Lignin Market Analysis & Overview:
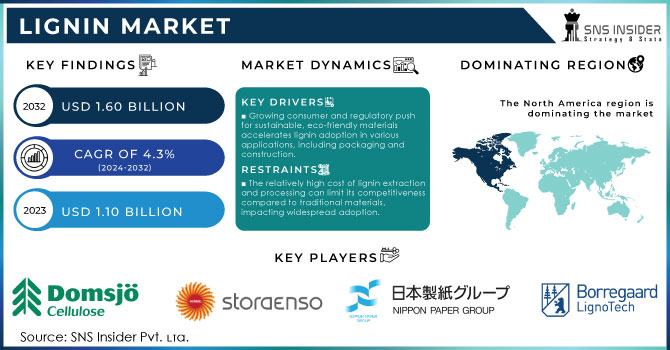
The Lignin Market Size was valued at USD 1.10 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 1.60 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 4.3% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Get More Information on Lignin Market - Request Sample Report
The lignin market is gathering high momentum with the growing demand for sustainable alternatives for many industries. Lignin, a complex organic polymer in the cell walls of plants, has emerged as one of the valuable by-products of the pulp and paper industry with broad applications in bio-based materials, adhesives, and coatings.
The lignin market growth is accomplished by several factors including the worldwide impetus toward environmental sustainability, the development of material science, and increasing priority given to reducing carbon footprint. Such versatility-exhibiting applications, from construction to packaging, are showing increased demand for environmentally friendly solutions. Key players are making investments in lignin-based technologies that spur innovation and create new products.
The changing lignin market trends in consumer preference for green alternatives is one of the major dynamics in the market, consequently forcing manufacturers to shift toward the adoption of lignin-based materials for sustainable applications. One good example of this surging importance of lignin can be experienced in recent glove coating technology. Scientists developed an environmentally friendly coating for protective gloves from lignin in September 2024. This invention demonstrates that lignin has the potential to replace synthetic chemicals in traditional coatings with biodegradable ones, hence making it feasible for industries seeking environmental friendliness.
Furthermore, the 3D printing technology improves efficiency and decreases waste in the coating process. This development underlines not only the flexibility of lignin in different applications but also its grand potential to meet the increasing demand for bio-based materials in everyday products. All these developments contribute to the continuous growth in the adoption of lignin in various industries.
Lignin finds applications in the automotive sector. A very good example comes from Nokian Tyres, who joined forces with UPM (United Paper Mills) in July 2024 to create a concept tire based on lignin-based materials. This has been a revolutionary step toward the manufacturing of more ecological tires by decreasing dependency on traditional components based on petroleum. The fact that lignin is used to produce tires highlights its strength and toughness for automotive usage. By embracing lignin in product development, the companies are saving not only on non-renewable resources but also standing in line with the global trend of moving toward greener manufacturing processes. These current developments open a pathway to further collaboration and wider use of lignin in industries where high-performance material is involved.
Meanwhile, the packaging industry is not an exception to the recent lignin technologies. Along with this, the introduction of the world's largest lignin production system into a Södra pulp mill in July 2024 marked another major milestone in capacity for lignin production. Large and full-scale production of lignin can be further used in everything from different packaging applications as a bio-based alternative to many synthetic coatings and adhesives.
Strategic expansion in production capacity is crucial to meet the continuously increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions, as more and more firms try to substitute conventional petroleum-based products with lignin. This also highlights the wider market dynamics, where lignin is increasingly recognized for its role in offering cost-effective and significant alternatives not only in packaging but also in several other industries.
Breakthroughs in material science and industrial production are continuously made in the lignin market. With companies including Nokian Tyres and Sodra ramping up their consumption of lignin-based products, applications for the material are surely increasing across various industries. Regarding the surge in R&D activities pointed toward the improvement of properties, development of better compatibility with existing manufacturing processes, and search for new the market is extremely promising. Lignin is expected to play a very important role in the transition to greener industrial processing due to the growing global demand for renewable materials.
Lignin Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
-
Growing Consumer and Regulatory Push for Sustainable, Eco-friendly Materials Accelerates Lignin Adoption in Various Applications Propel Market Expansion
The developing consumer and regulatory drive for the use of sustainable and green materials is considered one of the key factors accelerating the use of lignin in packaging, construction, and other industries. With growing environmental awareness, both consumers and industries are likely to demand those products which will ensure less harm to the environment and further assist in a circular economy. Stringent regulations and policies have been driving this change, taken by governments to decrease carbon footprint and encourage sustainability.
For instance, as many key players in the packaging industry are searching for replacements for traditional materials based on petroleum to respond to new regulations on packaging that demand less plastic usage and a higher degree of recyclability, lignin, naturally derived from wood and other plant components, becomes a very desirable replacement feedstock since it possesses both biodegradable and renewable properties. The lignin used in the construction industry is meant for developing eco-friendly composite materials and adhesives that replace synthetic chemicals and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources.
This trend is well-illustrated by an increase in using lignin-based insulation materials and structural components in energy-efficient and sustainable building practices. This rising market demand for such green alternatives, in turn, puts pressure on companies to invest in research and development to enhance the performance of lignin and expand the number of applications, meeting both consumer preference and regulatory requirements in the process. The result is a critical position that lignin occupies in this transition to more sustainable materials, inspired by a meeting of environmental responsibility with innovation.
-
Innovations in Processing Technologies Enhance Lignin’s Properties, Making it More Versatile and Cost-Effective for Diverse Industrial Uses
The innovations in processing technologies have significantly improved, up to these days, the properties of lignin to such a point that it has become a much more versatile and cost-effective material for a wide range of industrial applications. Advanced techniques of extraction and refinement allow for the production of lignin with higher purity and functionality, which could be used beyond the traditional uses. Recent chemical and enzymatic treatment methods have obtained high-performance new lignin derivatives that could be applied to advanced composite and polymer materials. These improved types of lignin source products possess higher mechanical strength and strong resistant properties that are required in advanced applications including the automotive and aerospace industries.
Besides this, new methods developed for the modification of lignin by grafting and cross-linking have been able to produce new materials with designed properties, suitable for such applications as specialty coatings, adhesives, and even pharmaceuticals. This advances not only the performance of this material but also the economic issues around it through optimization of the processes and higher yields. Advanced processing techniques have allowed the development of carbon fibers from lignin and would likely provide a further sustainable path ahead from conventional carbon fibers, which are normally used in lightweight, high-strength applications. The broader diffusion of these innovative solutions will be a driver for wider utilization of lignin within a variety of industries searching for affordable high-performance, environmentally friendly materials.
Restraints:
-
High Cost of Lignin Extraction and Processing can Limit its Competitiveness Compared to Traditional Materials, Impacting Widespread Adoption
The relatively high cost of extraction and processing is indeed a serious barrier to wider utilization, as this would blunt the material's competitiveness when compared to other more conventional and well-established materials. Special equipment and technologies are employed in isolating and purifying lignin from biomass through complicated and energy-intensive processes, contributing to the high production cost. For example, most of the extractions of lignin are still in need of expensive chemical treatment and involve a very long chain in processing steps to achieve quality and consistency for value creation.
As a result, this could be a very critical barrier for companies seeking to replace conventionally used and cheaper materials, such as plastics made from petroleum. Additionally, this cost difference highly impacts the ability of any lignin-based product to compete based on price, at least within traditionally price-sensitive markets like packaging and construction. But while this places lignin in a very good position to serve as an alternative that is friendly to the environment, its higher cost of production compared to existing products inhibits the spread of its application and states its use in niche applications where environmental benefits outweigh cost considerations.
Opportunity:
-
Expanding Research into Lignin-based Composites and Functional Materials Opens New Market Opportunities in the Automotive and Consumer Goods Sectors
The surging research expansion into lignin-based composites and functional materials is creating new market opportunities for industries including consumer goods and automotive by completely realizing the potential of lignin in various new applications. For instance, the current research aims to develop a high-strength, lightweight composite out of lignin for use in automotive components at decided ecological advantages and offering performance gains compared to conventionally used materials.
Similarly, lignin-based materials are also being developed for use in consumer products, such as green textiles and even consumer electronics, which would be long-lasting. These render different sustainable alternatives, along with surging appeal for the increasingly environmentally conscious consumer. These advances create new revenue generation opportunities while keeping up with the trend of sustainability, hence spurring interest and investment into lignin-based innovations across a wide array of industries.
Challenges:
-
Variability in Lignin Quality from Different Sources Can Affect its Performance in Applications, Posing a Challenge for Manufacturers Seeking Reliable, Standardized Products
The variabilities in the quality of lignin derived from different sources may be one of the barriers to the provision of a consistent and reliable product for the manufacturers. Indeed, the purity, chemical structure, and performance characteristics of the lignin-derived through the processing of various plant materials may differ. This inconsistency in the character may affect its effectiveness for specific applications, such as the formulation of high-strength composites or biobased adhesives where a uniform property profile will critically determine performance and reliability.
For instance, a difference either in molecular weight or in functional groups may affect lignin compatibility with other materials or diminish its potential to give the properties that are expected from them mechanically. Due to this fact, a manufacturer may have limited product quality consistency and also face difficulties complying with strict industry standards. In the final lignin market analysis, this might hamper the wider diffusion of the lignin-based solution and therefore limit market potential.
Lignin Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product
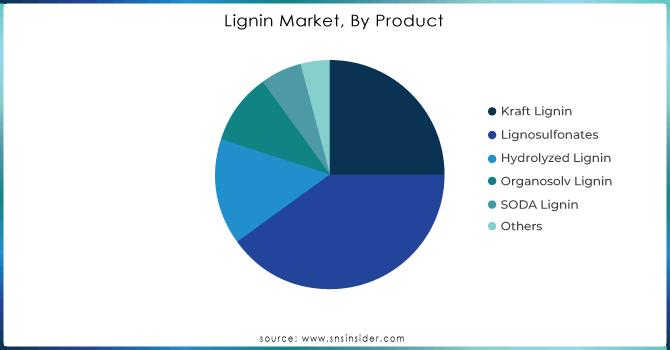
In 2023, Lignosulfonates dominated the market for lignin with a lignin market share of about 40%. This is due to the great number and variety of uses that have been found for lignosulfonates along with the established production process. In large amounts, the main uses of the lignosulfonates are concrete admixtures, soil conditioners, and additives for animal feeds. This versatility and economy make the material the choice in many industrial applications.
It means that, for instance, in the concrete mixtures of the construction industry, improving workability by the addition of lignosulfonates enhances strength, thus helping the demand to move toward high-performance construction materials. Other applications of the products in agriculture contribute to soil quality and improvements in crop yields, further strengthening their position as the leading segment in the lignin market.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Request For Customized Report
By Application
In 2023, the dispersants segment accounted for around 35% of the estimated share of the market. The leading position of this segment can be traced to the broad application of dispersants using lignin across many industries, most especially in construction and agriculture. Lignin dispersants help improve the workability and strength of mixtures in concrete formulations; thus, they are quite important in the making of high-quality concrete.
They also find applications in agriculture to enhance the efficacy of fertilizers and pesticides through better distribution and absorption. In such cases, lignin-based dispersants have been useful in stabilizing suspensions and preventing clumping-a fact considered critical for achieving consistency in construction materials and agricultural products. This versatility, added to the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient dispersants, constitutes the reason for their leading market share position within the lignin sector.
Lignin Market Regional Outlook:
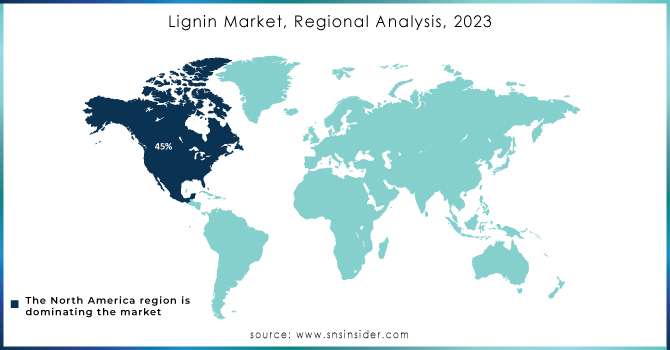
In 2023, Europe dominated the lignin market due to its strong industrial base, high demand for bio-based products, and supportive government regulations promoting sustainability. The market share for Europe in this sector was approximately 40%, with countries like Germany, Sweden, and Finland leading the charge. Germany's focus on renewable energy and the development of bioplastics significantly contributed to lignin's usage in various applications, such as adhesives and construction materials. Sweden and Finland, with their vast forestry resources, have established lignin production facilities that cater to both domestic and international markets.
For instance, the development of lignin-based phenolic resins in Sweden showcases innovative applications that enhance performance and sustainability in construction. Additionally, Finland's investment in lignin extraction technologies has improved yield and efficiency, further solidifying the region's leadership in the lignin market.
Moreover, the Asia Pacific region emerged as the fastest-growing area in the lignin market in 2023, with a significant CAGR. This growth can be attributed to increasing industrialization, rising demand for eco-friendly products, and significant investments in research and development. China, India, and Japan are key players in this growth trend, with China leading the charge due to its extensive agricultural output and the need for sustainable alternatives to petrochemicals.
For instance, China has invested heavily in lignin-based biopolymers for applications in packaging and textiles, showcasing a shift toward sustainable production methods. India's growing focus on renewable energy and waste management has also spurred lignin utilization, with several startups developing lignin-based solutions for biofuels and chemical production. Japan's advancements in lignin technology have enabled the country to explore diverse applications, further boosting its market potential.
Key Players:
The leading lignin companies are Domsjo Fabriker, Stora Enso, Nippon Paper Industries Co. Ltd., Borregaard LignoTech, West Fraser, UPM Biochemicals, Domtar Corporation, Changzhou Shanfeng Chemical Industry Co. Ltd., Burgo Group S.p.A, and Rayonier Advanced Material.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 1.10 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 1.60 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 4.3% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | •By Product (Kraft Lignin, Lignosulfonates, Hydrolyzed Lignin, Organosolv Lignin, SODA Lignin, Others) •By Application (Transportation Fuel, Construction Material, Dispersants, Carbon Fiber & Bio-based Carbons, Vanillin, Biopolymer, Animal Feed, Resins & Glues, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Domsjo Fabriker, Stora Enso, Nippon Paper Industries Co. Ltd., Borregaard LignoTech, West Fraser, UPM Biochemicals, Domtar Corporation, Changzhou Shanfeng Chemical Industry Co. Ltd., Burgo Group S.p.A, Rayonier Advanced Material and other key players |
| Key Drivers | •Growing consumer and regulatory push for sustainable, eco-friendly materials accelerates lignin adoption in various applications, including packaging and construction •Innovations in processing technologies enhance lignin’s properties, making it more versatile and cost-effective for diverse industrial uses |
| RESTRAINTS | •The relatively high cost of lignin extraction and processing can limit its competitiveness compared to traditional materials, impacting widespread adoption |

