Swappable Electric Vehicle Battery Market Report Scope & Overview:
Get more information on Swappable Electric Vehicle Battery Market - Request Sample Report
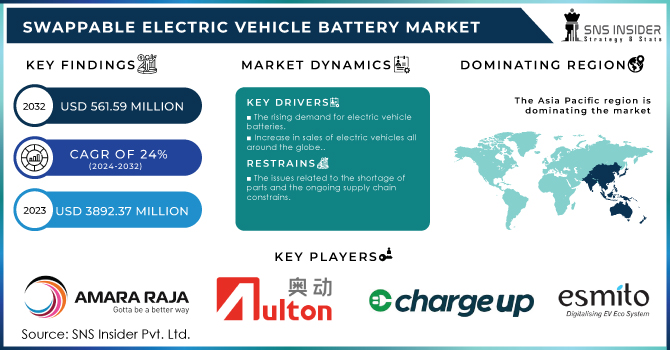
The Swappable Electric Vehicle Battery Market size is expected to reach USD 3892.37 Mn by 2032. and was valued at USD 561.59 Mn in 2023 and grow at a CAGR at 24% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Users of electric vehicles can easily swap out a discharged battery for a fully charged one at a swapping station, much like you might refill a conventional gasoline-powered automobile, without having to wait for the electric vehicle to charge. Usually, this process goes considerably more quickly than waiting for a complete recharge. Compared to charging an electric car, which can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours depending on the charging technique and battery capacity, changing a battery can be done in a matter of minutes. Swappable batteries can help drivers who are experiencing "range anxiety" by enabling them to rapidly resume driving without having to wait for a charge. This is particularly advantageous for commercial uses like buses, delivery trucks, and taxis.
To assure compatibility between various car models and manufacturers, a standardised battery architecture and switching infrastructure are required for swappable EVs to become practical. Such standards are being developed through several projects. The environmental impact of interchangeable batteries is influenced by various elements, including the production of the batteries, their recycling, and the energy sources used to charge them. Battery Recycling and disposing of them properly are crucial for reducing the environmental impact. Setting up a large network of battery-swapping stations can be expensive and demands a substantial financial commitment. Furthermore, it is essential to guarantee the reliability and security of changed batteries. Examples include Gogoro in Taiwan, which sells electric scooters with swappable batteries, and NIO in China, which launched battery-swapping facilities for its electric cars. Some businesses have investigated swappable battery systems.
The practical range of swappable EVs may be impacted by the distribution and accessibility of battery switching stations. Drivers can easily increase their range by swapping out depleted batteries for fully charged ones if there are swapping stations conveniently located along the route. The swappable batteries themselves can have a variety of designs and capacities. Smaller batteries may be used by some swappable EVs while larger batteries may be used by others. It can also adjust how many batteries can be changed in a single stop.
Market Dynamics
Driver
-
The rising demand for electric vehicle batteries
-
Increase in sales of electric vehicles all around the globe.
The advancements in EV technology have resulted in longer driving distances, quicker charging periods, and more cheap battery costs. As a result, EVs are now a more sensible and desirable option for consumers. Increasing consumer interest in greener transport solutions is a result of growing climate change and environmental awareness. EVs have no emissions from their tailpipes, making them a green option. To promote the use of EVs, many governments have put in place incentives. Tax credits, rebates, waived registration fees, and access to carpool lanes are a few examples of these incentives.
Restrain
-
The issues related to the shortage of parts and the ongoing supply chain constrains.
Opportunity
-
The support from government and the rising infrastructure.
-
The increase in investments for building the E/E ecosystem in the respective nations.
Many countries give people and companies cash incentives to construct EV charging stations. These incentives, which help to defray the cost of buying and installing charging equipment, might take the form of subsidies, tax credits, and refunds. Governments frequently allot cash for research and development (R&D) in the field of battery technology. The creation of cutting-edge battery components, energy storage systems, and charging technologies is supported by this financing. Governments may offer funds to institutions, such as utilities and private businesses, in order to develop the EV charging infrastructure. With the help of these incentives, charging stations can be set up in public spaces, on highways, and in commercial buildings.
Challenge
-
The lack of infrastructure in undeveloped nations and the issues related to the decomposition of used batteries.
Impact of Russia Ukraine War:
Nickel and cobalt, two essential raw elements used in batteries, are produced in substantial quantities in Ukraine. The production of batteries, especially those used in swappable battery systems, may be impacted by any interruptions in the supply of these technologies brought on by the conflict. This may result in cost increases and possible shortages. Tensions and conflicts in the geopolitical sphere might make it more difficult to make decisions about foreign investments and commerce. This unpredictability may influence investors' and businesses' willingness to allocate funds to the advancement of swappable battery material and associated infrastructure. During periods of global unrest, energy security issues take on greater importance. Governments might put infrastructure development and domestic energy generation ahead of measures for electric vehicles and batteries. Because of this war there has been a rise of 25% in the prices of batteries and the major reason which has caused this is the supply chain and the high prices of raw materials. The prices of raw materials have grown by 9.8% which will have a somewhat negative impact on market.
Segment Analysis:
By Station Type
The Swappable Electric Vehicle Battery Market is segmented based on the type of station in an automated and manual stations composition. So far, the market leaders are automated battery-swapping stations, covering about 65% of the share, largely because they are very efficient with an even smaller waiting time for the EVs. Thus, with the help of some advanced technologies, these stations are capable of conducting extremely fast and contactless replacements of batteries which is definitely attractive to the users who value convenience along with lower labor costs. Simultaneously, the market share of manual swap stations makes up about 35% as these serve the very regions with low adoption levels of the given technology where users are likely not to have access to automated systems. In any case, demand for manual stations will probably decline, and 10% of the arriving years would probably be converted into automated stations due to only awareness and infrastructure regarding automation keeping on increasing.
By Vehicle Type
Two-wheelers will continue to retain a market share of around 40%, mainly on electric scooters/motorcycles increasingly gaining acceptance in the urban space where there is increasing need for short-distance coverage. They are very good leads for battery swapping since they are of small dimensions and require fast charging solutions. Coming second to them are three-wheelers that gain 25% market share, most of which are used in locations where a much greater demand is felt for electric rickshaws that operate on swappable batteries to work better. Four wheelers comprise 20% of the market, and the reason that demand for swift battery swap is gaining momentum is that people are showing interest in electric cars, primarily in cities where the recharge infrastructure is becoming slowly available. Commercial Vehicles constitutes about 15% of the market because logistics companies and fleet operators would seek solutions to minimize downtime and optimize operational efficiency. The rest three segments are likely to gain as well with the electric vehicles’ entry, considering that the upgrade in battery swapping infrastructure shall cover all vehicle types.
By Service Type
The Swappable Electric Vehicle Battery Market can be mainly bifurcated into two service models, namely the subscription model and the pay-per-use model. Subscription Model is the largest market share that is put around 60%. This model offers access to users on a fixed monthly fee of access; once they seek services through the use of battery swapping, it enables comfort in terms of cost predictability. It appeals more particularly to frequent users of electric vehicles, like ride-hailing drivers and commercial fleet operators, who can count on the steady availableness of charged batteries without having to incur any up-front capital expenditure in buying batteries. On the other hand, the pay-per-use model takes up almost 40% market share, enabling users to pay only when they swap batteries. It makes for very infrequent and shy subscribers commit as such; this model avails one of the freedoms of use.
Regional Coverage
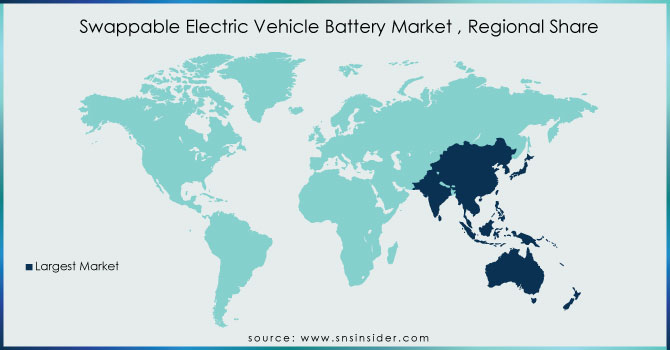
APAC will be the region which has the highest share because, China has been a major player in the market for battery-swappable devices. Swapable battery systems for electric scooters, motorcycles, and even certain electric vehicles have been introduced by a few Chinese electric vehicle manufacturers and startups. Battery-swapping facilities have been installed by businesses like NIO for their electric vehicles.
Based in Taiwan Electric scooters and a battery-swapping infrastructure are prominent features of Gogoro. Gogoro has extended to other areas and built up a substantial network of battery-swapping stations in Taiwan. For electric two-wheelers, India has expressed interest in battery-swappable Vehicle Type. Swapable battery solutions have been developed by several startups and businesses to address the issues with the nation's infrastructure for charging electric vehicles. Also, the market share of electric vehicles by sales China has the highest market share (59%) which contributes the growth of market in this region.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Request For Customized Report
Key Players:
Some of the major swappable electric vehicle battery market key players are:
-
Amara Raja Batteries Ltd :(Amara Raja Swappable Battery Solutions, Advanced Lead-Acid Battery Technologies)
-
Aulton New Energy: (Aulton Smart Battery Swap Stations, Battery Exchange Service)
-
ECHARGEUP: (ECHARGEUP Battery Swapping Stations, Mobile Battery Swapping Solutions)
-
Esmito Solutions: (Esmito Battery Swap Technology, Smart Battery Management Systems)
-
Gogoro: (Gogoro Smart Scooter, Gogoro Battery Swap Network)
-
KYMCO: (KYMCO Ionex Battery Swap System, KYMCO Electric Scooter Models)
-
Lithion Power: (Lithion Power Swappable Battery Packs, Energy Management Solutions)
-
NIO: (NIO Power Swap Station, NIO Battery as a Service (BaaS))
-
Numocity: (Numocity Battery Swapping Infrastructure, Cloud-Based Battery Management Solutions)
-
Oyika Ltd.: (Oyika Battery Swap Stations, Oyika Smart Battery Solutions)
-
Battery Swap Technologies: (Smart Battery Swap Stations, Battery Management Software)
-
Ample, Inc.: (Ample Battery Swapping Technology, Modular Battery Swapping System)
-
BAIC Group: (BAIC EV Battery Swap Stations, BAIC Electric Vehicle Models with Swappable Batteries)
-
Sun Mobility: (Sun Mobility Battery Swap Infrastructure, Smart Battery Solutions for EVs)
-
Revolt Motors: (Revolt Electric Motorcycle with Battery Swap, Revolt Battery Swap Infrastructure)
-
WattHive: (WattHive Battery Swapping System, Integrated Energy Management Solutions)
-
Triton Electric Vehicle: (Triton Battery Swapping Solutions, Triton Electric Vehicle Models)
-
Yulu Bikes: (Yulu Electric Bike Battery Swap Stations, Yulu Smart E-Bikes)
-
ChargePoint: (ChargePoint Battery Swap Solutions, Charging Network for Electric Vehicles)
-
Shell Recharge Solutions: (Shell Battery Swap Stations, Shell EV Charging Solutions)
Recent industry developments
-
For electric scooters and vehicles, respectively, businesses like Gogoro in Taiwan and NIO in China have been growing their swappable battery networks. For EV customers, these networks boost convenience and lessen range aversion.
-
Vehicle Type Diversification: Swapable battery Vehicle Type now includes electric cars, electric delivery vans, and other light electric vehicles in addition to electric scooters and motorcycles. The market for the Vehicle Type is made potentially larger by this diversification.
-
Industry associations and standards bodies are attempting to establish uniform standards for interchangeable batteries. Increasing interoperability and encouraging multiple manufacturers to embrace standards
| Report Attributes | Details |
| Market Size in 2023 | US$ 561.59 Million |
| Market Size by 2032 | US$ 3892.37 Million |
| CAGR | CAGR of 24% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Station Type (Automated, Manual) • By Vehicle Type (Two-Wheeler, Three-Wheeler, Four-Wheeler, Commercial Vehicles) • By Service Type (Subscription Model, Pay-per-use Model) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe [Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Amara Raja Batteries Ltd, Aulton New Energy, ECHARGEUP, Esmito Solutions, Gogoro, KYMCO, Lithion Power, NIO, Numocity, Oyika Ltd |
| Key Drivers | • The rising demand for electric vehicle batteries • Increase in sales of electric vehicles all around the globe. |
| Market Opportunity | • The support from government and the rising infrastructure. • The increase in investments for building the E/E ecosystem in the respective nations. |

