in certain regions and sectors.
OPPORTUNITY
-
In the retrofitting market, it is possible to retrofit existing machinery with automatic lubrication systems, enhancing efficiency and convenience without the need to buy new machinery.
-
Growing industrial sectors' demand for automated solutions, such as automatic lubrication systems, is increased by growing industries like manufacturing, construction, and mining.
CHALLENGES
-
Customization requirements could differ between industries and System Types of machinery, which could make compatibility and customization issues a major roadblock.
-
Upkeep and inspection Although manual lubrication is not as necessary with automatic systems, they still need to be monitored, maintained, and occasionally troubleshooted.
IMPACT OF RUSSIA UKRAINE WAR
Geopolitical conflicts can cause disruptions in the supply chain, which may limit the availability of resources required for manufacturing automatic lubrication systems. This can result in delays and even scarcity. In areas with conflict, infrastructure development and building initiatives may be delayed, which can lead to a decrease in demand for automated systems such as machinery and automatic lubrication systems. Geopolitical tensions and conflicts may also force firms to reduce investments and expenses, indirectly affecting the automated lubrication system market by decreasing demand for machinery and equipment.
Due to the current unpredictable situation, companies may choose to take more cautious measures, such as postponing or reducing investments in automation systems and equipment upgrades.
IMPACT OF ONGOING RECESSION
Supply chain delays Supply chain disruptions brought on by the recession may affect the availability of components and materials required to manufacture automatic lubrication systems. This could lead to production delays and extra expenses. Extended Sales Cycles Businesses may put off purchasing during a recession. Sales cycles may lengthen as businesses carefully consider their financial situations before making investments. Competition and innovation Some manufacturers may innovate and offer more reasonably priced or flexible products in an effort to adapt to changing market conditions. This could increase competition in the market for automatic lubrication systems.
KEY MARKET SEGMENTATION
By Lubrication Type
-
Grease-based Lubrication System
-
Oil-based Lubrication System
By System Type
-
Single-Line Lubrication System
-
Dual-Line Lubrication System
-
Multi-Line Lubrication System
-
Series Progressive Lubrication System
-
Circulating Oil Lubrication System
-
Oil and Air Lubrication System
By Industry
-
Steel
-
Manufacturing
-
Cement
-
Paper & Printing
-
Transportation
-
Construction
-
Agriculture
-
Mining
-
Power
.png)
Need any customization research on Automatic Lubrication System Market - Enquiry Now
REGIONAL COVERAGE
North America
-
US
-
Canada
-
Mexico
Europe
-
Eastern Europe
-
Poland
-
Romania
-
Hungary
-
Turkey
-
Rest of Eastern Europe
-
-
Western Europe
-
Germany
-
France
-
UK
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Netherlands
-
Switzerland
-
Austria
-
Rest of Western Europe
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Vietnam
-
Singapore
-
Australia
-
Rest of Asia Pacific
Middle East & Africa
-
Middle East
-
UAE
-
Egypt
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Qatar
-
Rest of the Middle East
-
-
Africa
-
Nigeria
-
South Africa
-
Rest of Africa
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
Colombia
-
Rest of Latin America
REGIONAL ANALYSES
The lubricating system market is divided into various regions including North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South East Asia-Pacific, China, Japan, India, Middle East, and Africa. Regional demand patterns correlate with the demand from end-use industries.
Europe has been the dominant region in terms of sales, and it is expected to continue its dominance in the end-use industry's demand for lubrication systems. The North American region is also expected to experience significant growth rates due to the expansion of its car fleet. Latin America is predicted to develop at a substantial CAGR during the forecast period due to its increasing industrialization. Similarly, the Middle East and Africa region is expected to grow significantly during the projected period, owing to an increase in construction activity.
Key Players
The major key players are SKF, Graco, BAIER + KOEPPEL, Timken, Bijur Delimon, Samoa, Klueber Lubrication, Perma-tec, Woerner, Dropsa, Cenlub Systems, ATS Electro-Lube, Oil-Rite, Simatec, Etna Products Inc and others.
Graco-Company Financial Analysis
RECENT DEVELOPMENT
Etna Products Inc: In April 2023, As part of its growth objectives, Etna Products Inc. successfully acquired the metalworking fluid line from JTM Products. The purchase aided the business in developing its technologies and a distribution network that would support manufacturing and the establishment of a center for research and development. The organization also concentrates on creating a growth strategy to strengthen its presence in the worldwide market.
Graco: In May 2023, The GCITM Series Cartridge Injector, the first automatic lubricating injector technology on the market, was introduced by Graco. This new lubricant has been developed to provide current injectors in its class with outputs that are twice as high at a cost that is lower for unplanned uptime and would result in labor cost savings.
| Report Attributes | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 1001.71 Mn |
| Market Size by 2031 | US$ 1424.55 Mn |
| CAGR | CAGR of 4.5% From 2024 to 2031 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2031 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Lubrication Type (Grease-based Lubrication System,Oil-based Lubrication System) • By System Type (Single-Line Lubrication System, Dual-Line Lubrication System, Multi-Line Lubrication System, Series Progressive Lubrication System, Circulating Oil Lubrication System, Oil and Air Lubrication System) • By Industry (Steel, Manufacturing, Cement, Paper & Printing, Transportation, Construction, Agriculture, Mining, Power) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | SKF, Graco, BAIER + KOEPPEL, Timken, Bijur Delimon, Samoa, Klueber Lubrication, Perma-tec, Woerner, Dropsa, Cenlub Systems, ATS Electro-Lube, Oil-Rite, Simatec, Etna Products Inc |
| Key Drivers | • Equipment Longevity and Maintenance automatic lubrication systems ensure consistent and precise lubrication, which can extend the lifespan of machinery and reduce maintenance downtime. • Efficiency and Lubrication Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption. • Worker Safety automatic lubrication systems can enhance worker safety by reducing the need for manual lubrication in potentially hazardous environments. |
| Market Restrain | • Purchasing and installing automatic lubrication systems may require a significant initial investment, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses. • Automatic lubrication systems may face slower adoption due to a lack of awareness in certain regions and sectors. |

