Global Diabetes Drug Market Size And Overview:
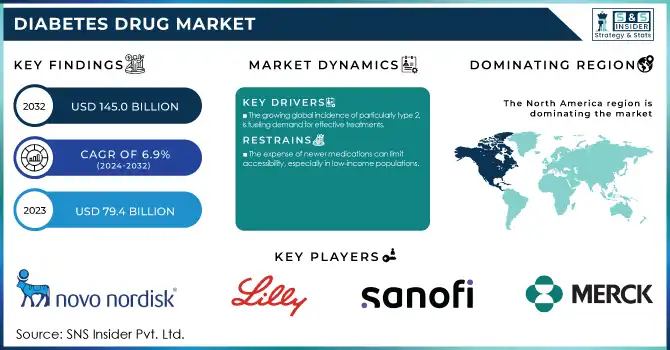
The Diabetes Drug Market Size was valued at USD 79.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 145.0 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Get more information on Diabetes Drug Market - Request Sample Report
This comprehensive report offers in-depth insights into the diabetes drug market. We analyze trends in the existing and future market, explore pricing strategies and drivers of drug pricing, and provide an overview of key patents governing the industry landscape. Our report provides an integrated picture of the diabetes drug market, by highlighting the latest updates and numbers in this fast-evolving field and providing stakeholders with all the tools to make the best strategic decision. There is an increasing incidence of diabetes due to changing lifestyles towards more sedentary behavior, urbanization, and increasing obesity, which is a major driver of the global diabetes drug market. Diabetes is directly associated with 284,049 deaths per year. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 537 million adults around the world had diabetes in 2021, and the number is expected to skyrocket to 783 million by 2045. According to a recent study in India known as the "diabetes capital", more than 212 crore people were affected in 2024.
Diabetes Drug Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
The growing global incidence of particularly type 2, is fueling demand for effective treatments.
The increasing incidence of diabetes remains one of the dominant factors fuelling growth in the diabetes drug market. A recent study states that 90% of people who are suffering from diabetes are having Type 2 diabetes. The rise is compounded by the fact that treatment remains scarce, especially in low- and middle-income countries. From August 2021 to August 2023, the overall prevalence of total diabetes was 15.8% among US adults, with diagnosed diabetes at 11.3% and undiagnosed diabetes at 4.5%. The prevalence was higher in men (18.0%) than in women (13.7%), and it increased with age and weight status. This data highlights the increasing global need for effective diabetes treatments. The burgeoning incidence, particularly in areas with impractical access to care, illustrates the urgent necessity for accessible, and radical diabetes medications to control this growing medical crisis.
Restraints
-
The expense of newer medications can limit accessibility, especially in low-income populations.
High treatment cost is one of the significant restraining factors affecting the market as it limits patient accessibility in the diabetes drug market. Most of the new, better diabetes drugs, like the GLP-1 receptor agonists or the SGLT2 inhibitors, are expensive, and too often out of reach for much of the population. The cost of diabetes treatment is not limited to the price of the medication itself accompanying expenses include device and regular monitoring and insulin delivery devices and doctor consultations.
Patients in low- and middle-income countries often struggle to afford these treatments, leading to poor disease management and increased complications. Moreover, the insurance coverage is highly variable as well and many plans do not cover the full cost of advanced diabetes drug, driving patients to less effective but cheaper options. The economic hurdle constrains market reach and widens gaps in the standard-of-care delivery for Diabetes management, hence impacting patients' long-term prognosis and increasing the chances of diabetes-related complications.
Opportunities
-
Growing diabetic populations in emerging markets present significant opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to expand their reach.
As global diabetes cases climb above 800 million, unprecedented opportunities await pharmaceutical companies and arise out of their reach with emerging market populations containing 90% of the untreated adult cases. Meanwhile, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals took the lead in India with a liraglutide biosimilar at 70% cost reduction of existing therapies, and firms like Hangzhou Jiuyuan Gene Engineering are also progressing on Semaglutide biosimilars ahead of the 2026 patent expiry. Governments are incentivizing production the PLI scheme in India is propping up generic GLP-1 drugs that would launch in 2026, and Eli Lilly has already planned to render Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) available in India by 2025 This diversification of therapeutics is underscored by new innovations such as Innovent Biologics’ Mazdutide near China’s 2025 approval as a dual-target obesity/diabetes drug. As diabetes prevalence exceeds 20% in parts of Latin America and the Middle East, companies are making affordability, screening integration, and partnerships a priority to address systemic shortfalls in detection and care.
Challenges
-
The expiration of patents for key diabetes drugs is leading to increased competition from generic drug manufacturers, potentially impacting market share and profitability.
The expiration of patents for drugs used to treat diabetes indicates the beginning of a competitive and economically challenging transformation period in the pharmaceutical market. This provides the opportunity for generic manufacturers to make their bioequivalent alternatives, typically priced 80-85% lower than branded versions, eroding the market dominance of originator companies. Innovators like Sanofi and Novo Nordisk face huge drops in revenue, forcing drastic strategic shifts to create next-generation formulations or find additional indications. Generics lower costs and provide access, but the path to entry is fraught. Patent thickets are commonly deployed by originators, which see secondary patents filed on delivery devices or formulations with a view to ensure competitors are delayed from entering the market. This slows generic market entry even more due to regulatory complexities and litigation risk. Meanwhile, quality issues such as NDMA contamination of metformin generics necessitate strict bioequivalence requirements. These dynamics strain profitability for innovators but drive systemic cost savings, reshaping diabetes care accessibility while challenging firms to innovate beyond patent-dependent models.
Diabetes Drug Market Segmentation Analysis
By Drug Class
In 2023, the GLP-1 Receptor Agonists segment dominated the market, as a result of their dual action of glycemic control and subcutaneous help. According to the UK National Diabetes Audit (2024), there had been a 22% rise in the number of people with type 1 diabetes receiving GLP-1 therapies, given evidence of their benefits in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. The WHO’s 2024 guidelines endorsing GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide for obesity management have expanded their adoption.
Insulin is poised for substantial growth, driven by rising type 1 diabetes cases and accessibility initiatives. In response to rising demand in lower-income regions, approvals for biosimilar insulins received a fast track from India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in 2024. Insulin is so expensive that worldwide it leaves over 100 million patients dependent on life-sustaining therapy suffering, as per the International Diabetes Federation (2024).
By Diabetes Type
The Type 2 diabetes segment dominated the market with the highest revenue share in 2023, According to the WHO, more than 90% of cases in 2023 are attributed to type 2 diabetes, and it was encouraged as a result of obesity and metabolic syndrome. According to the 2024 National Diabetes Statistics Report, 38.4 million adults in the U.S. had type 2 diabetes, of which 8.7 million were undiagnosed, the CDC said. The National Family Health Survey in 2023 exemplified this- some form of urban sedentary lifestyle was associated with a 15% increase in prevalence in metros. Governments have driven campaigns to reduce type 2 ultimately through lifestyle changes such as the EU 2025 Diabetes Prevention Pact campaign that indirectly increases the demand for oral antidiabetics and GLP-1 agonists.
By Route of Administration
The subcutaneous route held the largest revenue share in 2023, as it is the primary route of administration for diabetes medications, especially insulin, and is broadly accepted by patients because of its safety and convenience. Subcutaneous injections consist of injecting medication into the fatty tissue of the skin, usually resulting in slow absorption into the bloodstream. The constant release is essential to keep the blood glucose levels unchanged, particularly with slow-acting insulins. Subcutaneous injections are relatively easy for the patient to self-administer, allowing them to become their own doctor to a degree by controlling their diabetes with minimal clinical visits. Authorities in health have identified that with the proper care of diabetes, we can conclude the value of being below the skin. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for example, has authorized the use of numerous insulin products for subcutaneous (under-the-skin) delivery, simply reinforcing their effectiveness and safety.
By Distribution Channel
In 2023, the market was dominated by retail pharmacies due to convenience and availability at most pharmacies. Recent data in 2024, revealed that 63% of diabetes drugs were dispensed via retail channels, supported by generic affordability. The Inflation Reduction Act (2022) capped insulin copays at USD 35/month in the U.S. and raised retail procurement by Medicare beneficiaries. American Pharmacists Association (2020–2023) data indicate a 12% increment in SGLT2 inhibitor and DPP-4 retail prescriptions.
Diabetes Drug Market Regional Outlook
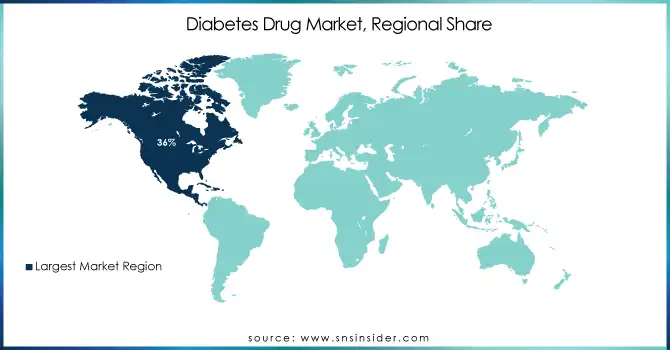
In 2023, the North American region dominated the market with a 36% market share. This leadership position is primarily attributed to the region's high obesity rates, with 42.4% of U.S. adults classified as obese. The advanced healthcare infrastructure in North America, particularly in the United States, further supports this market dominance. In 2024, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a diabetes prevalence of 11.6% which represents a significant patient population. The economic impact is evident in the $12 billion annual Medicare spending on antidiabetic medications, reflecting both the high cost of treatment and the extensive coverage provided.
Asia-Pacific is projected to grow the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is primarily propelled by gigantic diabetic figures of India and China stand at around 21 crores and 14 crores respectively. These figures highlight the vast market potential in the region. The expansion of the market is a key role played by government initiatives. As an example of this, the National Health Mission of India set aside ₹2,500 crore in 2024 for screening of diabetes, a clear stance towards early detection intervention. At the same time, the State Council of China has integrated AI-based diagnostics into rural healthcare systems, addressing the challenge of healthcare access in remote areas. These initiatives help provide better therapy to patients as well as drive the market upwards through increased diagnosis and availability of treatment.
Need any customization research on Diabetes Drug Market - Enquiry Now
Key Players
Key Service Providers/Manufacturers
-
Novo Nordisk A/S (Ozempic, Rybelsus)
-
Eli Lilly and Company (Mounjaro, Trulicity)
-
Sanofi (Lantus, Toujeo)
-
Merck & Co., Inc. (Januvia, Janumet)
-
AstraZeneca (Farxiga, Bydureon)
-
Boehringer Ingelheim (Jardiance, Trajenta)
-
Bayer AG (Glucobay, Acarbose)
-
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (Actos, Nesina)
-
Pfizer Inc. (Exubera, Ertugliflozin)
-
MannKind Corporation (Afrezza, Technosphere Insulin)
Key Users
-
Mayo Clinic
-
Cleveland Clinic
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
-
UnitedHealth Group
-
Kaiser Permanente
-
CVS Health (Aetna)
-
Cigna Corporation
-
Anthem, Inc.
-
Humana Inc.
-
Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
Recent Developments
-
Eli Lilly’s Mounjaro in India December 2024, approved for obesity and diabetes, targeting 11% of India’s projected obese population by 2035.
-
Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy EU Expansion January 2025, EMA-approved GLP-1 agonist entering 10 markets to address 32 million obese adults.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 79.4 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 145.0 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 6.9% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Drug Class (Insulin, SGLT2 Inhibitors, DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, Others) • By Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenous, Subcutaneous) • By Diabetes Type (Type 1, Type 2) • By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, Sanofi, Merck & Co., Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer AG, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Pfizer Inc., MannKind Corporation |

