Next Generation Memory Market Size
The Next Generation Memory Market Size was valued at USD 6.4 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 41.8 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 23.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Demand for Next Generation Memory is on the rise from the increasing demand of memory technologies, particularly in high-speed and energy-efficient applications. Applications in the automotive, healthcare, and telecommunications sectors are the key drivers for this demand. The emergence of technologies such as self-driving cars and IoT Devices has required memory with faster read/write and improved reliability. 2023 witnessed global semiconductor revenue of $573 billion, a 4.4% increase year-on-year according to World Semiconductor Trade Statistics (WSTS). This growth is primarily driven by memory technologies, with about 30% of the total sales revenues.
Get E-PDF Sample Report on Next-Generation Memory Market - Request Sample Report
Government initiatives play an important role in driving this growth. The CHIPS and Science Act in the United States directed $52 billion to strengthen U.S. leadership in semiconductor manufacturing and innovation including investment in memory. South Korea, too, has promised $450 billion by 2030 before its semiconductor supremacy strategy with a major focus on next-gen memory production. At the same time, "Made in China 2025" emphasizes self-reliance and invites the development of semiconductor manufacturing and non-volatile memory types. This benevolent backdrop of government assistance and technological growth is opening up new avenues for industry participants helping them build advanced solutions across various markets ranging from wearables to enterprise storage. This mix of public policy and private sector innovation will likely keep the market on a strong growth path.
Next Generation Memory Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
The rising need for advanced computing capabilities in artificial intelligence, deep learning, and data analytics has amplified the adoption of next-gen memory technologies like MRAM and ReRAM due to their high bandwidth and low latency characteristics.
-
The surge in Internet of Things (IoT) devices demands energy-efficient, high-speed, and reliable memory solutions, driving the development and integration of advanced non-volatile memory like PCM and FRAM into edge computing applications.
-
The shift towards decentralized computing and real-time data processing closer to the data source is boosting demand for fast and efficient memory systems.
Next-generation memory technologies, like MRAM (Magneto-Resistive RAM) and FRAM (Ferroelectric RAM), have been primarily driven by the explosive growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The total number of connected IoT devices is expected to surpass 29 billion globally by 2024, up from 23 billion in 2022. From smart cities to healthcare, and industrial automation to consumer electronics, these devices require high-speed, energy-efficient, and robust memory solutions in various sectors.
Since most IoT applications are deployed in a low-power environment, it is impossible to use traditional volatile memory such as DRAM or SRAM. The increasing popularity of non-volatile memory, for example MRAM, has sparked –because it can keep the information without power and provide a higher read/write speed. For example, Samsung's MRAM technology has demonstrated superior endurance and efficiency, allowing IoT devices to function optimally in edge computing scenarios without frequent battery replacements. Furthermore, the healthcare sector is a particularly good example of how demand for memory is being impacted by IoT. High-Reliability Energy Efficiency Memory for Wearable Health Monitors and Implantable Devices FRAM has very low power consumption and is less susceptible to radiation damage, making it suitable for medical applications where data integrity is of utmost importance. As IoT continues to disrupt industries, challenges faced by memory manufacturers are also driving specialized innovations that make next-generation memory, such as 3D NAND and DRAM, a necessity for enabling this explosion of global connectivity.
Restraints:
-
The production of next-gen memory involves advanced processes and materials, leading to increased costs, which may limit their adoption in price-sensitive markets.
-
Adopting new memory technologies into existing infrastructure can be complex and costly due to compatibility issues and the need for significant redesigns in system architecture.
High production costs are one of the major restraints for the next-generation memory market. Besides, fabrication processes for complex memory technologies including Resistive RAM (ReRAM), Magneto-Resistive RAM (MRAM), or even 3D XPoint are likewise complicated and require specific materials to manufacture. Moreover, these techniques typically need fresh data infrastructure and tools, which further increases the manufacturing cost. Additionally, scaling these innovations to commercial levels while ensuring reliability and efficiency poses a challenge, as defects or inconsistencies in manufacturing can lead to higher wastage and increased costs.
This low-cost barrier prevents widespread adoption, especially in areas with cost-sensitive applications such as consumer electronics and small-scale industrial installations. Enterprises with long-term investments in traditional memory types (DRAM or NAND) may not see an immediate ROI that warrants a switch to next-gen solutions relative to their performance advantages over other traditional memory types. As a result, cost-related constraints hinder the pace of commercialization and market growth for these emerging technologies.
Next Generation Memory Market Segment analysis
by Technology
The Next Generation Memory market was dominated in terms of revenue by non-volatile memory with more than 77% share worldwide in 2023. This dominance is attributable to the non-volatility of the technology, which is essential for any application that requires consistent integrity of data. The segment is driven by such technologies as Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM), Resistive RAM (ReRAM), and 3D XPoint. Such memory types have faster access time, and durability, and are much more energy-efficient than previous volatile memory types making them apt for high-performance computing, AI, and big data analytics.
Government policies and strategic investments further boost the adoption of non-volatile memory. For instance, under the European Union’s Digital Compass 2030 strategy, efforts to double semiconductor production include a significant focus on non-volatile memory innovation. The Chinese government, through its National IC Investment Fund, is channeling billions of dollars to enhance its semiconductor capabilities, including non-volatile memory development. These initiatives not only tackle supply chain weaknesses but also support strategic technological sovereignty in the current geopolitical environment. Moreover, the inclusion of non-volatile memory in products such as smartphones or laptops is also creating its need. As customers turn more towards non-volatile memory technology to meet their demand for faster, more efficient storage, the sector supports a significant share of overall revenue.
by Wafer Size
The 300 mm wafer size has led the Next Generation Memory market with 65% share in 2023 and 300 mm provides a higher yield and lower cost-efficient production. by using larger wafer sizes, semiconductor manufacturers can manufacture more chips per batch, improving efficiency and, by extension, minimizing waste. In memory technology for CMOS, this benefit is especially important as price performance is a strong driver for market competitiveness.
The introduction of 300 mm wafer technology has been significantly aided by government support. As an example, the Taiwanese government has made considerable investments to support 300 mm facility expansion in association with the dominant firms like TSMC. Likewise, South Korea's 2030 semiconductor investment plan worth $150 billion highlights that 300 mm wafer fabs are developed to satisfy the increasing global demand. These efforts are keeping technologically advanced semiconductor ecosystems ahead as well. This trend toward 300 mm wafers is also in harmony with the industry's advancing semiconductor packaging technologies such as 3D stacking, which is more ideally suited for larger and more flexible wafers. The overall drive to maintain high 300 mm wafer demand and keep these technologies on 300 mm will continue to keep these wafer sizes dominant with HBM3 and DDR5 benefiting from it as next-generation memory technologies.
by Application
The Next Generation Memory market in 2023 was dominated by the BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) vertical due to the growing dependence on resilient and secure memory technologies. The financial sector processes enormous amounts of financial transactions every day, thus complex and sophisticated memory solutions are imperative in ensuring high-speed processing of data with low latency. Technologies like Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) and Resistive RAM (ReRAM) play an essential role here, providing better resistive switching characteristics, etc. These memories play a critical role in supporting high-frequency trading platforms, real-time fraud detection systems, and secure data storage which is vital for BFSI.
Additionally, the increasing proliferation of digital banking and the use of AI for customer service, risk management, and analytics are driving the need for high-performance memory. For example, AI-driven analytics needs memory that can support a data processing cycle that involves costly data computation and data fetching operations, which next-generation architectures cater to with ease. Memory technologies such as 3D XPoint have boosted BFSI firms to faster data retrieval access which is an imperative to enhancing customer experiences and operational efficiency.
Next Generation Memory Market Regional Outlook
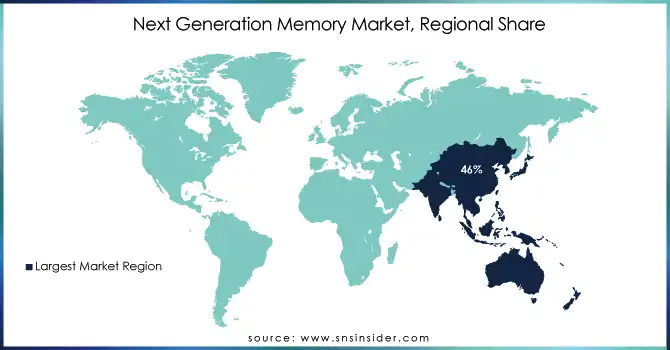
In the Next Generation Memory Market, Asia-Pacific was the largest region accounted for about 46% of the global market share in 2023. Such dominance is facilitated by the region's long semiconductor ecosystem and an unprecedented number of government and private sector vertical spending in the region. Asia-Pacific countries have major semiconductor manufacturers like Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix, which develop memory technology, as well as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. China, has made a continual effort to technological self-reliance through its "Made in China 2025" initiative, leading to large-scale investments in the manufacturing of semiconductors, especially for in-memory technologies. Geopolitical tensions spurred China to invest heavily in the expansion of domestic production in 2023, seeking self-sufficiency and independence from foreign suppliers. In line with this, South Korea rolled out an ambitious, decades-long initiative targeting global leadership in semiconductor markets with a $450 billion investment plan initially announced in late 2020, with considerable emphasis on advanced memory.
North America held the highest CAGR throughout the forecast timeframe, owing to the growth of advanced data center constructions and the prompt digitization of its market. The U.S. CHIPS Act is an example of a government program that enables growth in semiconductor production and innovation. The U.S. dominated the next-generation memory market with a significant share, driven by advancements in-memory technologies and a robust semiconductor industry. The U.S. government's Data Center Optimization Initiative (DCOI) is fostering this growth by focusing on building efficient data centers, closing underperforming ones, and enhancing public services. This strategy is expected to create significant opportunities and support market expansion.
Get Customized Report as Per Your Business Requirement - Request For Customized Report
Key Players
Service Providers / Manufacturers:
-
Samsung Electronics (Samsung MRAM, 990 PRO NVMe SSD)
-
Micron Technology, Inc. (3D XPoint, Micron LPDDR5X)
-
SK Hynix Inc. (HBM3, ReRAM)
-
Intel Corporation (Optane Memory, Persistent Memory DIMMs)
-
Western Digital Corporation (SanDisk SSD, BiCS Flash Memory)
-
Toshiba Corporation (Kioxia BiCS Flash, XL-Flash)
-
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (FRAM, MRAM Solutions)
-
Cypress Semiconductor (Infineon Technologies AG) (FRAM, SRAM-based Memory)
-
Everspin Technologies, Inc. (STT-MRAM, Toggle MRAM)
-
Avalanche Technology, Inc. (Persistent MRAM, High-Density MRAM)
Key Users
-
Apple Inc.
-
Google LLC
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
-
Tesla, Inc.
-
Microsoft Corporation
-
Sony Corporation
-
NVIDIA Corporation
-
Ford Motor Company
-
Intel Corporation (as an end-user for integrated solutions)
-
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
Recent Developments
-
Japanese firm Kioxia Corporation launches in April 2024, EXCERIA G2 series of SD memory cards. With storage up to 1TB, this new lineup exceeds the high-performance, high-capacity demands of videographers and aims even beyond extended 4K video recording.
-
Micron's planned $4 billion expansion of U.S. non-volatile memory manufacturing facilities was announced in July 2024. This action is backed by the federal incentives in the CHIPS Act and replaces the idea of shipping semiconductors across borders because of the political significance of local production of these components.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 6.4 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 41.8 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 23.2% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Wafer Size (200 mm, 300 mm) • By Technology (Volatile {SRAM, Magneto-Resistive Random-Access Memory (MRAM), Ferroelectric RAM (FRAM), Resistive Random-Access Memory (ReRAM), Nano RAM, Other}, Non-volatile {Hybrid Memory Cube (HMC), High-bandwidth Memory (HBM)}) • By Application (BFSI, Consumer Electronics, Government, Telecommunications, Information Technology, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Micron Technology, Inc., SK Hynix Inc., Intel Corporation, Western Digital Corporation, Toshiba Corporation, NXP Semiconductors N.V., Cypress Semiconductor (Infineon Technologies AG), Everspin Technologies, Inc., Avalanche Technology, Inc. |
| Key Drivers | • The rising need for advanced computing capabilities in artificial intelligence, deep learning, and data analytics has amplified the adoption of next-gen memory technologies like MRAM and ReRAM due to their high bandwidth and low latency characteristics. • The surge in Internet of Things (IoT) devices demands energy-efficient, high-speed, and reliable memory solutions, driving the development and integration of advanced non-volatile memory like PCM and FRAM into edge computing applications. |
| Restraints | • The production of next-gen memory involves advanced processes and materials, leading to increased costs, which may limit their adoption in price-sensitive markets. |

