Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Size Analysis:
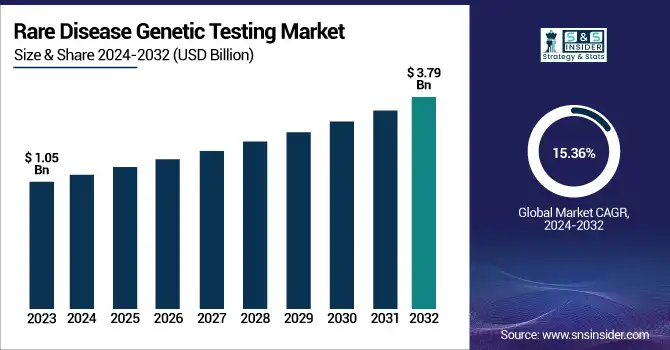
The Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market was valued at USD 1.05 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 3.79 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.36% over the forecast period of 2024-2032. This report identifies the incidence and prevalence of rare diseases as driving demand for early and correct diagnostic solutions through increased demand. The research considers trends in the utilization of genetic testing by regions based on improvements in sequencing technologies as well as widening newborn screening programs. It further investigates healthcare expenditure on rare disease genetic testing with differences in the sources of funds, such as government programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket spending affecting access. The report touches on technological breakthroughs, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and analytics powered by artificial intelligence (AI), that enhance diagnostic efficacy and decrease turnaround times. Regulation and policy patterns drive market development, with governments introducing frameworks that advance test standardization and reimbursement. Market penetration issues and accessibility impediments are further examined, focusing on inequalities regarding the availability of tests across different healthcare systems. In addition, patient and physician awareness patterns are changing, with more education efforts enhancing early diagnosis and treatment rates.
To Get more information on Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market - Request Free Sample Report
The U.S. Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market was valued at USD 0.31 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 1.18 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 16.01% over the forecast period of 2024-2032. In the United States, the rare disease genetic testing market is growing as a result of robust federal initiatives, increasing precision medicine investments, and enhanced collaborations between biotech companies and research organizations to improve early detection and tailored treatment approaches.
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
The increasing prevalence of rare diseases is a major driver for the rare disease genetic testing market, with over 300 million people worldwide affected by these conditions.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial since nearly 80% of rare diseases have a genetic origin. The increasing uptake of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) has transformed diagnostics by allowing for rapid, cost-efficient, and high-throughput genetic testing. Advances in technology, including AI-based genomic analysis, have further improved diagnostic accuracy. Government support and research funding have played a major role in supporting market growth. For instance, initiatives such as the Undiagnosed Diseases Network (UDN) in the United States and Genomics England's 100,000 Genomes Project have enhanced access to genetic testing. Expanded newborn screening programs for inherited metabolic diseases also support market growth. Moreover, increased Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) genetic testing has promoted genetic screening, increasing awareness and early detection of diseases. The increase in pharma partnerships for precision medicine and orphan drug development also underlines market growth. Biopharmaceutical firms increasingly count on genetic tests to determine patient populations for drugs with a precise target, driving demand. The declining price of genetic sequencing—from USD 100 million in 2001 to below USD 600 in 2023—has also stimulated adoption in healthcare environments.
Restraints
-
The market faces significant restraints, primarily due to high costs and reimbursement limitations.
Even with the reduction in sequencing prices, full genetic testing can still cost between USD 1,000 and USD 5,000 and is thus expensive. Insurers only cover genetic tests for a given disease in most cases, and this restricts patient access. Ethical issues and privacy around the storage and sharing of genetic information are also limiting factors. Based on the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH), a shortage of regulated data-sharing policies limits the promise of large-scale genomic studies. Furthermore, there is a shortage of awareness and trained personnel that limits large-scale adoption. Most healthcare professionals are not trained to analyze complex genetic test reports, which causes delays in diagnoses. In developing countries, a shortage of genomic infrastructure and specialized laboratories limits access. Lack of standardized regulatory systems across regions also makes it difficult to expand markets. Though programs such as the EU's Orphan Drug Regulation promote research into rare diseases, the intricate process of regulatory approval for genetic tests postpones commercialization. In addition, high rates of false positives and misdiagnosis caused by inadequate variant databases undermine market credibility. To overcome these constraints, policy changes, improved reimbursement schemes, and investments in genomic training are necessary.
Opportunities
-
The rare disease genetic testing market presents substantial opportunities, particularly in personalized medicine and precision therapeutics.
Technological leaps in gene therapy and CRISPR-based diagnostics are creating new opportunities for precision treatments. The growth of whole genome sequencing (WGS) programs in national healthcare systems, for example, China's 1 Million Genomes Project, offers enormous expansion opportunities. The growing implementation of AI and machine learning in genetics analysis improves diagnosis accuracy, enhancing clinical decision-making. Partnerships between biotechnology companies and genetic testing companies are speeding up rare disease biomarker discovery, hence quicker diagnosis and treatment development. Growth in newborn screening programs, particularly in Latin America and the Asia-Pacific regions, is yet another key growth driver. Growing Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) genetic testing is offering an untapped market segment opportunity, with vendors such as Color Genomics and 23andMe increasing the scope of their rare disease tests. Moreover, telehealth-delivered genetic counseling is enhancing access and overcoming geographical constraints. Greater electronic health record (EHR) integration with genetic databases is simplifying test interpretation and tailored treatment advice. The trend toward universal genomic data-sharing platforms, including the Global Variome Project, seeks to enhance genetic variant interpretation, opening new doors for rare disease diagnosis and drug discovery.
Challenges
-
The market faces several challenges, primarily due to complex regulatory hurdles and data standardization issues.
Unlike other diagnostic tests, genetic testing must adhere to strict regulations such as CLIA, CAP, and IVDR in various markets, which poses challenges to entering global markets. There is no unified classification of genetic variants in databases, causing test interpretation inconsistencies. In the American Journal of Human Genetics study, more than 25% of genetic variants are misclassified, posing a risk of misdiagnosis. Another challenge lies with patient unwillingness due to fears of genetic discrimination despite laws such as the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA). Lack of large amounts of diverse genetic databases leads to diminished diagnostic performance among underrepresented populations. Infrastructural restraints in low-income areas prohibit universal use of genetic testing. Cybersecurity and data privacy are another pressing concern, with over 60 million health records hacked in 2023, raising the risk of genomic data compromise. Furthermore, the very high rate of failure for rare disease drug development, as almost 90% of orphan drug trials fail, undermines investment confidence in genetic diagnostics. These challenges need to be overcome through international regulatory harmonization, enhanced genomic data diversity, strengthened cybersecurity frameworks, and better genetic education programs.
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Segmentation Analysis
By Disease
In 2023, the segment of immunological disorders led the rare disease genetic testing market, with the highest share of 10.5%. This leadership was fueled by the growing incidence of autoimmune and immune deficiency diseases, along with advances in genetic diagnostics enhancing early diagnosis. Government programs and increasing investments in immunogenetics research also helped boost market growth.
Conversely, the endocrine & metabolism diseases category proved to be the fastest-growing segment. The demand was fueled by an elevated number of inherited metabolic disorders, coupled with increased awareness and accessibility of genetic testing. The growth of newborn screening programs for metabolic disease caused the demand for genetic testing in this segment to increase.
By Technology
The Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) segment was the market leader in 2023 with the highest share of 33.9%. NGS was driven by its throughput, cost-effectiveness, and capacity to analyze multiple genetic variations at once. Its uptake was also boosted by the decreasing price of sequencing and advances in bioinformatics for diagnosing rare diseases.
By Specialty
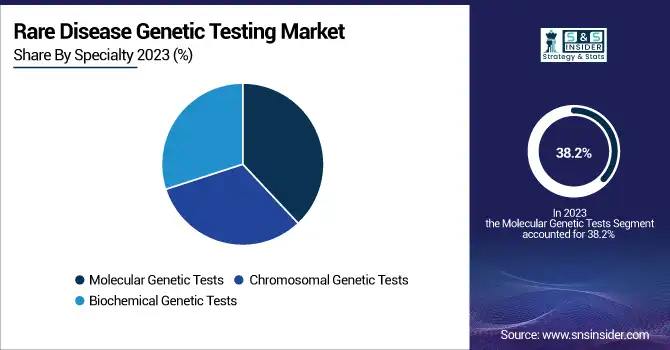
The segment of molecular genetic tests led the rare disease genetic testing market in 2023 with the highest revenue contribution of 38.2%. The leadership of this segment was due to its high precision in detecting single-gene mutations and hereditary disorders. Increasing demand for molecular methods, such as whole exome and whole genome sequencing, also contributed to market share.
By End Use
Among end users, research laboratories & CROs were the dominant market in 2023, with a share of 43.6%. This was mainly because of the growing emphasis on research related to rare diseases, growth in the number of clinical trials, and collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and genetic testing service providers. The need for sophisticated genetic analysis in drug discovery and personalized medicine played a crucial role in dominating this segment.
The diagnostic laboratories category was recognized as the most rapidly growing segment. The growing incorporation of genetic testing within regular clinical diagnostics, along with enhanced access to genetic counseling, fueled this expansion. Increased patient awareness and support for rare disease diagnosis by regulation also played an essential part in widening this segment.
Regional Insights
North America held the largest share in the rare disease genetic testing market in 2023, fueled by sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, high usage of genetic testing, and robust government support. The U.S. dominates the market because of programs like the All of Us Research Program, which seeks to sequence one million genomes for precision medicine. The availability of leading genetic testing firms, such as Invitae, Illumina, and Natera, has also increased market growth. In addition, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Undiagnosed Diseases Network (UDN) are increasing access to genetic diagnostics, speeding up early disease detection.
Europe is next as a leading market because of the EU's Orphan Drug Regulation and high-volume sequencing initiatives such as Genomics England's 100,000 Genomes Project. Germany, France, and the UK are investing in incorporating genomic medicine into national healthcare systems, fueling demand.
The Asia-Pacific region is the most rapidly growing, fueled by growing adoption of genetic testing, expanding healthcare investments, and huge patient bases. China's 1 Million Genomes Project and India's Genome India Initiative are revolutionizing the landscape. Japan's USD 1.3 billion investment in rare disease research has further fueled growth. With growing newborn screening programs and increasing awareness of genetic disorders, the Asia-Pacific market is likely to experience the highest growth rate in the coming years.
Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market Key Players
-
Quest Diagnostics Inc. – Neurome, GeneDx, ClariTest
-
Centogene N.V. – CentoGenome, CentoXome, CentoArray, CentoMetabolic
-
Invitae Corp. – Invitae Rare Disorders Panel, Invitae Comprehensive Neuromuscular Disorders Panel
-
3billion, Inc. – Rare Disease Genetic Testing Panels, Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
-
Arup Laboratories – ARUP Exome Test, Targeted NGS Panels for Rare Diseases
-
Eurofins Scientific – NMD Panel, Exome NGS for Rare Diseases
-
Strand Life Sciences – Strand RareGen, Whole Genome Sequencing for Rare Diseases
-
Ambry Genetics – Ambry Exome, Rare Disease NGS Panels
-
PerkinElmer, Inc. – PerkinElmer Genomics, Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
-
Realm IDX, Inc. – Rare Disease Exome Testing, Genomic Sequencing Panels
-
Macrogen, Inc. – Rare Disease NGS Panels, Whole Genome Sequencing
-
Baylor Genetics – Baylor Exome, Rare Disease Gene Panels
-
Color Genomics, Inc. – Color Genetic Risk Panels, Rare Disease Testing
-
Health Network Laboratories – HNL Genetic Testing Panels
Recent Developments in the Rare Disease Genetic Testing Market
-
Feb 2025: Strand Life Sciences, a subsidiary of Reliance Industries, launched the StrandOmics Portal, a digital platform aimed at enhancing rare disease diagnosis. The company also announced affordable genetic testing to improve accessibility and precision in rare disease detection.
-
Jan 2025: The Centre for Genetic Disorders at Banaras Hindu University (BHU) introduced new initiatives to enhance the research and diagnosis of genetic diseases in Varanasi. The development aims to improve access to advanced genetic testing and counseling.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 1.05 billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 3.79 billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 15.36% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Disease [Neurological Disorders, Immunological Disorders, Hematology Diseases, Endocrine & Metabolism Diseases, Cancer, Musculoskeletal Disorders, Cardiovascular Disorders, Dermatology Diseases, Other Rare Diseases] • By Technology [Next-generation sequencing, Array Technology, PCR-based Testing, FISH, Sanger Sequencing, Karyotyping] • By Specialty [Molecular Genetic Tests, Chromosomal Genetic Tests, Biochemical Genetic Tests] • By End Use [Research Laboratories & CROs, Hospitals & Clinics, Diagnostic Laboratories] |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Quest Diagnostics Inc., Centogene N.V., Invitae Corp., 3billion Inc., Arup Laboratories, Eurofins Scientific, Strand Life Sciences, Ambry Genetics, PerkinElmer Inc., Realm IDX Inc., Macrogen Inc., Baylor Genetics, Color Genomics Inc., Health Network Laboratories. |

