Smart Grid Security Market Report Scope & Overview:
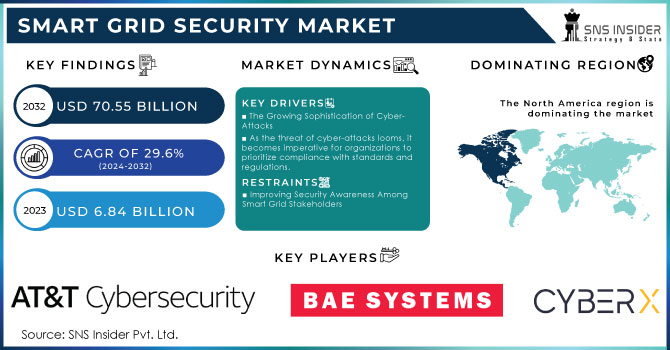
Smart Grid Security Market was valued at USD 8.05 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 33.24 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.14% from 2024-2032.
The Smart Grid Security Market is seeing substantial expansion due to the rising demand for sophisticated energy systems, especially with the implementation of smart grids. This increase is propelled by the demand for improved security measures to safeguard these grids against cyberattacks and weaknesses, which have become more common with the incorporation of IoT devices and digital technologies. Recent studies indicate that 93% of organizations experienced two or more identity-related breaches over the past year, and by 2024, the global average expense of a data breach has risen to USD 4.88 million, representing a 10% rise compared to 2023. As these technologies enhance energy management efficiency, they also bring new risks, raising concerns about grid safety. As a result, energy firms are putting more resources into strong security measures to protect their systems, driving the continuous growth of the industry.
As smart grids expand worldwide, the need for robust security measures is anticipated to rise alongside the growing complexity of cyber threats. The transition from conventional energy systems to more integrated, digital networks has opened up new opportunities for cyberattacks, compelling grid operators to emphasize cybersecurity. This has led to increased interest in sophisticated technologies, including real-time monitoring, encryption, and anomaly detection, to avoid service interruptions and maintain a stable energy supply. Consequently, participants throughout the energy industry are pursuing advanced security solutions to address these changing threats, thus propelling the market's expansion.
Looking ahead, the Smart Grid Security Market is well-positioned for continued expansion, with numerous opportunities emerging as the energy sector becomes increasingly digitalized. The rapid deployment of smart grids in emerging markets presents a particularly strong growth opportunity, as these regions work to modernize their energy infrastructure. Moreover, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources requires secure, distributed systems to manage energy production and consumption effectively. To meet these needs, integrating advanced AI and machine learning into grid security will be critical, offering a wealth of opportunities for companies specializing in smart grid security technologies.
Smart Grid Security Market Size and Forecast:
-
Market Size in 2023: USD 8.05 Billion
-
Market Size by 2032: USD 33.24 Billion
-
CAGR: 17.14% from 2024 to 2032
-
Base Year: 2023
-
Forecast Period: 2024–2032
-
Historical Data: 2020–2022
To Get More Information on Smart Grid Security Market - Request Sample Report
Smart Grid Security Market Trends:
-
Increasing adoption of smart grid technologies driving demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions
-
Rising cyber threats targeting IoT-enabled grid infrastructure and smart meters
-
Growing deployment of AI-based monitoring, anomaly detection, and real-time threat response
-
Expansion of cloud-based security platforms for scalable grid protection
-
Strengthening regulatory frameworks for critical energy infrastructure security
-
Accelerating integration of renewable energy sources requiring secure, distributed grid systems
Smart Grid Security Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Growing Adoption of Smart Grid Technologies and the Need for Robust Security Measures
The rapid expansion of smart grid technologies is transforming traditional power grids into highly interconnected and automated systems. The increasing deployment of smart meters, IoT-connected devices, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind enhances operational efficiency and grid management. However, this integration also introduces new security vulnerabilities. Cyber threats targeting these interconnected devices and systems can lead to significant disruptions, data breaches, and even physical damage to infrastructure. As these technologies continue to evolve, the need for advanced cybersecurity measures becomes crucial to protect against potential risks. The growing reliance on smart grid innovations directly contributes to the heightened demand for specialized security solutions, ensuring the integrity and resilience of the entire grid ecosystem.
-
The Increasing Demand for Data Protection in the Expanding Smart Grid Ecosystem
Smart grids generate vast amounts of operational and personal data through connected devices, sensors, and meters. As utilities and consumers become more dependent on this data for managing energy usage, grid performance, and predictive maintenance, safeguarding this information becomes increasingly vital. Data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive information can lead to serious consequences, including privacy violations, financial losses, and disruption of grid operations. Moreover, with the growing implementation of IoT devices and smart meters, the attack surface for cybercriminals continues to expand, creating greater vulnerabilities. As a result, the need for robust data protection solutions becomes paramount to ensure the security and privacy of both operational and customer data. This increasing focus on securing vast data flows drives the demand for advanced security technologies, ensuring the integrity and reliability of smart grid systems.
Restraints
-
High Implementation Costs and Their Impact on Smart Grid Security Adoption
The deployment of advanced security measures in smart grids requires significant financial investment, which can be a barrier for utilities with limited budgets. Initial costs include purchasing cybersecurity technologies, upgrading infrastructure to accommodate new security systems, and the ongoing expenses of maintaining these solutions. These investments may be challenging for utilities, especially smaller or resource-constrained ones, that already face financial pressure to modernize and maintain aging grid systems. Furthermore, the costs associated with training personnel to manage new security technologies and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations add to the financial burden. As a result, many utilities may delay or forgo implementing comprehensive security measures, leaving their smart grid infrastructure vulnerable to cyber threats and other risks. The high cost of implementation, therefore, slows the widespread adoption of essential security technologies.
-
Interoperability Challenges in Smart Grid Security: Managing Diverse Devices and Systems for Seamless Protection
The smart grid ecosystem consists of a diverse range of devices, sensors, and systems from different manufacturers, each with unique technologies and communication protocols. This diversity can create significant interoperability challenges when it comes to ensuring consistent and seamless security across the entire grid infrastructure. Integrating these various components into a unified security framework is often difficult, as different devices may not be compatible with each other or with the security solutions implemented. This lack of standardization can lead to gaps in protection, making it harder to detect and respond to threats across the network. As a result, utilities may face difficulties in maintaining a secure, resilient grid environment, which hinders the efficient deployment of comprehensive cybersecurity measures. The complexity of managing interoperability issues can delay or limit the effectiveness of smart grid security strategies.
Smart Grid Security Market Segmentation Analysis
By Service
In 2023, the Professional Services segment held the largest revenue share of approximately 65% in the Smart Grid Security Market. This dominance can be attributed to the increasing complexity of smart grid deployments, which require specialized expertise in designing, implementing, and maintaining robust security solutions. Professional service providers offer a range of tailored solutions, including consulting, integration, and security audits, addressing the unique needs of utilities, which drives their demand and adoption.
The Managed Services segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of around 18.38% from 2024 to 2032. As utilities face an increasing volume of cyber threats and regulatory pressures, they are increasingly outsourcing security management to third-party providers. Managed services offer cost-effective, scalable, and continuous monitoring of grid security, enabling utilities to focus on core operations while ensuring high levels of protection. This growing reliance on external security experts fuels the rapid expansion of the Managed Services segment.
By Deployment Type
In 2023, the Cloud segment dominated the Smart Grid Security Market, capturing about 60% of the revenue share. The primary reason for this dominance is the scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency offered by cloud-based solutions. Cloud platforms enable utilities to rapidly deploy and update security measures across vast, distributed networks without significant infrastructure investment, making them an attractive option for smart grid operators looking to improve cybersecurity while managing costs.
The On-Premises segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of approximately 18.50% from 2024 to 2032. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for greater control over security measures, particularly in industries where sensitive data and compliance requirements are paramount. On-premises solutions offer utilities the ability to manage their security infrastructure in-house, ensuring tighter control over critical systems and data, a key factor as cyber threats become more sophisticated and regulations become more stringent.
By Application
In 2023, the Smart Applications segment led the Smart Grid Security Market with the largest revenue share of approximately 60%. This dominance is largely due to the growing reliance on advanced applications that enhance grid performance, operational efficiency, and security. Smart applications, such as predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and automated threat detection, are crucial for securing complex smart grid networks, driving their widespread adoption across utilities looking to optimize their infrastructure.
The Smart Meters segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of about 18.90% from 2024 to 2032. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing deployment of smart meters to collect real-time energy usage data, enabling utilities to improve grid management and customer service. As smart meters become more integrated with advanced security features, their role in safeguarding the grid from cyber threats becomes even more essential, fueling demand for enhanced security solutions within this segment.
By Security Type
In 2023, the Network Security segment held the largest revenue share of approximately 41% in the Smart Grid Security Market. This dominance is primarily driven by the increasing need to safeguard critical communication networks within smart grids. As smart grids rely on interconnected devices and systems, securing these networks from cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access becomes essential for ensuring grid integrity and reliability, making network security a top priority for utilities worldwide.
The Endpoint Security segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of about 18.64% from 2024 to 2032. This growth is fueled by the increasing number of connected devices, such as smart meters and sensors, that act as entry points for potential cyber threats. As the volume of endpoints in smart grids expands, utilities are increasingly focused on securing these devices to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure the overall security of the grid infrastructure, driving the demand for advanced endpoint security solutions.
Smart Grid Security Market Regional Analysis
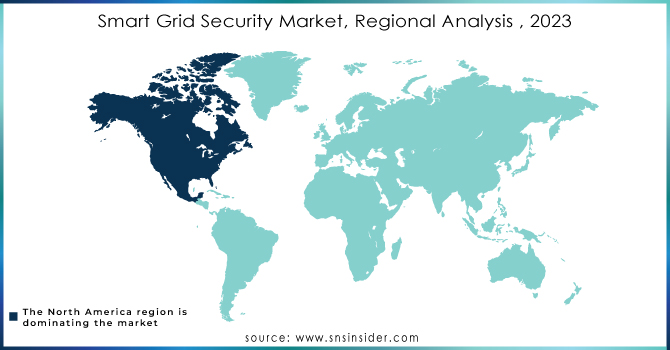
In 2023, North America dominated the Smart Grid Security Market with the largest revenue share of approximately 44%. This leadership position is attributed to the region's early adoption of smart grid technologies, coupled with significant investments in grid modernization and cybersecurity. North America’s mature energy infrastructure, strong regulatory frameworks, and the presence of key market players have further fueled demand for advanced security solutions, solidifying its dominance in the global market.
The Asia Pacific segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 18.90% from 2024 to 2032. This rapid growth is driven by the region's expanding energy demand, urbanization, and government initiatives to modernize grid infrastructure. As countries in Asia Pacific increasingly deploy smart grids to optimize energy distribution and enhance operational efficiency, the need for robust security measures to protect these advanced systems is accelerating, making the region a key growth area for smart grid security solutions.
Do You Need any Customization Research on Smart Grid Security Market - Enquire Now
Key Players
-
AT&T Cybersecurity (AT&T Cybersecurity Platform, Managed Threat Detection)
-
CyberX (CyberX IoT Security Platform, CyberX for Smart Grid)
-
BAE Systems (Secure Data Exchange, Advanced Threat Detection)
-
Cisco (Cisco Smart Grid Security, Cisco Identity Services Engine)
-
Intel Corporation (Intel Security for IoT, Intel IoT Security Platform)
-
IBM (IBM QRadar, IBM Resilient)
-
IOActive, Inc (IoT Security, Vulnerability Management)
-
Siemens (Siemens Smart Grid Security Solutions, Siemens Industrial Security)
-
Symantec (Symantec Advanced Threat Protection, Symantec Endpoint Protection)
-
Sophos (Sophos XG Firewall, Sophos UTM)
-
Leidos (Leidos Cybersecurity Solutions, Leidos Security Operations Center)
-
Alert Logic (Alert Logic Cloud Security, Alert Logic Managed Detection and Response)
-
N-Dimension Solutions, Inc (N-Dimension Grid Watch, N-Dimension Network Security)
-
Elster Solutions (Elster Smart Grid Solutions, Elster Energy Management)
-
AlertEnterprise (AlertEnterprise Security Platform, AlertEnterprise Identity and Access Management)
-
McAfee, LLC (McAfee Total Protection, McAfee Network Security)
-
HP India Sales Private Limited (HP Enterprise Security, HP Data Security)
-
Eaton (Eaton Power Systems, Eaton Cybersecurity Solutions)
-
VeriSign, Inc (VeriSign DNS Security, VeriSign Managed DNS)
-
Broadcom (Broadcom Cybersecurity Solutions, Broadcom IoT Security)
Recent Developments:
-
In 2023, BAE Systems and National Highways extended their collaboration to strengthen cybersecurity measures against evolving threats. This partnership focuses on enhancing the security of critical infrastructure, ensuring robust protection against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
-
In 2024, Siemens Smart Infrastructure launched the SICAM Enhanced Grid Sensor (EGS) to enhance grid transparency for operators. This technology aims to optimize the use of existing infrastructure, prevent overloading, and support efficient power distribution, with a focus on enabling the integration of renewable energy sources and digitalizing distribution grids.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 8.05 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 33.24 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 17.14% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Security Type (Endpoint Security, Database Security, Network Security, Application Security) • By Solution (Antivirus and Antimalware, Firewall, Identity and Access Management (IAM), Encryption, Security and Vulnerability Management, Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Others) • By Service (Professional Service, Managed Service) • By Deployment Type (Cloud, On-Premises) • By Application (Smart Meters, Smart Application, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | AT&T Cybersecurity, CyberX, BAE Systems, Cisco, Intel Corporation, IBM, IOActive, Inc, Siemens, Symantec, Sophos, Leidos, Alert Logic, N-Dimension Solutions, Inc, Elster Solutions, AlertEnterprise, McAfee, LLC, HP India Sales Private Limited, Eaton, VeriSign, Inc, Broadcom |
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 18.90% from 2024 to 2032.
Ans: North America dominated the market with approximately 44% of the revenue share in 2023.
Ans: The Managed Services segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 18.38% from 2024 to 2032.
Ans: The Professional Services segment held the largest revenue share of approximately 65% in 2023.
Ans. Smart Grid Security Market was valued at USD 8.05 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 33.24 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.14% from 2024-2032.

