Peptide Antibiotics Market Size Analysis:
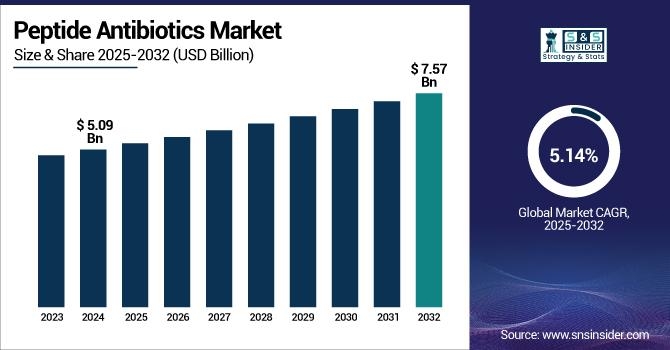
The Peptide Antibiotics Market size was valued at USD 5.09 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 7.57 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.14% over the forecast period of 2025-2032.
To Get more information on Peptide Antibiotics Market - Request Free Sample Report
The peptide antibiotics market is growing steadily with the increasing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and the pressing demand for new therapeutic agents. Peptide antibiotics possess broad-spectrum activity and less resistance development, which makes them promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics. Growing R&D spending, positive regulatory support, and improvements in peptide synthesis technologies are further driving the market.
The U.S. peptide antibiotics market size was valued at USD 1.94 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.84 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.92% over the forecast period of 2025-2032.
In July 2024, the CDC published its report on antimicrobial resistance threats in the United States, 2021–2022, wherein it found six categories of hospital-onset bacterial antimicrobial-resistant infections grew together by a total of 20% during the COVID-19 pandemic years versus before the pandemic, with an all-time high in 2021 and continued high levels in 2022. The report also reported an almost five-fold increase in reported clinical cases of Candida auris, a yeast resistant to drugs that spread in healthcare facilities and can lead to serious illness, from 2019 through 2022.
The U.S. leads the North American peptide antibiotics market due to its advanced pharmaceutical R&D centers, strong regulatory system, and significant investments in combating antimicrobial resistance. Its well-established healthcare infrastructure and grants for the development of new antibiotics also contribute to this leadership.
Peptide Antibiotics Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Emerging Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Driving the Market Growth
Antimicrobial resistance is among the most critical health threats worldwide, according to the CDC. In the U.S., more than 2.8 million antimicrobial-resistant infections occur each year since bacteria continue to develop resistance against conventional antibiotics, making many therapies useless. This has dictated a requirement for novel therapies able to function powerfully against recalcitrant microbes. Antibiotics that target peptides represent a perfect answer in that they possess unique modes of action, ranging from the destabilization of bacterial membranes or even the inhibition of specific proteins, which complicates resistance in bacteria. As healthcare systems struggle with increasing challenges in treating resistant infections, the need for peptide antibiotics keeps growing, making them a key element in the future peptide antibiotics market growth.
-
Increasing Prevalence of Hospital-Acquired Infections (HAIs) Propelling the Market Growth
Hospital-acquired infections, such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and surgical site infections, are of serious concern in clinical practice, especially in intensive care units. These infections are usually caused by resistant bacteria and need to be treated with effective antibiotics. Peptide antibiotics, particularly in injectable forms, are usually employed in hospitals to treat such life-threatening infections because they exhibit broad-spectrum activity and a rapid onset of action. The rising rate of surgical procedures, longer hospital stays, and immunocompromised hosts have all led to an increase in HAIs, hence the need for reliable and innovative antimicrobial agents, such as antibiotic resistance and peptides.
As reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), on average, 1 out of every 31 patients who are hospitalized each day will have at least one healthcare-associated infection.
The CDC estimates that almost 5% of all hospitalizations result in a healthcare-associated infection and cause approximately 722,000 infections and 75,000 deaths each year in the U.S.
Restraint
-
High Production Costs and Sophisticated Manufacturing Restricting the Market Growth
Peptide antibiotics require advanced synthesis protocols, which are complicated and technology-intensive. This is coupled with high production costs and the ability to produce in large quantities, particularly among small and medium-scale manufacturers. The resulting high cost reflects on prices and reimbursement rates in price-sensitive markets.
The world faces a severe access and pipeline crisis of antibiotics, with woefully insufficient research and development pipeline to meet increasing antimicrobial resistance. The immediate need is for greater efforts to ensure equitable access to new and existing vaccines, diagnostics, and medicines. Apart from the cost of disability and death, AMR has a substantial economic cost.
For Instance, Antimicrobial resistance, the World Bank estimates, could lead to an additional USD 1 trillion in healthcare spending by 2050 and global GDP losses between USD 1 trillion and USD 3.4 trillion annually by 2030.
Peptide Antibiotics Market Segmentation Insights
By Product
The non-ribosomal synthesized peptide antibiotics segment dominated the peptide antibiotics market share with 72.16% in 2024 because of their extensive activity and increased stability compared to ribosomally synthesized peptides. Non-ribosomal peptides are produced with a modular enzyme system, which enables the production of highly diverse, powerful antibiotics with fewer problems related to resistance. This is especially effective against multidrug-resistant pathogens, which are increasingly becoming a threat across the globe. Their capacity to act against a broad spectrum of infections, such as skin infections and hospital-acquired infections, has helped them dominate the market.
The ribosomally synthesized peptide antibiotics segment is expected to exhibit the fastest growth during the forecast period. These peptides are produced by the ribosome and are typically less complex and cheaper to manufacture than non-ribosomal peptides. Advances in peptide synthesis technologies and increasing research on their antimicrobial activity are driving their strong growth. The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is also fueling the quest for ribosomal peptides as effective and affordable alternatives to traditional antibiotics, which is driving growth in this segment.
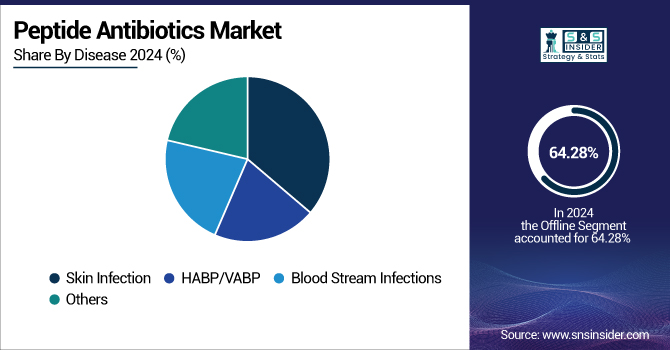
By Disease
The skin infection segment led the peptide antibiotics market with a 36.22% share in 2024 due to the vast number of bacterial skin infections, including impetigo and cellulitis, that require effective antimicrobial therapies. Peptide antibiotics, particularly non-ribosomal synthesis, have shown strong efficacy in killing resistant strains like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), which mostly cause skin infections. Also, the increasing realization regarding the shortcomings of conventional antibiotics and the rising rate of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) related to the skin added to the dominance of this segment.
The bloodstream infections (BSI) segment is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth during the forecast period, with a 5.77% CAGR, owing to the rising number of patients with bloodstream infections due to multidrug-resistant bacteria. Bloodstream infections, such as sepsis, need quick and effective treatments, and peptide antibiotics have shown great promise in fighting these life-threatening infections.
By Route of Administration
The injectable segment dominated the peptide antibiotics market with a 44.18% market share in 2024 because injectable products provide more efficacy and quicker therapeutic response, particularly in severe infections. Injectable peptide antibiotics are also extensively used in hospitals to treat systemic and serious infections, such as bloodstream infection and hospital-acquired infection. The products ensure that the medication enters the body through the blood rapidly, allowing a faster response than oral antibiotics.
The oral segment is expected to register the highest growth during the forecast period since the need for less convenient, cost-effective, and patient-friendly solutions increases. Oral peptide antibiotics are easy to administer and can be used for outpatient or self-treatment, making them highly sought after by patients as well as medical professionals. Advancements in oral delivery technologies that improve the stability and bioavailability of the peptide antibiotics are driving growth in this segment.
By Distribution Channel
The hospital pharmacies segment led the peptide antibiotics market with 42.13% due to the major role played by hospitals in the treatment of severe and complex infections. Peptide antibiotics are typically prescribed for severe, multidrug-resistant infections, which are typically treated in hospital settings, particularly for hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) or bloodstream infection patients. Hospitals possess the requisite infrastructure in the form of trained healthcare personnel and the capability to administer intravenous or injectable preparations of antibiotics, which makes hospital pharmacies the first line of distribution for these specialized drugs.
The online pharmacies segment is anticipated to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period due to the increasing use of the e-commerce business model and customer preference for handy home delivery of drugs. Increasing awareness of peptide antibiotics and the requirement for alternative drug therapies against infection-resistant strains results in online pharmacies being a relatively more convenient proposition for patients in areas with inferior healthcare infrastructure.
Regional Outlook
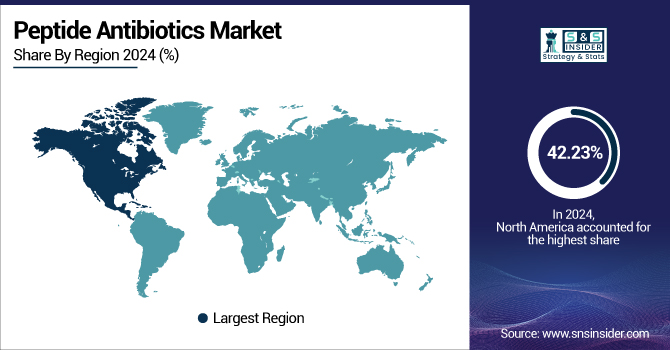
North America dominated the peptide antibiotics market in 2024 with a share of 42.23% because of its well-developed healthcare infrastructure, high concentration of top drug companies, and the highest R&D investments in antibiotics. The region has supportive government programs and investments directed towards fighting antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and is supplemented by institutions such as the CDC and BARDA, promoting the release of new peptide therapeutics. Also, intense awareness among doctors and healthcare workers and an entrenched regulatory structure help new antibiotics reach the market speedily and come to commercial scale rapidly, enhancing the peptide antibiotics market analysis.
For instance, in March 2022, the UN General Assembly adopted resolution A/RES/76/257, calling for a second High-level Meeting on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), held in 2024 with support from the Quadripartite Organizations and the Global Leaders Group. The Permanent Representatives of Barbados and Malta were appointed as co-facilitators in October 2023. The meeting aimed to drive ambitious commitments across human, animal, agri-food, and environmental sectors.
The Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the peptide antibiotics market, with a 6.10% CAGR over the forecast period due to growing infectious disease burdens and mounting rates of AMR in countries such as China and India. The region is seeing increasing access to healthcare, high urbanization rates, and increased investments in pharma R&D. Further, favorable government initiatives and a high rise in generic and biosimilar manufacturing facilities are driving peptide antibiotic development and adoption.
Europe is the most prominent region in the peptide antibiotics market with a strong pharmaceutical base, high R&D spending, and active antimicrobial resistance efforts. Germany and France are leaders in innovation and take-up, supported by supportive regulation and healthcare policies.
Germany leads the peptide antibiotics market in Europe with its superior pharma infrastructure, high R&D investment, and anti-antimicrobial resistance (AMR) regulatory pushes. The nation has experienced a rapid rise in bacterial infections, such as skin and blood infections, increasing the need for effective treatments through peptides. Government policies, including favorable reimbursement schemes and funding initiatives, have also promoted the growth and uptake of peptide antibiotics market trends.
Latin America is experiencing moderate peptide antibiotics market growth due to increasing consciousness about antimicrobial resistance, increasing investments in the healthcare sector, and gradual construction of pharmaceutical infrastructure in countries such as Brazil and Mexico. But economic imbalances, shortages of healthcare in rural regions, and uneven regulatory environments are slowing the rate of market growth.
In the Middle East & Africa (MEA), the region is witnessing steady growth driven by improved healthcare infrastructure, particularly in South Africa and Saudi Arabia, and a growing focus on addressing resistant infections. Although non-ribosomal synthesized peptide antibiotics are also picking up pace in the region, economic constraints and healthcare disparities continue to be dampening factors to their large-scale adoption.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Peptide Antibiotics Market Key Players
Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bachem Holding AG, Sandoz, Ipsen S.A., Merrion Pharmaceuticals, Taiwan Liposome Company, PolyPeptide Group, Melinta Therapeutics, and other players.
Recent Developments
-
In April 2025, Pfizer Inc. announced that it is ending development of danuglipron (PF-06882961), an oral glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist currently in development for treating chronic weight.
-
In February 2025, Teva Pharmaceuticals, a U.S. affiliate of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Alvotech announced the U.S. launch of SELARSDI (ustekinumab-aekn) injection. This biosimilar to Stelara (ustekinumab) is indicated to treat psoriatic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis in children, and psoriatic arthritis.
-
In February 2025, The Novo Nordisk Foundation launched its Catalyst Grants, which were first launched in 2024, to speed up innovation and speedy testing of novel ideas in three areas of focus: antimicrobial resistance (AMR), invasive pathogenic fungi, and harnessing innate immunity against airborne viral infections.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.09 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 7.57 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 5.14% From 2025 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2021-2023 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | •By Product (Ribosomally Synthesized Peptide Antibiotics, Non-ribosomal Synthesized Peptide Antibiotics) •By Disease (Skin Infection, HABP/VABP, Blood Stream Infections, Others) •By Route of Administration (Oral, Injectable, Topical, Others) •By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Poland, Turkey, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa), Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Agilent Technologies, Shimadzu Corporation, Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bachem Holding AG, Sandoz, Ipsen S.A., Merrion Pharmaceuticals, Taiwan Liposome Company, PolyPeptide Group, Melinta Therapeutics, and other players. |

