Lysosomal Storage Disease Treatment Market Report Scope & Overview:
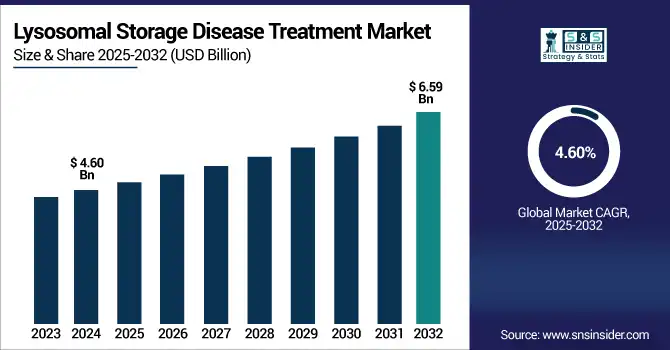
The lysosomal storage disease treatment market size was valued at USD 4.60 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 6.59 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.60% over 2025-2032.
To Get more information on Lysosomal-Storage-Disease-Treatment-Market - Request Free Sample Report
The lysosomal storage disease treatment market is undergoing exceptional change on account of rapid growth in new and innovative treatments. The increasing prevalence and earlier diagnoses made possible by newborn screening and genetic testing are driving treatment requirements for the 70+ lysosomal storage disorders known globally.
In January 2025, REGENXBIO announced encouraging results from its Phase I/II study for its AAV-based therapy RGX-121 for the treatment of MPS II, which was an important milestone in CNS-targeted therapies that would influence future lysosomal storage disease treatment market trends.
Enzyme Replacement Therapies (ERTs), chaperone therapies, and gene therapies are being pursued vigorously by the likes of Sanofi (Genzyme), Takeda, Amicus Therapeutics, and BioMarin, among others, in a buzzing R&D area. The Company will spend more than USD 300 million on next-gen therapies for Fabry and Pompe disease to provide a context of the Growing lysosomal storage disease treatments market size and competitive landscape.
Regulatory incentives, including orphan drug landscape designations, priority review processes, and sympathetic reimbursement policies in the US, EU, and Japan, are also driving access. Rising patient consciousness, public-private partnerships, and better healthcare infrastructure will also contribute to the demand for the lysosomal storage disease treatment market, particularly as diagnosis-to-treatment conversion rates gain noticeable traction.
In June 2024, AVROBIO re-launched its lentiviral gene therapy program for Gaucher disease following funding, strengthening investor confidence, and increasing lysosomal storage disease treatment market share within the gene therapy segment.
Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
-
Rising R&D Investments, Diagnostic Advancements, and Regulatory Support Fuels Market Expansion
The lysosomal storage disease treatment market is growing due to rapid development in the field of the genetics and increased spending on R&D. Advances in diagnostics, including whole-exome sequencing (WES) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), are making it possible to identify LSDs, such as Niemann-Pick and MPS III, in the earliest stages of symptomatic presentation, which can facilitate earlier medical intervention. The NIH reports that rare diseases research funding was more than USD 5.2 billion in 2023, and a significant percentage went toward gene and enzyme treatment development for LSDs. Other companies like Ultragenyx and JCR Pharmaceuticals are building their pipelines with new delivery methods, including blood-brain barrier-penetrating ERTs.
In a positive regulatory environment, accelerated approval was granted for the use of Pombiliti (cipaglucosidase alfa) in combination with Opfolda (miglustat) for late-onset Pompe disease by the FDA in 2023. Data from the first clinical trial for late-onset Pompe disease were released in 2021. The EMA’s PRIME scheme and Japan’s Sakigake designation are other instances to propel LSD drug development. There are also increasing numbers of rare disease awareness issues and increasing acceptability of reimbursement in certain key healthcare systems that are pushing for the adoption of therapy. Alongside this, strategic industry partnerships and the advent of gene editing technologies are substantially impacting treatment options and strengthening this market's forward trajectory.
Restraints:
-
High Treatment Costs, Limited Patient Access, and Manufacturing Complexities Hamper the Market Growth
Innovation aside, several serious obstacles continue to obstruct the LSD treatment market, including the high cost of therapies, restricted availability on a global scale, and significant obstacles to biomanufacturing. Enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs) are estimated to be around USD 300,000–USD 500,000 per patient per year, posing a significant burden on healthcare resources, particularly in resource-poor countries.
For instance, the annual price tag of Elaprase (idursulfase) for Hunter syndrome is more than USD 375,000, and the gene therapies under development for Batten disease or MPS III are likely to top USD 1 million per dose. Access limitations in several markets, along with payer scepticism toward newer treatments, particularly gene and chaperone therapies, slow market penetration. Moreover, LSDs frequently need intravenous infusions for life, which is burdensome for patients and health care systems.
Biologic production, in particular ERTs and viral vectors for gene therapy, remains extremely complex, with batch-to-batch variability a reality, while global manufacturing capacity is constrained. Meanwhile, disrupted supply chains and the requirement for cold-chain storage compound problems of delivery inefficiency. Moreover, most LSDs are ultra-rare, which reduces the economic motivation to develop therapies for all subtypes. Regulatory challenges to prove long-term safety, particularly in gene therapy, are another factor that can set back product approval and lead to higher expenses. Together, these constraints undermine scalability, affordability, and access, particularly in underserved areas.
Segmentation Analysis:
By Therapy Type
ERT (Enzyme Replacement Therapy) was the largest segment in the therapy type segment in 2024, and is anticipated to hold the market share of more than 61.3% during 2025-2032. The role of ERT in LSD treatment. ERT has been the therapy of choice for LSDs, and approvals are many years old, with proven clinical efficacy and broad application in diseases like Gaucher, Fabry, and Pompe disorders. The fact that its successful reimbursement backing and adoption by doctors have helped it to maintain a stronghold.
Gene therapy developed as the fastest growing segment during the forecast period due to growing number of approval and robust pipeline developments of one-time treatment which has a potential cure. Its early success with disorders such as MPS II (Hunter Syndrome) and Krabbe disease, coupled with regulatory assistance in the form of both the orphan drug and fast-track designations, is driving its development.
By Application
Gaucher disease emerged as the leading segment in 2024, accounting for a share of 26.7%. Among the LSDs, it is the most common, with a range of confirmed treatment modalities, including several ERTs and SRTs, owing to a larger treated patient pool and commercial activity.
With increasing prevalence driven by the implementation of newborn screening programs and the life-threatening nature of disease, the mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS I, II, III, etc) represent by far the fastest growing application area with a need for CNS-directed therapies. A number of clinical trials involving gene transfer, and intrathecal enzyme delivery are working to meet the need and speed the implementation of treatment.
By Route of Administration
Intravenous (IV) administration remained the largest administration type with 68.1% market share in 2024. The majority of ERTs and infusions currently in use in hospital settings are administered intravenously; this remains the standard route of administration for treating Gaucher, Fabry, and Pompe diseases.
Oral administration is the fastest growing route because it includes the growing use of oral SRTs (like eliglustat, and miglustat) and chaperone therapies (like migalastat). Oral formulations enhance patient convenience, compliance and access especially for at home care.
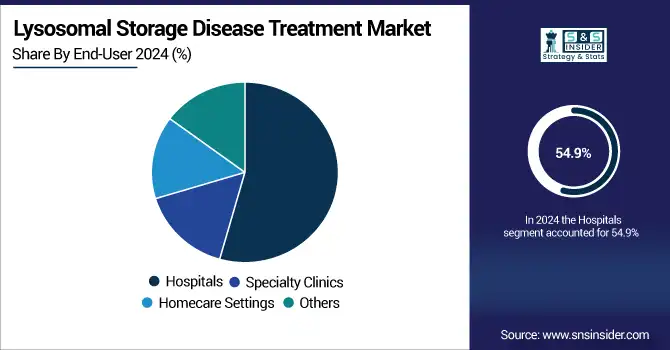
By End-User
Hospitals were the largest revenue contributor, 54.9% in 2024, owing to their infrastructure set up for IV infusions, cold-chain storage, and specialized monitoring of LSD treatments.
The homecare end-user segment is anticipated to register the highest CAGR, driven by adoption of patient-centric models of care, increasing availability of oral treatment options, and growing trend of homebased infusion operators. This movement is being further bolstered by insurance expansions and an increased merging with telehealth.
Regional Analysis:
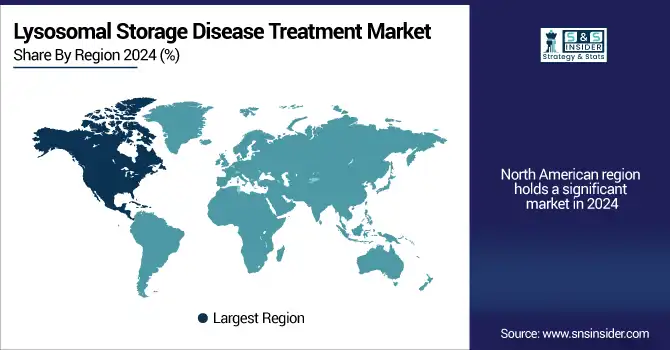
The lysosomal storage disease treatment market in 2024 was led by North America on account of the robust health care infrastructure, superior diagnostic technologies, and rapid uptake of novel therapies. The area contributed a substantial portion, mainly due to high treatment rates and public coverage for treatment.
The U.S. Lysosomal Storage Disease Treatment market size was valued at USD billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of % over 2025-2032. The U.S. was seen as the leading market due to FDA-backed accelerated approvals, the common use of enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs), and enormous R&D spending. As per NIH numbers, more than USD 2 billion has been invested solely in 2023 in research of rare diseases, such as lysosomal disorders. Canada is likewise witnessing surging adoption of SRTs and gene therapies on account of evolving healthcare policies. The increasing patient support networks, increasing collaborations with the pharmacies, orphan drugs availability and pharmaceuticals launch contribute to North America’s dominant position in the lysosomal storage disease treatment market, along with market share.
The second fastest growing region in the lysosomal storage disease treatment market is Europe, on account of an increase in newborn screening, centralized treatment protocols, and the availability of orphan drug incentives under EMA (European Medicines Agency). Germany, the region’s powerhouse, has the highest public healthcare spending and the best access to marketed treatments, including Fabrazyme, Elaprase, and Myozyme. Germany can be considered an important game player, owing to its strong clinical testing infrastructure and SHI (Statutory Health Insurance) coverage. Nations such as France and the UK are also strengthening the MPS practices and initiating oral and home-based treatments, which in turn have fueled the market demand. Owing to EMA’s PRIME scheme, the approvals for gene therapy are speeding up, aiding novelty throughout Europe for the lysosomal storage disease treatment market analysis.
Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market in the lysosomal storage disease treatment market due to the increasing accessibility of the healthcare sector, the rising awareness, and the initiation of several government policies for rare disease management. of dominant country is Japan, with national registry of rare diseases, newborn screening, and many ERT approved by Nanbyo system. Japan is also the frontrunner in clinical trials, with domestic players such as JCR Pharmaceuticals advancing CNS-penetrating ERTs. China is gaining momentum in expanding its diagnostic infrastructure and has included several LSDs on the national reimbursement drug list (NRDL). Its “Healthy China 2030” policy involves rare disease inclusion and support for early genetic testing. The uptake of diagnostic genetic testing is growing in India and South Korea, and the availability of therapy is increasing through global drug approvals, which is driving demand for the market in the region.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Key Players:
Prominent lysosomal storage diseases treatment companies operating in the market include Pfizer Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (formerly Shire Plc), Sanofi (via Genzyme), BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., Johnson & Johnson (Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd), Amicus Therapeutics Inc., Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sigilon Therapeutics Inc., Orphazyme A/S, AVROBIO Inc., Freeline Therapeutics, Sangamo Therapeutics, REGENXBIO Inc., Orchard Therapeutics, Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A., Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd, Lysogene S.A., and Inventiva Pharma.
Recent Developments:
-
In June 2025, Amicus Therapeutics received Japanese regulatory approval for Pombiliti (cipaglucosidase alfa) in combination with Opfolda (miglustat) to treat adults with late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD), further expanding its global commercial footprint following U.S. and EU authorizations.
-
In May 2025, Novartis initiated a Phase I/II trial in May 2025 for DFT383, its lentiviral HSC gene therapy candidate targeting pediatric cystinosis, marking its latest entry into the LSD gene therapy space.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.60 billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 6.59 billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 4.60% From 2025 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2021-2023 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Therapy Type (Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) (Velaglucerase Alfa, Taliglucerase Alfa, Agalsidase Beta, Laronidase, Imiglucerase, and Others), Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT) (Eliglustat, Miglustat, and Others), Gene Therapy (AAV-Based Gene Therapy (e.g., for Fabry and Gaucher), Lentiviral Vector-Based Therapy, and Others), and Chaperone Therapy (Migalastat, Others) • By Application (Gaucher Disease, Fabry Disease, Pompe Disease, Mucopolysaccharidoses, Cystinosis, Niemann-Pick Disease, and Others) • By Route of Administration (Intravenous (IV), Oral, Subcutaneous, and Others) •By End-User (Hospitals, Specialty Clinics, Homecare Settings, and Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (U.S., Canada), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Russia, Poland, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, ASEAN Countries, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Egypt, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Pfizer Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (formerly Shire Plc), Sanofi (via Genzyme), BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., Johnson & Johnson (Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd), Amicus Therapeutics Inc., Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sigilon Therapeutics Inc., Orphazyme A/S, AVROBIO Inc., Freeline Therapeutics, Sangamo Therapeutics, REGENXBIO Inc., Orchard Therapeutics, Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A., Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd, Lysogene S.A., and Inventiva Pharma. |

