Healthcare Education Market Size Analysis:
Get more information on Healthcare Education Market - Request Sample Report
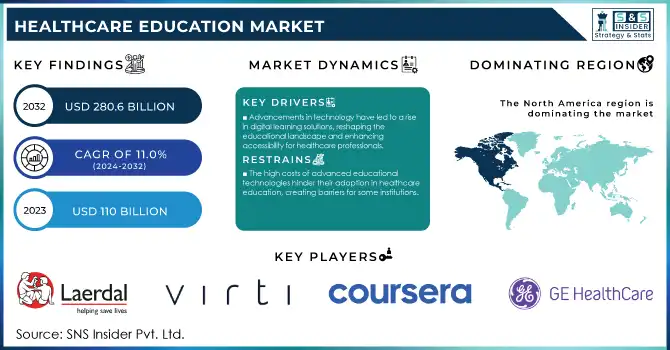
The Healthcare Education Market Size was valued at USD 110 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 280.6 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 11.0% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Various drivers are contributing to the strong growth of the Healthcare Education market. Emerging technologies such as e-learning platforms, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality are transforming healthcare education delivery with adaptive, engaging, and immersive learning and also increasing their accessibility. The increasing demand for healthcare professionals, fueled by an aging population and the need for pandemic preparedness, further propels market expansion. Government initiatives worldwide are playing a crucial role in supporting healthcare education. As an example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that employment of both radiologic and MRI technologists is expected to grow 9% by the year 2030, which translates into about 21,600 more jobs. Similar programs in Europe with respect to Horizon 2020/Horizon Europe are championing healthcare education and innovation. Other Asian countries are also focusing on health education such as "Healthy China 2030" in China and National Health Policy in India.
Interprofessional education (IPE) is a key component of the market, and with the fast pace of digitalization and advancement in technology, the increased focus on the utilization and integration of technology into training programs is expected. Japan, for example, emphasizes collaboration among different healthcare students during their education. Investment into healthcare infrastructure in the Middle East and Africa is creating a requirement for healthcare personnel as well as training programs. Being forced into more digital learning platforms due to the COVID-19 pandemic has driven the need for ongoing medical education and flexibility in sanitation learning. The healthcare environment is changing and so is the educational sector, which strives to train professionals to meet the diversified needs of the population worldwide.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Advancements in technology have led to a rise in digital learning solutions, reshaping the educational landscape and enhancing accessibility for healthcare professionals.
-
An aging population and the need for improved pandemic preparedness have heightened the demand for qualified healthcare workers, driving the expansion of educational infrastructure and training programs.
-
The incorporation of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare education is enhancing training methodologies and broadening the scope of educational programs.
Digital learning is transforming healthcare education more accessible and effective than ever before. As technology is developing, e-learning channels are taking the place of physical classes, virtual classrooms, and mobile apps have given varied tools to individuals to learn new skills and knowledge at their own pace. For example, there has been a huge increase in the use of Learning Management Systems (LMS) in healthcare to deliver training. According to a survey by Global Healthcare Education Review in the year 2023, it was found that 76% of healthcare professionals believe e-learning platforms more engaging for upskilling compared to conventional ones. The major platforms such as Coursera and edX have specialized healthcare courses, from medical coding to patient care to telemedicine, attracting professionals from across the world.
Reflecting the remote learning requirement. A report released by Education Tech Insights in 2024 stated that 85% of the medical schools across the globe adopted some form of digital learning during the pandemic which many of the institutions have held to since it is efficient and scalable. In addition, the medical training sector is being revolutionized by AR and VR. For example, Johns Hopkins University utilized VR simulations for training surgical students in realistic environments from the comfort of their lab. Similarly, 3D Organon is an AR-based anatomy learning app that addresses interactivity and immersion. These achievements highlight the dual benefits of digital learning improved educational outcomes and addressing the rapidly evolving industry demand for our burgeoning healthcare workforce.
Restraints:
-
Limited internet connectivity and inconsistent electricity supply in certain developing areas hinder access to online education, posing challenges to the widespread adoption of digital learning solutions.
-
The high expenses associated with implementing advanced educational technologies can be a barrier for some institutions, limiting the adoption of innovative solutions in healthcare education.
-
Some educators and institutions may be hesitant to embrace new technologies, preferring traditional teaching methods, which can impede the integration of modern educational tools.
One significant restraint in the healthcare education market is the high cost associated with implementing advanced educational technologies. Solutions such as virtual reality (VR) simulators, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven learning platforms, and augmented reality (AR) applications demand massive investments in infrastructure and training. Most of these institutions, especially those located in developing or underfunded regions, do not have the means to procure these state-of-the-art technologies. Beyond procurement, another cost burden comes in the form of maintaining and upgrading these solutions, as well as ensuring technical support for them. Furthermore, educators themselves need training to make use of these technologies, which increases costs. These high prices may lead to an inequality in good education, given that they restrict smaller institutions or poorer regions from innovating. This affordability gap hinders the rapid proliferation of technology-facilitated education and stifles fair opportunity for the advancement of healthcare education worldwide.
Healthcare Education Market Segmentation Analysis
By Provider
The market was dominated by the universities and academic centers segment which represented a 32% share in 2023. This dominance is supported by several factors, including the significant role that these institutions are responsible for across the entire spectrum of healthcare education programs. Supporting this trend are government statistics backing the American Society of Radiologic Technologists estimate that shows around 350,000 radiologists are registered and working in the healthcare environment. Most of the universities and academic centers are stationed closer to medical research and innovations, thus exposing students to the latest technologies and developments in the world of medicine. These are also heavily state-funded and state-supported institutions. One such example would be Germany, where the federal and state governments invest heavily in healthcare education, particularly through programs like the Excellence Initiative or grants from the German Research Foundation (DFG). This support allows universities to keep their facilities fully equipped, hire world-class faculty, and build robust curricula to reflect the changing needs of the healthcare arena. In addition, colleges and colleges tend to work with hospitals and provide healthcare providers, so students are also capable of work and utilities to read on the website. Interprofessional education (IPE) is playing a greater role in the curricula of countries such as Japan which only adds to the appeal of university-based healthcare-oriented education by attracting individuals from across multiple healthcare professions.
By Application
In 2023, the radiology segment held the largest market revenue share. This leadership position can be attributed to several factors, backed by government statistics and industry trends. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, radiologic and MRI technologists can expect to see around 9% growth in employment through 2030, which suggests demand for this field will remain strong. They are fueled by the rising incidence of chronic diseases and an older population too, which all rely heavily on these diagnostic imaging services. The increasing role of recent medical imaging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning is driving demand for new radiology skill sets. Moreover, government efforts to enhance healthcare infrastructure and increase access to diagnostic services also contribute to the segment's expansion. The medical imaging market is expected to grow in some regions such as Europe owing to high investment in research and developments by public as well private sectors. This, coupled with the major role imaging has in modern healthcare from early detection of diseases to planning and monitoring of treatment, further drives the dominance of the radiology segment. With the increasing focus on preventive care and early intervention in the healthcare systems globally, the need for qualified radiologists and technologists is also increasing, fuelling the growth of radiology courses.
By Delivery Mode
In 2023, the classroom based courses held the largest market share in 2023. This dominance can be attributed to several factors, despite the growing popularity of e-learning solutions. The future of classroom-based education in healthcare is still backed up by government statistics and industry trends. Many health professionals work in medically hands-on roles, and thus they need hands-on training in a classroom or laboratory, not online. As an example, approximately 350,000 radiologists are registered to work within a healthcare environment according to the American Society of Radiologic Technologists, with most performing basic training in classroom-focused curricula. This will be the case until regulatory requirements in many countries are aligned as they still require a minimum amount of in-person training hours before a healthcare professional can be licensed and/or continue to practice. The classroom atmosphere also allows students to directly interact with their instructors and even fellow student groups, which is important for the development of critical dispositions and professional networking. When government initiatives are made to support healthcare education, the focus is generally on new buildings and facilities. For instance, in Germany, the federal and state governments make significant investments in healthcare education by supporting first-rate universities and research programs. It further underlines the significance of in-person learning with this investment in physical infrastructure. Additionally, the combination of psychology labs, along with technology, has improved real-life learning experiences for students by offering an approach in a controlled environment to skill practice.
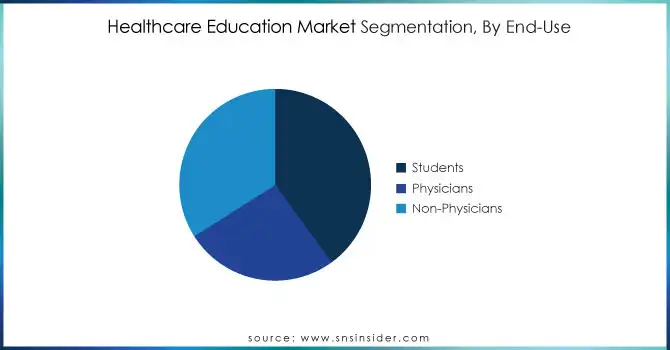
By End Use
The students segment dominated the market and held the highest revenue share 40% In 2023. Such supremacy is backed up by determined government statistics and business trends. Increased number of enrolments in various health care education due to the high demand of every specialty of health care professionals as compared to last decade. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics report states that "Employment of healthcare occupations is expected to grow 15% from 2019 to 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding about 2.4 million new jobs." The government's efforts to alleviate shortages in the healthcare workforce have increased funding and support for student education. In the USA, for example, the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) offers grants and scholarships to help people study in various healthcare fields, particularly in areas that lack sufficient care. The student segment also holds the largest share owing to the widening spectrum of healthcare education which includes interdisciplinary programs and niche tracks to cater to the changing needs of the healthcare industry. Moreover, the technological advancements in healthcare education like the use of virtual reality and simulation-based learning have made these programs more appealing and accessible to students, increasing enrollment rates.
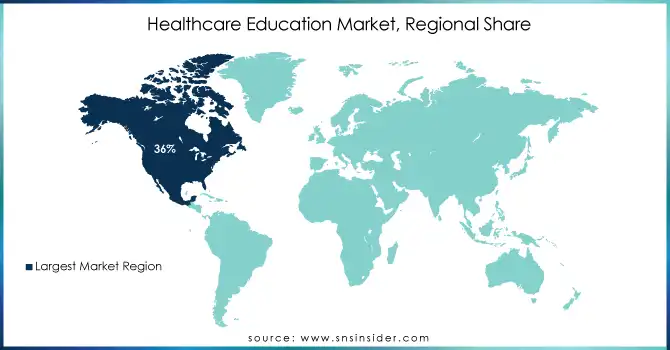
Regional Analysis
North America region dominated the healthcare education market with a revenue share of 36% in 2023. Factors contributing to this leadership position include the availability of comprehensive healthcare infrastructure, a well-trained workforce, high investment in education and training, and rigorous ongoing medical education (CME). The area's best hospitals, medical schools, and large research institutions provide an ideal environment for clinical training with access to state-of-the-art technology and a wide variety of patient populations. The vast range of available healthcare education through public and private funding allows much of the population access to healthcare education.
On the other hand, the fastest growth is being witnessed from the Asia Pacific region with the expected gain in market share. Several factors drive this growth which include rising government expenditure on healthcare education, a large and still growing population demanding healthcare services, and the increase in medical and nursing schools. Countries like China, India, and Japan are only now starting to shift national health policies and initiatives to prioritize health education. The healthcare education sector is significantly fueled by initiatives such as China's "Healthy China 2030" initiative and India's National Health Policy for Health and Wellness Centres.
Recent developments:
-
In January 2024, Wolters Kluwer collaborated with Kortext to begin offering the Lippincott Medical Education eBook library to make MCQs and other medical resources more accessible to universities and students across India.
-
GE Healthcare partnered with DePuy Synthes in 2023 to offer additional capabilities with its OEC 3D Imaging System to more U.S. hospitals and their surgeons and patients.
-
In September 2023, the Chinese Ministry of Education introduced guidelines to enhance medical education, focusing on modernizing healthcare curricula.
Key Players
Key Service Providers/Manufacturers
-
Laerdal Medical: Resusci Anne (CPR training manikin), SimMan 3G (patient simulator)
-
Virti: Immersive Learning Platform, Virtual Patient Simulations
-
Coursera Inc.: Healthcare Management Courses, Medical Neuroscience Course
-
Elsevier: ClinicalKey (medical reference platform), Evolve (educational resources)
-
GE Healthcare: Healthcare Learning System, Ultrasound Training Solutions
-
Koninklijke Philips NV: Philips Learning Center, Ultrasound e-Learning
-
Medtronic: Medtronic Academy (training platform), Surgical Training Program
-
Olympus Corporation: Endoscopy Training, Surgical Procedure Training
-
Siemens Healthineers: PEPconnect (online education platform), Imaging Training Solutions
-
Stryker: Stryker Education Portal, Surgical Simulation Training
-
Zimmer Biomet: Zimmer Biomet Institute (education and training), Surgical Skills Workshops
-
Canon Medical Systems Corporation: Medical Imaging Training, Ultrasound Education Programs
-
FUJIFILM Holdings: Synapse Education (imaging informatics training), Endoscopy Training Programs
-
SYMPLR: Healthcare Compliance Training, Credentialing Solutions
-
Siemens Healthineers: syngo.via (imaging software training), Laboratory Diagnostics Education
-
3D Systems: Simbionix (surgical simulators), Virtual Reality Training Modules
-
CAE Healthcare: Vimedix (ultrasound simulator), Lucina (maternal fetal simulator)
-
Wolters Kluwer: UpToDate (clinical decision support), Lippincott Procedures (nursing education)
-
HealthStream: Learning Center (healthcare workforce development), Compliance Training Solutions
-
Relias: Healthcare Learning Management System, Clinical Skills Training
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 110 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 280.6 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 11.0% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Provider (Continuing Medical Education Providers, Educational Platforms, Learning Management Systems, Universities and Academic Centers, OEMs/Pharmaceutical Companies, Medical Simulation) • By Delivery Mode (Classroom-based Courses, E-learning Solutions) • By Application (Academic Education, Cardiology, Radiology, Neurology, Pediatrics, Internal Medicine, Others) • By End-use (Students, Physicians, Non-Physicians) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Laerdal Medical, Virti, Coursera Inc., Elsevier, GE Healthcare, Koninklijke Philips NV, Medtronic, Olympus Corporation, Siemens Healthineers, Stryker, Zimmer Biomet, Canon Medical Systems Corporation, FUJIFILM Holdings, SYMPLR, 3D Systems, CAE Healthcare, Wolters Kluwer, HealthStream, Relias. |
| Key Drivers | • Advancements in technology have led to a rise in digital learning solutions, reshaping the educational landscape and enhancing accessibility for healthcare professionals. • An aging population and the need for improved pandemic preparedness have heightened the demand for qualified healthcare workers, driving the expansion of educational infrastructure and training programs. |
| Restraints | • Limited internet connectivity and inconsistent electricity supply in certain developing areas hinder access to online education, posing challenges to the widespread adoption of digital learning solutions. • The high expenses associated with implementing advanced educational technologies can be a barrier for some institutions, limiting the adoption of innovative solutions in healthcare education. |

