5G Base Station Market Report Scope & Overview:
The 5G Base Station Market size is valued at USD 53.74 billion in 2025E and is expected to reach USD 443.78 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 30.2% over 2026-2033.
The 5G base station market is growing as more people want high-speed internet, the Internet of Things is becoming more popular, and the government is working on digital infrastructure projects. Mobile network operators put standalone 5G deployments at the top of their list so that ultra-reliable, low-latency connections can support self-driving cars, smart factories, and immersive AR/VR apps. Open RAN architectures break apart established vendor ecosystems, while advances in massive MIMO, beamforming, and network slicing improve spectral efficiency. The use of edge computing and private 5G networks in businesses and industries is also driving market expansion globally.
83% of mobile operators accelerated 5G base station deployments in 2025, achieving 40% faster data speeds and 60% lower latency while supporting 50 billion connected IoT devices globally through advanced network slicing capabilities.
5G Base Station Market Size and Forecast:
-
Market Size in 2025E: USD 53.74 Billion
-
Market Size by 2033: USD 443.78 Billion
-
CAGR: 30.2% from 2026 to 2033
-
Base Year: 2025E
-
Forecast Period: 2026–2033
-
Historical Data: 2022–2024

To Get more information on 5G Base Station Market - Request Free Sample Report
5G Base Station Market Trends:
-
Rapid adoption of open RAN architectures enabling multi-vendor interoperability and reducing 5G infrastructure deployment costs by 25-30%.
-
Increasing deployment of small cells in urban dense environments to enhance network capacity and coverage for 5G millimeter-wave applications.
-
Growing integration of AI-driven network optimization tools for dynamic spectrum sharing and predictive maintenance of 5G base stations.
-
Accelerated transition from 5G non-standalone to 5G standalone architectures supporting network slicing for enterprise applications.
-
Expanding deployment of massive MIMO antennas with 64T64R and 128T128R configurations to improve spectral efficiency and user capacity.
U.S. 5G Base Station Market is valued at USD 24.18 billion in 2025E and is expected to reach USD 210.65 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 31.4% over 2026-2033.
The U.S. 5G Base Station Market is growing rapidly, driven by nationwide 5G deployments, rising data demand, and investments in advanced telecom infrastructure, supporting faster connectivity and next-generation digital applications.

5G Base Station Market Growth Drivers:
-
Exponential Growth in Mobile Data Traffic and Proliferation of Bandwidth-Intensive Applications Drives Market Expansion Globally
In 2025, global mobile data traffic rose to 250 exabytes per month, owing to 4K and 8K video streaming, cloud gaming, and business video conferencing. 5G base stations can send data 10 to 20 times faster than 4G LTE, and they have latencies of less than 5 milliseconds, which makes real-time applications possible. To handle traffic loads, network operators use upgraded base stations that use massive MIMO and carrier aggregation technology. The COVID-19 epidemic sped up the process of going digital. Reliable high-speed internet is now necessary for remote business, telehealth, and distant learning, which has changed the way networks need to be set up globally.
Mobile operators deployed 4.2 million 5G base stations globally in 2025, handling 78% of total mobile data traffic while supporting 120 million fixed wireless access connections as fiber alternatives.
5G Base Station Market Restraints:
-
High Capital Expenditure Requirements and Uncertain Return on Investment Timelines May Hamper Global Market Growth
It costs 2.5 to 3 times as much to set up a 5G network as it does to set up a 4G LTE network. Macro base stations cost between USD 25,000 and USD 40,000 each, and tiny cells cost between USD 3,000 and USD 8,000 each. Due to fierce competition, mobile carriers are seeing slower revenue growth. 5G ARPU premiums are only 10–15% higher than 4G services. Payback periods can last 7 to 9 years in markets with a moderate density, which puts a pressure on operators' balance sheets. Emerging markets that do not make much money from 4G have a hard time justifying 5G investments. This could lead to a digital divide between urban and rural economic zones in developing areas.
65% of tier-2 mobile operators delayed 5G deployments beyond 2026 due to capital constraints, with 40% seeking infrastructure sharing agreements to reduce deployment costs by 35%.
5G Base Station Market Opportunities:
-
Enterprise And Industrial Sector Adoption of Private 5G Networks Creates New Revenue Streams for Base Station Manufacturers Through Customized Solutions for Vertical Applications
Private 5G networks are used in the manufacturing, logistics, mining, and energy industries to offer ultra-reliable communications for industrial automation, AGV coordination, and remote control of equipment. Dedicated network slices ensure performance metrics with availability over 99.999% and latencies under 10 milliseconds. Base station makers make industrial-grade gear that can work in a wider range of temperatures, is certified for use in dangerous environments, and has easier-to-use administration interfaces. The global private 5G network market is growing at a rate of 45% per year, which means that by 2027, there will be a USD 12 billion equipment opportunity, especially in automotive plants, smart ports, and offshore energy projects that need reliable wireless access.
Industrial enterprises deployed 42,000 private 5G networks globally in 2025, utilizing specialized base stations with time-sensitive networking capabilities achieving 80% productivity improvements in automated manufacturing facilities.
5G Base Station Market Segment Highlights:
-
By Type: Macro Cells led with 68.4% share, while Small Cells is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 42.6%.
-
By Operational Frequency: Sub 6 GHz led with 71.3% share, while Above 6 GHz is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 48.2%.
-
By Network Architecture: 5G Non-Standalone led with 63.8% share, while 5G Standalone is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 52.4%.
-
By Component: Hardware led with 74.2% share, while Services is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 35.8%.
-
By Core Network: Network Function Virtualization led with 58.6% share, while Software Defined Networking is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 39.3%.
-
By End-Use: Commercial led with 46.7% share, while Industrial is the fastest-growing segment with CAGR of 44.9%.
5G Base Station Market Segment Analysis:
By Type: Macro Cells Led the Market, While Small Cells is the Fastest-Growing Segment
Macro Cells dominate 5G deployment by providing extensive coverage up to several kilometers using high-power transmissions up to 200W, employing massive MIMO with 64-128 antenna elements in mid-band spectrum (3.5-3.8 GHz) to balance coverage and capacity, achieving user speeds of 200-500 Mbps in urban and 50-150 Mbps in suburban areas while leveraging the existing 4G infrastructure for cost-effective colocation to accelerate rollout and optimize capex.
Small Cells represent the fastest-growing segment, where femtocells, picocells, and microcells address capacity gaps in dense urban areas, stadiums, hubs, and campuses, with millimeter-wave versions at 26/28 GHz delivering multi-gigabit speeds within 100-200 meters using beamforming, supported by a 60% annual increase in indoor deployments for fixed wireless and private networks, and integrated discreetly into street furniture and building facades as distributed antenna systems evolve to enhance in-building 5G coverage across commercial real estate.

By Operational Frequency: Sub 6 GHz Led the Market, while Above 6 GHz is the Fastest-growing Segment Globally
Sub-6 GHz spectrum, particularly within the 3.3-4.2 GHz range, serves as the global 5G workhorse by optimally balancing coverage and capacity, supporting channel bandwidths up to 100 MHz for macro cell ranges of 2-3 kilometers, while dynamic spectrum sharing in the 1.8-2.1 GHz bands accelerates 5G deployment using existing assets and lower 600-700 MHz bands enable expansive rural coverage exceeding 10 kilometers for IoT and digital inclusion.
The millimeter-wave spectrum above 6 GHz demonstrates the fastest growth, with harmonized allocations like 24.25-29.5 GHz providing 400-800 MHz of contiguous bandwidth for extreme capacity, enabling 5-8 Gbps peak speeds via beamforming in dense urban hotspots, stadiums, and fixed wireless access, while higher bands such as 40 GHz and 70 GHz are being standardized for advanced backhaul and fronthaul solutions in dense network architectures.
By Network Architecture: 5G Non-Standalone Led the Market, while 5G Standalone is the Fastest-Growing Segment
5G Non-Standalone architecture dominates initial deployments by leveraging existing 4G LTE core networks for control while 5G New Radio delivers enhanced mobile broadband, enabling rapid launch within 12-18 months via dual-connectivity to optimize investments and reuse infrastructure for 2-3x throughput gains, with over 3.2 million global NSA base stations projected by 2025 primarily in mid-band for smartphone-centric use.
5G Standalone is expected to be the fastest-growing segment as operators transition to native cloud-native 5G cores, unlocking network slicing, ultra-reliable low-latency communications, and massive IoT for industrial and enterprise applications with deterministic performance, a shift accelerated by 3GPP Releases 16 and 17 enhancements for time-sensitive networking, integrated access backhaul, and non-terrestrial network support to drive vertical industry transformation beyond 2025.
By Component: Hardware Led the Market, while Services is the Fastest-growing Segment Globally
The hardware segment, comprising radio units, baseband units, and massive MIMO antennas, constitutes the largest market share, with radio units alone representing 45% of total hardware value through advanced 64T64R antenna arrays and integrated RF components, while baseband units virtualize into distributed and centralized units on commercial servers and millimeter-wave radios utilize 256-512 element phased arrays for electronic beam steering, all benefiting from semiconductor innovations that cut power consumption by 40% per generation.
The services segment is the fastest-growing, expanding at a 35.8% CAGR, as it encompasses network planning, AI-driven optimization, and managed services, evolving into Network-as-a-Service models, which are critical for addressing 5G deployment complexities and are in especially high demand for private 5G networks where enterprises rely on external expertise for installation, operation, and maintenance.
By Core Network: Network Function Virtualization Dominated the Market, while Software Defined Networking is the Fastest-growing Segment Globally
Network Function Virtualization leads 5G core network transformation by replacing proprietary hardware with virtualized functions, such as AMF, SMF, and UPF, deployed as cloud-native containers, enabling elastic scaling, reducing power consumption by 60%, and leveraging orchestration frameworks, such as ONAP for automation.
Software Defined Networking exhibits the fastest growth by decoupling control and user planes to enable dynamic traffic engineering and network slicing, where SDN controllers program distributed user plane functions and integrate with transport technologies like segment routing, ultimately combining with NFV to create fully programmable networks that support Network-as-a-Service models, allowing enterprises to provision customized network slices with specific performance characteristics through APIs and digital portals.
By End-Use: Commercial Segment Led the Market, while Industrial is the Fastest-growing Segment Globally
Commercial applications segment dominates the 5G base station deployment, primarily driven by mobile network operators enhancing mobile broadband for consumers with 100+ Mbps average speeds, expanding into fixed wireless access to replace traditional broadband, and supporting smart city infrastructure through network slicing.
The industrial applications demonstrate the fastest growth, as sectors, such as manufacturing and logistics deploy private 5G networks to enable time-sensitive networking with sub-10ms latency, connect massive numbers of sensors, and operate mobile robotics via ultra-reliable communications, fueling innovation in ruggedized hardware, localized spectrum, and vertically-optimized network slices with guaranteed performance isolation.
5G Base Station Market Regional Analysis:
Asia Pacific 5G Base Station Market Insights:
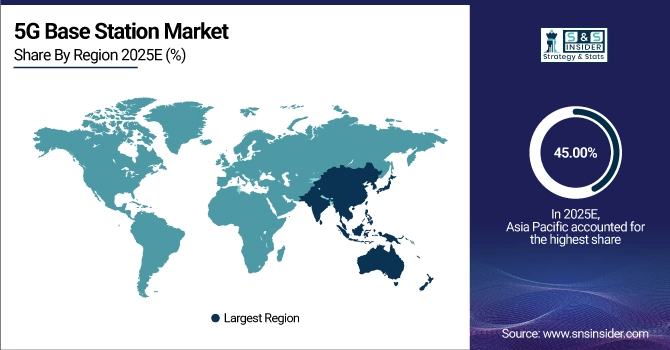
In 2025, the Asia Pacific region had the largest share of the 5G Base Station Market, with 45.00% as China had 2.3 million base stations, South Korea and Japan were early adopters, the government was promoting a digital economy, and there was a strong ecosystem for making telecommunications equipment. High population density, widespread smartphone use, and strong digitalization of industry are all factors that are boosting demand for private 5G networks in manufacturing areas in the region.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
North America 5G Base Station Market Insights:
Over 2026 to 2033, North America is predicted to increase at a CAGR of 28.7% due to the widespread millimeter-wave installations for fixed wireless access, a competitive mobile operator environment, enterprise 5G adoption, and government programs to expand broadband access in rural areas. The area is ahead of the rest of the world in 5G standalone core installations and network slicing for vertical industry applications.
Europe 5G Base Station Market Insights:
In 2025, Europe had 22.50% of the market share due to coordinated spectrum allocation across EU member states, a strong legislative focus on network security, the growth of open RAN projects, and the use of 5G in the automotive and manufacturing industries. The area focuses on network sharing agreements and neutral host models to get the most out of deployment expenses.
Middle East & Africa and Latin America 5G Base Station Market Insights:
The Middle East & Africa and Latin America together captured 12.00% market share in 2025, with growth driven by Gulf Cooperation Council countries' early 5G adoption, spectrum allocations in key markets, such as Brazil and Mexico, and increasing mobile data consumption. These regions prioritize 5G for economic diversification and digital inclusion initiatives.
5G Base Station Market Competitive Landscape:
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. was founded in 1987 and is based in Shenzhen, China. It has a 35% market share and is the world's leading 5G infrastructure company. The company provides complete 5G solutions, such as Massive MIMO AAUs, BladeRRU devices, and CloudCore networks, in more than 170 countries. Huawei spends 22% of its sales on research and development, with a focus on improving antenna algorithms and energy efficiency.
-
March 2025, Huawei launched its fifth-generation Massive MIMO with 384 antenna elements achieving 50% higher energy efficiency and supporting 10 Gbps peak rates in commercial networks.
Ericsson AB
Established in 1876, Ericsson AB headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, provides 5G radio access networks with 25% global market share. The company's Street Macro and AIR solutions support all frequency bands with Ericsson Silicon chipset innovations. Ericsson manages 140+ live 5G networks worldwide with strong positions in North America and Europe.
-
February 2025, Ericsson introduced its Integrated Access Backhaul solution enabling rapid small cell deployment without fiber backhaul, reducing deployment costs by 40% in dense urban environments.
Nokia Corporation
Founded in 1865, Nokia Corporation headquartered in Espoo, Finland, delivers 5G AirScale base stations with ReefShark chipsets across 80+ live networks. The company leads in 5G standalone core deployments and network slicing implementations. Nokia's portfolio includes mmWave solutions and industrial-grade private wireless networks for enterprise applications.
-
January 2025, Nokia launched its next-generation AnyRAN solution enabling cloud RAN on any server hardware with accelerated performance matching purpose-built baseband units.
5G Base Station Market Key Players
-
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
-
Ericsson
-
Nokia Corporation
-
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
-
Fujitsu Limited
-
NEC Corporation
-
Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
-
Cisco Systems, Inc.
-
NVIDIA Corporation
-
Intel Corporation
-
CommScope
-
Juniper Networks, Inc.
-
VMware, Inc.
-
Xilinx, Inc.
-
Mavenir Systems, Inc.
-
Keysight Technologies
-
Altiostar Networks, Inc.
-
Casa Systems, Inc.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 31.7 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 340.3 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 30.2% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Type (Small Cells, Femto Cells, Pico Cells, Micro Cells, Macro Cells) • By Operational Frequency(Sub 6 GH, Above 6 GHz) • By Network Architecture(5G Standalone, 5G Non-Standalone) • By Component(Hardware, Radio Remote Unit (RRU), Baseband Processing Unit (BPU), MIMO, Others, Services) • By Core Network(Software Defined Networking, Network Function Virtualization) • By End Use Frequency(Commercial, Residential, Industrial, Government, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, ZTE Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Fujitsu Limited, NEC Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Cisco Systems, Inc., NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, CommScope, Juniper Networks, Inc., VMware, Inc., Xilinx, Inc., Parallel Wireless, Inc., Mavenir Systems, Inc., Keysight Technologies, Altiostar Networks, Inc., Casa Systems, Inc. |

