Newborn Screening Market Size Analysis
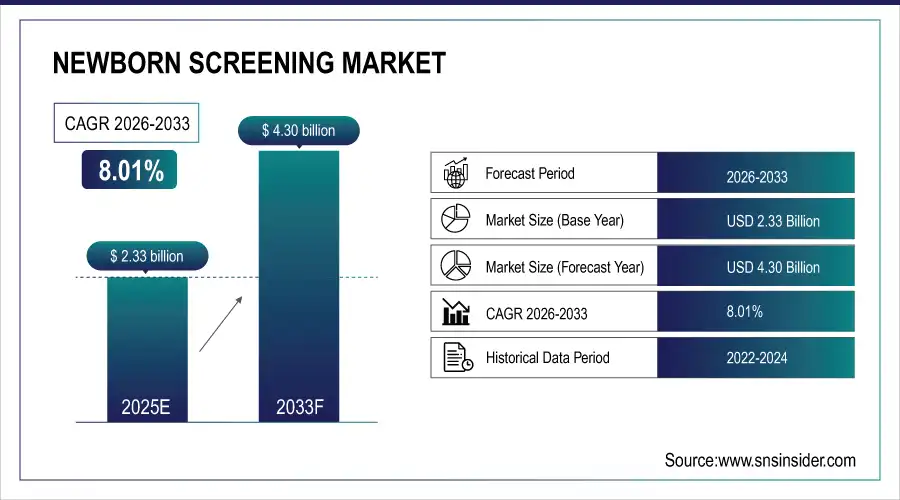
Newborn Screening Market was valued at USD 2.33 billion in 2025E and is expected to reach USD 4.30 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.01% from 2026-2033.
The Newborn Screening Market is growing due to rising demand for early detection of metabolic, genetic, and rare disorders, supported by expanding national screening programs and higher birth rates in developing regions. Technological advancements—especially in NGS, molecular assays, and MS/MS—are driving adoption of advanced screening panels. Increased government funding, better healthcare infrastructure, and growing awareness among parents further reinforce market expansion. Additionally, improved reimbursement frameworks and the shift toward comprehensive genomic screening accelerate long-term growth.
Newborn Screening Market Size and Forecast
-
Newborn Screening Market Size in 2025: USD 2.33 Billion
-
Newborn Screening Market Size by 2033: USD 4.30 Billion
-
CAGR: 8.01% from 2026 to 2033
-
Base Year: 2025E
-
Forecast Period: 2026–2033
-
Historical Data: 2022–2024
To Get more information On Newborn Screening Market - Request Free Sample Report
Newborn Screening Market Trends
-
Asia Pacific led the newborn screening market in 2024, driven by the world’s highest birth rates India and China accounting for over 27 million annual births and expanding national screening programs that significantly boost adoption of MS/MS, molecular, and NGS technologies.
-
Advances in MS/MS, molecular assays, and NGS—now capable of detecting 50–100+ disorders—combined with increased government funding, broader reimbursement, and AI-enabled analytics, are accelerating global newborn screening adoption and driving sustained double-digit growth across several developing economies.
-
Rising prevalence of metabolic, genetic, and congenital disorders
-
Technological advancements in mass spectrometry and molecular assays
-
Strong growth from emerging markets, especially Asia Pacific
-
Shift toward expanded screening panels covering more disorders
-
Increasing focus on cost-effective early diagnosis and intervention
U.S. Newborn Screening Market was valued at USD 0.62 billion in 2025E and is expected to reach USD 1.11 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.52% from 2026-2033.
The U.S. newborn screening market is expanding due to robust state-mandated programs, advances in genetic and molecular testing, and rising demand for early diagnosis of rare disorders. Growing adoption of NGS, strong reimbursement, and continuous technology upgrades further support market growth.
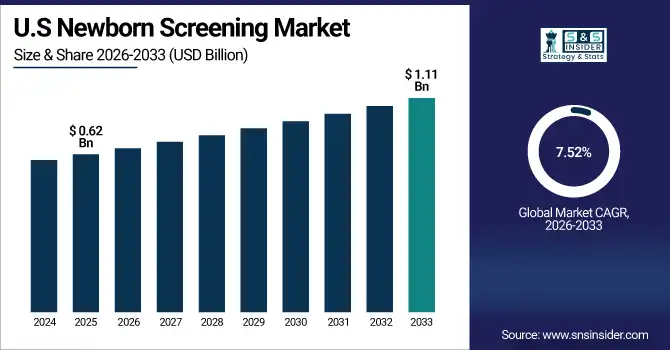
State-mandated U.S. newborn screening covers nearly millions of births annually, with programs detecting 30–60+ disorders per panel. Growing adoption of NGS and molecular assays, supported by strong reimbursement and federal–state coordination, is expanding nationwide screening accuracy and reach.
Newborn Screening Market Growth Drivers:
-
Advancements in genetic testing technologies have enabled early detection of various congenital conditions, prompting higher demand for newborn screening programs.
The increment in the newborn screening programs has been largely driven by advancements in genetic testing technologies that have greatly improved the diagnosis of congenital conditions. Recent projects emphasize this trend. In October 2024, NHS England announced a world-first study to screen 100,000 newborns for over 200 genetic conditions through whole genome sequencing (WGS). This approach is used for the routine screening of treatable, rare conditions shortly after birth so that there can ideally be timely intervention to improve or save lives.” So far, more than 500 blood samples have been collected at 13 hospitals, which will soon expand to about 40 hospitals nationwide. Also in August 2024, Queensland, Australia, became the first in the world to offer an advanced heel prick test that can detect hundreds of genetic conditions in newborns. Funded by a $5.5 million federal grant, this effort will initially test 60,000 babies where their parents consent, with the plan to add conditions as treatments are available.
In the United States, a study published in October 2024 found that genome sequencing detected 120 babies with serious and treatable health conditions among 4,000 tested newborns. In contrast, conventional screening techniques identified only 10 of those cases. This significant disparity highlights the efficacy of advanced genetic testing in early disease detection. These developments reflect a global shift towards integrating comprehensive genetic testing into standard newborn screening protocols, aiming to facilitate early diagnosis and intervention for a broader spectrum of congenital conditions.
Newborn Screening Market Restraints:
-
Ethical concerns, such as consent, privacy, and the potential psychological impact on families, pose challenges to the widespread adoption of newborn screening programs.
Ethical issues greatly affect the implementation of neonatal screening programs. A major concern is genetic discrimination, which occurs when people identified with certain genetic traits could be discriminated against in the workplace or their access to insurance. For example, the services of a U.S. startup that will screen embryos for intelligence have raised concerns that they promote genetic superiority and social inequality. Another major issue is privacy. When genetic data from newborns are collected and stored, strict protections are needed to ensure these aren’t accessed or used inappropriately. Without appropriate data protection, there can be data breaches exposing sensitive personal information. Informed consent is yet another contentious concern. Ensuring full parental comprehension of the risks implications, and limitations, of genetic testing, especially when results might prognosticate future health risks without consequential specificity, is also quite challenging. This uncertainty can be stressful and anxiety-provoking for families. Moreover, the possibility of false positives or uncertain results may lead to unnecessary interventions or emotional distress.
Newborn Screening Market Opportunities:
-
The development and widespread adoption of point-of-care testing solutions offer timely and convenient diagnostic capabilities, enhancing accessibility and efficiency in newborn screening.
POC testing solutions have a considerable opportunity for improved diagnosis and intervention of numerous congenital disorders through integration into newborn screening programs. Existing methods for newborn screening are considered tedious procedures requiring centralized laboratories and longer waiting periods for results that delay vital medical treatments. Conversely, POC testing allows for rapid, in-field testing to enable diagnosis and treatment. Recent developments highlight this potential. In September 2023, Mylab Discovery Solutions launched 'MyNeoShield,' a patent-pending POC device to run all seven standard newborn screening tests. This device gives results in four hours a tremendous leap over traditional methods, which could take 24 hours or more. Such rapid turnaround times are crucial, especially in remote or underserved areas where timely medical action within the critical 48-hour window is essential.
In Queensland, Australia, "the world's first" new rollout began around mid-2024, deploying a more sophisticated heel prick test to identify hundreds of genetic illnesses in newborns. This will greatly increase the number of disorders going from 32 to up to 50 which can be detected earlier leading to improved intervention and treatment outcomes. USD 5.5 million for this project from the federal government, which is significant due to POC testing being funded by a public health program in their state. Most notably, several of these developments highlight a global momentum towards autosomal recessive POC testing being used in newborn screening due to the need for rapid, non-invasive, and cost-effective diagnostic alternatives. Point-of-care comprehensive screenings also expedite diagnoses and guarantee that infants receive timely medical treatments, which leads to better outcomes and a decreased incidence of congenital disorders.
Newborn Screening Market Segmentation Analysis
By Technology
The tandem mass spectrometry segment dominated the market and accounted for a 25% share in the newborn screening market in 2023. The technology's high sensitivity, specificity, and simultaneous detection of multiple disorders have contributed to this substantial market share. The advent of tandem mass spectrometry technology has revolutionized newborn screening by allowing multiple metabolic disorders to be tested on a single blood spot. Data from government statistics corroborates how significant technology like this is in newborn screening programs. For example, the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) states that tandem mass spectrometry enables the detection of over 50 unique disorders, whereas previously there were only a few detectable disorders. Such expansion has resulted in the earlier diagnosis and treatment of rare but serious genetic disorders, positively impacting the health of patients for both themselves and their families.
Tandem mass spectrometry's ability to process large numbers of samples rapidly and accurately has made it a valuable tool for use in public health screening programs. As many states are now screening for 20–30 different disorders in their routine state early newborn screening panels, it is no surprise that adoption of this technology has been reported by State health departments. The cost-effectiveness of tandem mass spectrometry in detecting multiple disorders from a single test has also contributed to its widespread adoption, aligning with government efforts to improve healthcare efficiency and reduce long-term medical costs associated with late-diagnosed genetic disorders.
By Test Type
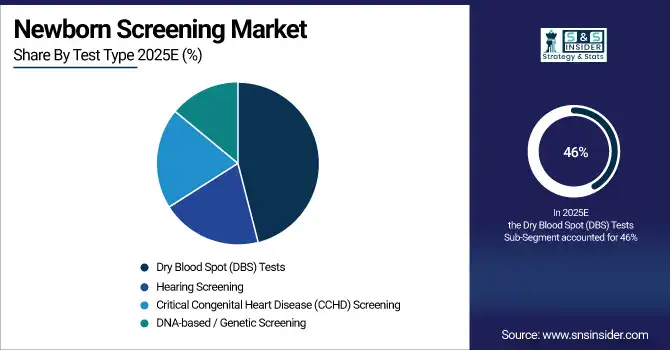
In 2023, dry blood spot tests led the newborn screening market with more than 46% of the revenue share. This substantial market share can be attributed primarily to the simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability of dry blood spot testing in global newborn screening programs. The prevalence and success of dry blood spot tests are highlighted in government statistics. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly all of the 4 million babies born in the United States each year undergo newborn screening using dry blood spot tests. Such a high coverage rate speaks to the accessibility of the test and acceptance of the test in healthcare systems.
According to the U.K. National Health Service (NHS), more than 97% of all newborns in 2023 were screened in the appropriate time frame for bloodspot testing, illustrating how deeply embedded the test has become in postnatal care. Dry blood spot tests, for example, can identify many disorders by analyzing a small sample, making them ideal for high-throughput screening initiatives. They are the cornerstone of newborn screening programs worldwide owing to their ease of collection, stability in transport, and ability to facilitate multiple analyses. In addition, WHO has highlighted dry blood spot testing as a pivotal component in advancing newborn screening efforts in low- and middle-income countries, emphasizing its role in global health initiatives targeting the prevention of fatal or debilitating conditions in infants that are amenable to treatment intervention.
By Product
In 2023, the instruments segment accounted for the largest market share 74%. significantly to the overall newborn screening tests, the need for specialized instruments is paramount to conduct these tests successfully and promptly in various healthcare settings. Recent government data shows the potential importance of more advanced screening instruments for newborns. According to the U.S. Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), advances in screening equipment have led to the successful implementation of newborn screening programs that test for more than 30 different conditions in a majority of states, a dramatic increase from just a few decades ago. These advances have enabled the expansion of newborn screening to more disorders that can be detected accurately and efficiently with sophisticated screening tools.
The increase in market share of the instruments segment is also owing to continuous government investments in upgrading newborn screening infrastructure. For example, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's (CDC) Newborn Screening Quality Assurance Program assists state health departments in monitoring and improving their screening which facilitates improved quality testing throughout the country. Well-maintained and well-calibrated instruments are essential to meet the high sensitivity and specificity demanded by newborn screening tests, according to data collected by the program. Furthermore, the FDA among other regulatory bodies has been highly engaged in validation, further facilitating and propelling innovation in the market. These approvals have also resulted in the advent of better, faster, and more precise screening tools which helped establish the dominance of the instruments segment in the newborn screening market.
By Application
Metabolic Disorders most national newborn screening programs prioritize metabolic conditions, which require MS/MS-based testing and generate significant testing volume. Their broad inclusion across global panels, strong clinical evidence, and established workflows ensure they remain the most widely screened application category.
Genetic / Rare Diseases are NGS-based newborn screening expands, enabling detection of conditions previously undetectable through biochemical tests. Rising prevalence awareness, national genome programs, and enhanced reimbursement support drive rapid integration of genetic testing into newborn screening, accelerating growth in this segment.
Newborn Screening Market Regional Insights
North America Newborn Screening Market Insights
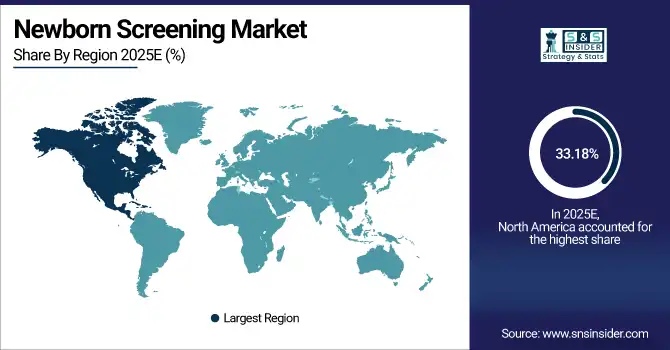
North America dominated the single-axis solar tracker market with a 33.18% share in 2025 due to large-scale utility solar deployments, strong policy incentives, grid modernization efforts, and high investment from leading developers. Mature project pipelines, favorable tax credits, and widespread adoption of advanced tracking technologies further reinforce the region’s dominant market position. Top of FormBottom of Form
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
The U.S. holds 80.5% of North America’s newborn screening market due to strong infrastructure and mandatory programs, while Canada is the fastest-growing, driven by healthcare
Asia Pacific Newborn Screening Market Insights
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of about 9.37% from 2026–2033, driven by massive solar capacity additions in China, India, and Australia, declining tracker costs, and rapid expansion of utility-scale projects. Supportive renewable-energy targets, rising electricity demand, and government-backed clean-energy investments accelerate the adoption of single-axis solar trackers across the region.
Asia Pacific’s newborn screening market is driven by strong government initiatives, rising awareness, and growing adoption of MS/MS and DNA-based assays. China holds 40.2% of 2024 revenue, while India grows fastest. Dried blood spot tests lead with 42%, and CCHD screening expands rapidly.
Europe Newborn Screening Market Insights
The Europe newborn screening market is expanding steadily, driven by strong government mandates, harmonized public-health policies, and growing emphasis on early detection of rare and genetic disorders. Countries such as the U.K., Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands are advancing screening panels, integrating NGS and metabolic testing. Increased reimbursement support, rising awareness, and investments in laboratory modernization further strengthen market adoption across the region.
In 2023, tandem mass spectrometry accounted for the largest technology share at 24.7%, while electrophoresis is anticipated to grow fastest over the coming years. Over 1.7 million births are screened annually across 23 EU countries under established programs like EUROCAT, reflecting widespread coverage and strong regional commitment to newborn health
Middle East & Africa and Latin America Newborn Screening Market Insights
The Middle East & Africa newborn screening market is gradually expanding, supported by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising awareness of genetic and metabolic disorders, and growing government initiatives in countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and South Africa. Latin America is witnessing similar progress, with Brazil, Mexico, and Chile strengthening national screening programs, improving laboratory capacity, and adopting advanced technologies such as MS/MS and molecular assays. However, both regions still face challenges related to funding, coverage gaps, and workforce shortages.
Saudi Arabia leads MEA with 96% hospital-based newborn screening coverage and strong adoption of MS/MS and molecular assays, while Brazil, Mexico, and Chile drive Latin America’s progress. However, both regions still face funding, coverage gaps, and workforce limitations hindering full-scale implementation.
Key Players in the Newborn Screening Market
-
PerkinElmer, Inc. (EnLite Neonatal TREC Kit, NeoBase 2 Non-Derivatized MSMS Kit)
-
Natus Medical Incorporated (ALGO 5 Newborn Hearing Screener, Echo-Screen III Hearing Screener)
-
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (Neonatal hTSH kit, VARIANT™ NBS Sickle Cell Program)
-
GE Healthcare (Giraffe Incubator Carestation, Corometrics 170 Series Fetal Monitor)
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Neonatal Total Galactose Kit, MassARRAY System)
-
Agilent Technologies, Inc. (SureScan Microarray Scanner, 2100 Bioanalyzer)
-
Waters Corporation (ACQUITY UPLC System, Xevo TQ-S Mass Spectrometer)
-
Trivitron Healthcare (Neomass AAAC Kit, Newborn Screening Software)
-
Baebies, Inc. (SEEKER Platform, FINDER Platform)
-
Medtronic plc (INVOS™ Cerebral/Somatic Oximeter, Nellcor™ Pulse Oximetry)
-
Masimo Corporation (Rad-97 Pulse CO-Oximeter, Pronto Pulse CO-Oximeter)
-
Zentech S.A. (Neonatal G6PD Assay, NeoMass AAAC Kit)
-
Demant A/S (AccuScreen Newborn Hearing Screener, MADSEN AccuScreen)
-
Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. (Welch Allyn Spot Vision Screener, Panda Warmer)
-
Revvity (GSP® Neonatal Screening System, DELFIA® Xpress System)
-
Natera, Inc. (Panorama Non-Invasive Prenatal Test, Horizon Carrier Screening)
-
OZ Systems (eSP™ Newborn Screening Management Software, Telepathy CCHD Screening)
-
Abionic SA (IVD CAPSULE PSP, IVD CAPSULE Ferritin)
-
Metascreen (Metascreen Metabolic Screening Test)
-
Cordlife Group Limited (Metascreen Newborn Metabolic Screening, Eyescreen Paediatric Vision Screening)
Newborn Screening Market Competitive Landscape:
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Agilent Technologies, Inc. advanced its laboratory and diagnostics portfolio with major 2024–2025 developments. In 2024, it launched the Advanced Dilution System (ADS 2) to automate ICP-MS/OES workflows and acquired Sigsense Technologies to strengthen AI-driven lab optimization. In 2025, Agilent’s NovoCyte Opteon spectral flow cytometer earned a top industry innovation award, reinforcing its leadership in analytical and diagnostic technologies.
-
21 Feb 2025: Agilent’s NovoCyte Opteon spectral flow cytometer won “Best New Drug Discovery & Development Product of 2024”.
Bio‑Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. reported notable progress across 2024–2025, driven by expanding diagnostics capabilities and strong financial performance. In 2024, the company posted steady revenue growth led by its Clinical Diagnostics segment. By 2025, Bio-Rad strengthened its molecular diagnostics portfolio with the expansion of its droplet digital PCR platforms following the Stilla acquisition, reinforcing its leadership in high-precision life-science and clinical testing technologies.
-
7 Jul 2025: Launched new droplet-digital PCR (ddPCR) platforms following acquisition of Stilla Technologies – QX Continuum and QX700 series.
Danaher Corporation
Danaher Corporation strengthened its position in life sciences and diagnostics through key 2024–2025 developments. In 2024, the company appointed a Chief Data & AI Officer and released its comprehensive Sustainability Report, emphasizing innovation and ESG commitments. In 2025, Danaher reported steady revenue growth, reflecting strong performance across its bioprocessing, diagnostics, and analytical-instruments businesses, reinforcing its leadership in global healthcare technology.
-
5 Jun 2024: Appointed Martin Stumpe as Chief Data & Artificial Intelligence Officer – reflecting Danaher’s focus on AI/automation
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025E | USD 2.33 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 4.30 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 8.01 % From 2026 to 2033 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2033 |
| Historical Data | 2022-2024 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | •By Test Type (Dry Blood Spot (DBS) Tests, Hearing Screening, Critical Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Screening, DNA-based / Genetic Screening) • By Technology (Tandem Mass Spectrometry (TMS), PCR / Molecular Assays, Immunoassays (ELISA, FIA, etc.), Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)) • By Product Type (Reagents & Assay Kits, Instruments / Analyzers, Hearing Screening Devices, Consumables & Accessories) • By Application (Metabolic Disorders, Hormonal Disorders, Hematological Disorders, Hearing & CCHD Disorders, Genetic / Rare Diseases) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada), Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Poland, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, ASEAN Countries, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Colombia, Rest of Latin America). |
| Company Profiles | PerkinElmer, Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., Natus Medical Incorporated, Trivitron Healthcare Pvt Ltd, Danaher Corporation, GE Healthcare, Masimo Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., AB Sciex LLC, Waters Corporation, Demant A/S, Baebies Inc., ZenTech S.A., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, LifeCell International Pvt Ltd, MP Biomedicals LLC, Illumina, Inc., LabCorp (Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings), Natera, Inc. |

