Hereditary Testing Market Size Analysis
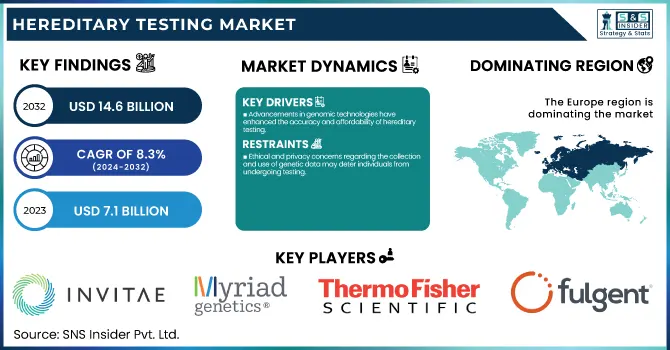
The Hereditary Testing Market Size was valued at USD 7.1 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 14.6 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The report provides a comprehensive overview of the hereditary testing market, including the key trends and insights that are shaping the industry. It also analyses incidence and prevalence data, the increasing volume and growth of genetic testing, market penetration by regions, and identifying the leading and emerging markets. The report analyzes healthcare expenditure, detailing government, insurance, and out-of-pocket spending. Moreover, it delves into technological advancements including next-generation sequencing (NGS) and AI-based analysis, which are improving accuracy and reducing costs.
To Get more information on Hereditary Testing Market - Request Free Sample Report
It assesses the regulatory and reimbursement environment, gaining independence into approvals, reimbursement trends, and country preferences. These data-driven insights help stakeholders navigate market opportunities and challenges effectively. The hereditary testing market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing awareness of genetic disorders, advancements in genomic technologies, and rising healthcare expenditure. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), approximately 10% of adults in the United States have a rare disease, many of which are genetic in nature.
Hereditary Testing Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Advancements in genomic technologies have enhanced the accuracy and affordability of hereditary testing.
The rapid development of genomic technologies has closely been associated with the field of hereditary testing, helping improve the accuracy and feasibility of genetic testing. One major milestone is the significant decrease in the cost of whole genome sequencing (WGS). Since the initial mapping of the human genome in 2003, sequencing costs have plummeted from approximately USD 3 billion to under USD 1,000, making genetic testing more attainable for a broader population. In the clinical arena, these technological advances have begun to result in innovative applications. For example, NHS England is running a world-first program to test 100,000 newborns for more than 200 genetic diseases using WGS. At the same time, this initiative seeks to enable early diagnosis and treatment, which could revolutionize patient outcomes. For example, in Queensland Australia, a rapid heel prick test that screens for hundreds of genetic diseases in newborns has been rolled out. It is a sweeping expansion from the previous test, which screened for just 32 disorders, and is available for the first time to 60,000 babies as part of enhanced screening.
Furthermore, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is helping interpret complex genetic data. Research institutions, such as the Murdoch Children's Research Institute, are using these technologies to address the challenge of diagnosing rare childhood diseases, using AI-driven tools to increase the rate of diagnosis for affected children to as much as 70%. These developments represent a significant evolution in hereditary testing, powered by technological progress and focused healthcare efforts that promise to make genetic diagnostics more accurate and widely available.
Restraints:
-
Ethical and privacy concerns regarding the collection and use of genetic data may deter individuals from undergoing testing.
Hereditary testing has been greatly restricted due to ethical and privacy concerns. Recent events have amplified public concern about the safety and misuse of genetic data. In October 2023, 23andMe, a prominent genetic testing company, experienced a data breach affecting approximately 6.9 million users. The exposed information consisted of sensitive details like names, birth years, location, and genetic ancestry and raised concerns about how third-party entities could potentially misuse it. Likewise, in October 2024, Nebula Genomics found itself on the receiving end of a federal class-action lawsuit in Chicago. The lawsuit alleged that the company had violated Illinois' Genetic Information Privacy Act by collecting and distributing genetic information without appropriate consent. The lawsuit also targeted large tech companies including Meta, Microsoft, and Google, alleging they had gained from improper access to personal genetic data for advertising.
These cases raise unsettling, unique vulnerabilities of genetic data handling and have contributed to rising public skepticism. A survey conducted in late 2024 found that 68% of respondents were concerned about the privacy of their genetic information, and 52% said they might not take a genetic test if their data could potentially be misused. The growing mistrust poses a major threat to the expansion of the hereditary testing market as people begin to weigh the pros of testing against the cons of their personal privacy.
Opportunities:
-
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning can improve the interpretation of genetic data, leading to more accurate and actionable insights.
The application of AI and ML in genetic testing provides promising potential to improve the precision and efficacy of genomic data interpretation. AI-based tools are capable of processing large and intricate datasets from genomics, unveiling patterns and mutations often too subtle for the human eye to discern. For example, AI has been applied in metagenomic analyses that have been able to identify a wide range of vertebrate hosts and Plasmodium parasites in samples of Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes, enhancing our understanding of vector-borne disease. In 2024, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry went to the creators of AlphaFold, an AI tool that can predict 3D protein structures with stunning accuracy. Revolutionary Implications for Genomics As protein structures are the keys to the locks of gene functions and interactions, this discovery has far-reaching consequences for genomics. The technological advancements in genomic sequencing methods and the growing need for personalized medicine. Companies like Insitro are using A.I. to create novel screenings and treatments for diseases including ALS and cancer. Insitro's goal is to use machine learning to understand genetic samples and extract causal mechanisms that traditional studies in this field often miss, which will expedite the finding of effective therapies.
Challenges:
-
The high cost of hereditary testing services can be a significant barrier, particularly in developing countries with limited healthcare resources.
The current high price of hereditary testing services is a significant barrier to access, especially in developing countries with inadequate health resources. In India, for instance, the cost of genetic tests ranges from ₹7,000 to ₹80,000, depending on the complexity and type of test. Additionally, most health insurance plans in these areas do not cover genetic testing, meaning the patient pays for a large portion of the cost out of the box. Further, indirect costs including follow-up visits, additional imaging studies, and chronic management of these conditions where applicable add to the economic burden. Unfortunately, this scenario usually creates a gap in access to genetic testing facilities, as a result of which early diagnosis of diseases and personalized treatment are being compromised for many hereditary disorders in populations from resource-constrained regions.
Hereditary Testing Market Segmentation Analysis
By Disease Type
In 2023, the hereditary non-cancer testing segment dominated the market and accounted for over 79% revenue share of the market. This large share can be credited to several factors such as the high prevalence of non-cancer genetic disorders and increased awareness about prenatal and newborn screening. As per the World Health Organisation (WHO), genetic disorders and congenital anomalies account for nearly 2-5% of all live births worldwide. In the United States, more than 12,000 babies are diagnosed with genetic or congenital disorders each year through newborn screening programs, according to the CDC. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute, more than 7,000 specific genetic disorders have been identified, with new ones emerging every year. This vast number of non-cancer genetic conditions contributes to the segment's dominance. Moreover, governmental initiatives have also significantly contributed to the growth of non-cancer genetic testing. For instance, the U.S. Newborn Screening Saves Lives Reauthorization Act of 2014 has led to comprehensive screening programs across all 50 states, covering at least 31 core conditions. These factors, combined with advancements in testing technologies and increasing public awareness, have solidified the hereditary non-cancer testing segment's leading position in the market.
By Technology
Molecular testing accounted for 54% of the revenue of the market in 2023. This dominance can be attributed to the high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of molecular testing techniques in detecting genetic variations. These molecular diagnostics tests have been reported to have a sensitivity and specificity greater than 95% for many genetic disorders (NCBI). Due to their reliability and clinical utility, many molecular diagnostic tests for hereditary conditions have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Historical data from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Genetic Testing Registry shows a significant increase in the number of available molecular tests, from approximately 1,000 in 2012 to over 75,000 in 2022, demonstrating the rapid adoption and development of this technology. In addition, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have expanded coverage of molecular diagnostic tests. Such government support has been instrumental in fuelling the growth of the segment. The dominance of the molecular testing segment is also supported by its broad application for detecting a wide variety of genetic alterations including single nucleotide polymorphisms to large chromosomal alterations.
Hereditary Testing Market Regional Insights
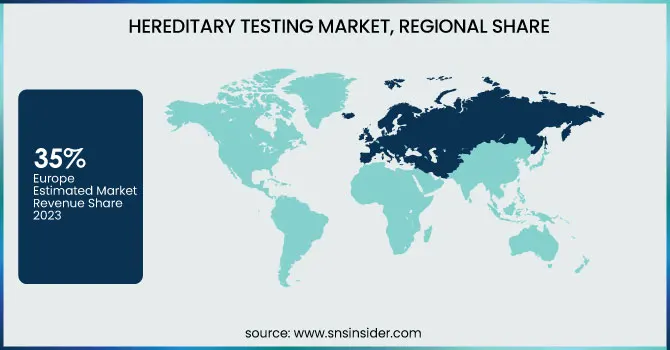
Europe dominated the hereditary testing market with a 35% revenue share in 2023. The region's advanced healthcare infrastructure and a strong focus on genetic research contributed significantly to its market leadership. Many countries in Europe made significant investments in genomic initiatives, like the UK’s 100,000 Genomes Project which catalyzed genetic testing technologies development and adoption. Furthermore, favourable government policies and investment in genetic research created an ecosystem conducive to market expansion. Demand for hereditary testing was also fuelled by the high prevalence of genetic disorders in European populations. For example, the European Cancer Information System estimated by 2035 that there would be 3.13 million new cancer cases in Europe, leading to greater demand for diagnostic genetic testing. In addition, several key players offering genetic tests and the high uptake of advanced treatments in the European region resulted in market dominance in this region. While it varied among countries, the regulatory framework in Europe was generally supportive of the approval and commercialization of tests. This allowed numerous genetic tests to be available at several major companies in the area.
On the other hand, the hereditary testing industry in Asia-Pacific is growing at the highest CAGR. The growth can be attributed to awareness regarding healthcare, disposable income, and government initiatives to enhance access to genetic testing. For example, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has set up a genetic testing laboratory network across the country to improve diagnostic capabilities. The Chinese National Health Commission has integrated genetic testing into its national health strategy and promotes it as a part of regular healthcare. In 2023, approximately 25% of the global market share in the Asia-Pacific region was accounted for, indicating substantial potential for growth. This growth is propelled by factors such as large population bases, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing prevalence of genetic disorders in countries like India and China. Asian genetic and rare disorder prevalence is greater than the world average (WHO-2023), which makes it necessary to expand genetic testing services in Asia.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Key Players in Hereditary Testing Market
Key Service Providers/Manufacturers
-
Invitae Corporation (Invitae Genetic Test, Carrier Screening Test)
-
Myriad Genetics, Inc. (MyRisk Hereditary Cancer Test, Foresight Carrier Screen)
-
Quest Diagnostics Incorporated (BRCAvantage, ClariTest Core)
-
Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp) (Integrated Genetics, Hereditary Cancer Panel)
-
Illumina, Inc. (TruSight Hereditary Cancer, VeriSeq NIPT Solution)
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Ion Torrent Oncomine, CarrierSeq ECS)
-
23andMe, Inc. (Health + Ancestry Service, Carrier Status Reports)
-
Fulgent Genetics (Comprehensive Cancer Panel, X-Linked Panel)
-
Color Health, Inc. (Color Hereditary Cancer Test, Genetic Health Screen)
-
Bionano Genomics, Inc. (Saphyr System, Genetic Disease Testing Solutions)
Key Users (Hospitals, Research Institutions, and Clinics Using These Services):
-
Mayo Clinic
-
Cleveland Clinic
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
-
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
-
Stanford Health Care
-
MD Anderson Cancer Center
-
Boston Children's Hospital
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
-
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Recent Developments in the Hereditary Testing Market
-
In June of 2024, Illumina, Inc. introduced its latest high-throughput sequencing platform, purpose-built for large-scale hereditary disease applications. This development was intended to expand testing capacity and shorten turnaround times for genetic diagnoses.
-
In September 2024, Myriad Genetics announced the launch of a new pan-cancer panel, which tests for genetic mutations that can lead to more than 30 hereditary cancers. This launch was supported by NCI-funded research.
-
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) acknowledged the need for a large-scale genomic study of rare hereditary disorders, launching a $500 million, five-year initiative in January 2025 to help improve understanding of these conditions and diagnostic capabilities.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 7.1 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 14.6 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 8.3% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Disease Type (Hereditary Cancer Testing {Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Stomach/Gastric Cancer, Uterine Cancer, Melanoma, Sarcoma, Pancreatic Cancer, Others}, Hereditary Non-cancer Testing {Genetic Tests [Cardiac Diseases, Rare Diseases, Other Diseases], Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis & Screening, Newborn Genetic Screening, Non-invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) & Carrier Screening Tests}) • By Technology (Cytogenetic, Biochemical, Molecular Testing) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Invitae Corporation, Myriad Genetics, Inc., Quest Diagnostics Incorporated, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp), Illumina, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., 23andMe, Inc., Fulgent Genetics, Color Health, Inc., Bionano Genomics, Inc. |

