Thin Film Photovoltaics Market Size & Trends:
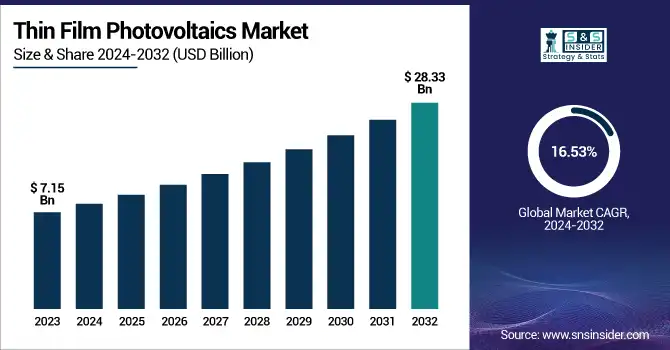
The Thin Film Photovoltaics Market was valued at 7.15 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 28.33 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 16.53 % from 2024 to 2032. Driven by growing investments in renewable energy infrastructure and favorable government incentives. This growth is underpinned by key performance metrics such as high material utilization rates, with thin film technologies using significantly less raw material than traditional silicon-based panels.
To Get more information on Thin Film Photovoltaics Market - Request Free Sample Report
In the United States, the market was valued at USD 2.0 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 6.62 billion by 2032 WITH CAGR 14.20%. Furthermore, the market benefits from a low efficiency degradation rate averaging around 0.4% annually which ensures long-term performance stability. Installed capacity trends show a steady increase in global deployments, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America, where demand for lightweight, flexible solar modules is surging. Additionally, thin film solar modules offer faster energy payback and reduced carbon footprint, enhancing their appeal in utility-scale and commercial applications. These factors, combined with technological advancements and strong policy support, are expected to sustain market momentum through 2032.
Thin Film Photovoltaics Market Dynamics:
U.S. Tax Breaks and Tariffs Drive Growth in Thin Film Photovoltaics Market
The recent extension of the U.S. CHIPS Act's 25% investment tax credit to solar ingot and wafer manufacturing is set to significantly influence the thin film photovoltaics (TFPV) market by redirecting capital toward domestic production. Thin film technologies, which often rely on cadmium telluride or CIGS rather than traditional crystalline silicon, stand to benefit from increased incentives favoring vertically integrated operations. As the U.S. Treasury clarified that solar ingot and wafer manufacturing qualifies for the same tax treatment as semiconductors, companies are now strategically realigning investments to take full advantage of the credit.
This shift supports American-made photovoltaic technologies, potentially giving an edge to established TFPV manufacturers that already operate within U.S. borders. In addition to tax incentives, new tariff policies such as proposed 100% tariffs on imported semiconductors and electronics are expected to make foreign solar equipment significantly more expensive. This could further accelerate reshoring of production, benefiting TFPV firms that are less reliant on foreign supply chains. With over USD 52.7 billion allocated under the CHIPS Act, including USD 39 billion for manufacturing and USD 13.2 billion for R&D, the cumulative impact of financial incentives and protectionist trade policies could increase U.S. thin film solar production capacity by more than 25% by 2027.
Drivers:
-
Cost-Efficiency and Sustainability of Thin Film Solar Technology
Thin film solar modules offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional silicon-based panels, benefiting from innovations in perovskite and CIGS technologies that reduce production costs while improving efficiency. These films, especially perovskites, use abundant, low-cost materials and require less material overall, leading to reduced waste and environmental impact. Studies by Columbia University and NREL highlight that perovskite thin films can significantly lower energy use in manufacturing, reducing cumulative energy consumption by over 80%. Thin films also solve the fragility issues of silicon, which is prone to micro cracks, with First Solar offering guarantees for crack resistance. Although thin film solar cells typically have lower efficiency (7-22%) than silicon, advancements like Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) thin films can achieve higher efficiency, further driving their appeal in the market.
Restraints:
-
High Installation Complexity Limits Thin Film PV Deployment
Thin film panels often require larger surface areas to match the energy output of traditional silicon modules, leading to increased land and structural requirements. Additionally, their lightweight and flexible nature demands specialized mounting systems, intricate wiring setups, and custom installation equipment, all of which drive up labor and infrastructure expenses. These factors can significantly reduce the cost advantages gained during production. For large-scale or utility projects where efficient space usage and upfront investment are critical, these elevated installation requirements present a financial hurdle. Consequently, while thin film photovoltaics offer technological promise, their cost-intensive deployment processes remain a major barrier, especially in markets where silicon-based alternatives continue to dominate due to their simpler, more standardized installation needs.
Opportunities:
-
Perovskite Power Surge Unlocking the Next Frontier in Thin Film Photovoltaics
Recent advancements in perovskite solar technology are unlocking significant opportunities in the thin film photovoltaics market. Breakthroughs such as Oxford PV and Trina Solar’s patent licensing for perovskite-silicon tandem cells signal commercial viability, while recent lab achievements show record efficiencies of 24.6% and flexible designs combining perovskite with CIGS materials. These innovations not only enhance power output but also improve durability, as shown by protective films extending operational life under extreme heat and humidity beyond 1,000 hours. The increased resilience and performance make thin film solar cells more suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential rooftops to flexible electronics. These developments are crucial for expanding the market’s reach, especially in sectors that demand lightweight, high-efficiency, and scalable solar solutions, thereby positioning perovskite-enhanced thin films as a transformative force in the global transition to renewable energy.
Challenges:
-
Durability and Degradation Concerns in Thin Film Photovoltaic Technologies
Thin film photovoltaics, including organic photovoltaics and perovskites, face significant challenges regarding long-term durability and degradation. Unlike traditional silicon solar cells, thin film materials are highly sensitive to environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation. Over time, these factors contribute to performance degradation, causing a decrease in the efficiency and lifespan of the panels. For instance, perovskite-based cells are prone to instability when exposed to moisture or extreme temperatures, hindering their reliability in outdoor conditions. While advancements like Ubiquity Solar's acquisition of Alta Devices’ GaAs thin-film cells show promise, particularly for lightweight applications such as drones and satellites, ongoing improvements are needed in material durability. Understanding these degradation mechanisms and enhancing the performance of thin film materials under real-world conditions is crucial for the scalability of this technology in commercial markets.
Thin Film Photovoltaics Market Segment Analysis:
By Material
Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) thin film solar technology continues to lead the market, contributing approximately 28% of the global revenue in 2023. This dominance is due to its cost-effectiveness, relatively high efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity, and the availability of low-cost manufacturing processes. CdTe modules are increasingly popular in large-scale utility projects because of their lower upfront costs compared to silicon-based panels. Despite challenges with efficiency compared to other technologies, CdTe has been a preferred choice for affordable solar power generation, particularly in regions where cost sensitivity is a major factor.
The Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) segment is expected to experience the fastest growth in the thin film photovoltaics market from 2024 to 2032. This is driven by its higher efficiency compared to other thin-film technologies, such as CdTe, as well as its ability to be used in flexible and lightweight applications. CIGS solar cells can be applied to a wide range of surfaces from building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), building-integrated photovoltaics to bendy customer electronics. Its versatility, combined with continued advancements in efficiency and decreasing costs, are helping make CIGS a desirable option for commercial and residential installations. Ongoing research and development activities for improving the stability of CIGS cells and making them more scalable are further encouraging their adoption, in turn creating a significant opportunity of growth for the segment during the upcoming decade.
By Technology
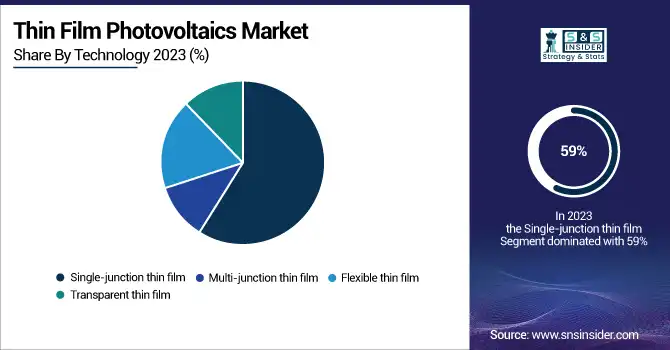
The single-junction thin film segment is projected to dominate the largest share of revenue in the thin film photovoltaics market, accounting for around 59% in 2023. This dominance is primarily due to the established commercial success and cost-effectiveness of single-junction thin film solar cells, particularly those made from amorphous silicon (a-Si) and cadmium telluride (CdTe). These cells are widely used in both residential and commercial applications because of their lower manufacturing costs, relatively simple production processes, and good performance in low-light conditions. As a result, single-junction thin film solar cells remain the preferred option for many large-scale solar installations. Ongoing technological advancements to enhance efficiency and durability are expected to further solidify the segment's market leadership over the coming years, ensuring its continued growth and widespread adoption.
The transparent thin film segment is expected to experience rapid growth during the forecast period from 2024 to 2032. This growth is driven by advancements in materials like transparent conductive oxides and perovskite solar cells, which allow for high optical transparency without sacrificing efficiency. Transparent thin film solar panels can be integrated into windows, facades, and other architectural elements, offering new opportunities in building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). The demand for aesthetically pleasing and energy-efficient solutions in urban environments is fueling interest in transparent thin films for both residential and commercial buildings. Additionally, their potential in emerging applications like solar-powered electronics and wearables further expands their market potential. As technology improves, the cost-effectiveness and performance of transparent thin films will continue to attract investment and drive market growth.
By Installation Type
The ground-mounted segment dominated the thin film photovoltaics market, accounting for approximately 54% of the revenue in 2023. This dominance is attributed to the large-scale nature of ground-mounted installations, which are typically more efficient for solar power generation due to their ability to capture maximum sunlight without space limitations. These systems are commonly used in utility-scale solar farms, where space is abundant, and large arrays of panels can be deployed. Ground-mounted thin film solar panels benefit from their flexibility in design and installation, offering cost-effective solutions for high-energy production in rural and open areas. With the increasing demand for renewable energy and the growing shift towards sustainable power generation, ground-mounted thin film systems are expected to remain a key segment in the market, driving further adoption globally.
The building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) segment is the fastest-growing within the thin film photovoltaics market from 2024 to 2032. BIPV systems integrate solar technology directly into the building’s architecture, such as in windows, roofs, and facades, providing an aesthetically pleasing and efficient alternative to traditional solar panels. As the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable construction grows, BIPV is becoming increasingly popular in both residential and commercial buildings. The growing use of sustainable building materials, along with the development of thin film technologies, is anticipated to lead to an increase in BIPV applications and will be a significant factor in opening up its market in the solar energy sector during the forecast period.
By Application
The utility-scale power generation segment dominates the thin film photovoltaics market, accounting for around 61% of the revenue share in 2023. This segment involves large-scale solar power plants that generate significant amounts of electricity, typically feeding into the grid. Thin film technologies like CdTe and CIGS are particularly suited for utility-scale projects due to their lower manufacturing costs and ability to be deployed in large, open areas. The growing demand for renewable energy, coupled with government incentives and policies supporting green energy, has significantly boosted the adoption of utility-scale thin film solar installations. These projects offer the potential for substantial power generation and are expected to continue driving growth in the thin film photovoltaics market, especially as the world shifts toward more sustainable energy solutions.
The Building-integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) segment is expected to experience the fastest growth from 2024 to 2032. BIPV involves integrating photovoltaic panels into the building structure itself, such as roofs, windows, or facades, providing an aesthetic and efficient energy solution. This segment is gaining traction due to the increasing demand for energy-efficient buildings and the push for sustainability in the construction industry. BIPV systems not only help reduce energy consumption but also contribute to a building's overall design, making them an attractive option for architects and developers. With rising awareness of renewable energy and supportive government incentives, BIPV is expected to see rapid growth, especially in residential, commercial, and urban developments, driving the demand for thin film solar technologies.
By End User
The agricultural segment dominated the thin film photovoltaics market, accounting for approximately 39% of the revenue in 2023. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of solar energy solutions in agricultural settings, such as solar-powered irrigation systems, greenhouse energy solutions, and solar installations for rural farms. Thin film solar panels are particularly well-suited for agriculture due to their flexibility, lightweight nature, and ability to be integrated into various structures without taking up significant land area. These systems provide reliable and sustainable energy sources for farming operations, helping to reduce energy costs and improve operational efficiency. As the agricultural sector seeks more sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, the demand for thin film photovoltaics in this industry is expected to continue to rise.
The commercial and industrial segment is expected to experience significant growth over the forecast period from 2024 to 2032. Commercial buildings, factories, and industrial facilities are demanding sustainable energy solutions to propel this expansion. Thin film photovoltaics are cheaper, flexible solar power solutions helping businesses lower energy bills and greenhouse gas emissions. The need for thin film solar panels is likely to increase as enterprises pursue sustainability goals and profit from government incentives for adopting renewable energy. Additionally, advancements in technology and improved efficiency will further support the expansion of this segment in the coming years.
Thin Film Photovoltaics Market Regional Overview:
The North America segment dominated the market with a substantial share of around 41% in 2023. This dominance is attributed to strong government support, including incentives and policies promoting renewable energy adoption, particularly solar power. The region's increasing focus on sustainable energy solutions and the growing demand for residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar projects contribute to its leading market position. Additionally, advancements in thin film photovoltaic technology, along with the rising awareness of environmental concerns, are driving the adoption of solar energy in North America, further boosting the market's growth.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the fastest growth in the thin film photovoltaics market from 2024 to 2032. This increasing demand for renewable energy has contributed to the energized growth of the solar energy market, especially in countries such as China, India, and Japan. The rapid expansion is driven by the large-scale adoption of solar power, favorable policies by the government and financial incentives, and investments in infrastructure in the region. Moreover, the reduction of the cost of thin film solar to date, coupled with greater efficiency, is enhancing their suitability for use in residential and commercial applications. In addition, rising focus on sustainable energy sources, energy security as well as environmental concerns augments the adoption of thin film photovoltaics in Asia Pacific.

Get Customized Report as per Your Business Requirement - Enquiry Now
Major Players in Thin Film Photovoltaics Market along with their Products:
-
First Solar (USA): CdTe modules
-
Solar Frontier (Japan): CIS modules
-
Hanergy Thin Film Power Group (China): Flexible CIGS panels
-
MiaSolé (USA): CIGS technology
-
Ascent Solar Technologies (USA): Lightweight flexible CIGS panels
-
Solibro GmbH (Germany): CIGS modules
-
Global Solar Energy (USA): CIGS-based thin film solar panels
-
SunPower Corporation (USA): High-efficiency silicon solar panels
-
Tata Power Solar (India): Thin-film PV modules
-
Solexel (USA): High-efficiency silicon-based thin-film solar cells
-
Pristine Sun (USA): Thin-film solar installations
-
Nanosolar (USA): CIGS-based thin-film technology
-
GCL-Poly Energy (China): CIGS thin-film solutions
-
SolarWorld (Germany): High-efficiency thin-film panels
-
Sharp Solar (Japan): Amorphous silicon-based thin-film solar cells
List of companies that provide raw materials and components for the Thin Film Photovoltaics Market:
-
3M (USA)
-
Dupont (USA)
-
First Solar (USA)
-
AGC Solar (Japan)
-
Hanergy (China)
-
SolarWorld (Germany)
-
MiaSolé (USA)
-
Solibro GmbH (Germany)
-
Applied Materials (USA)
-
Shenzhen Sungrow Power Supply Co. Ltd. (China)
-
BASF (Germany)
-
Trina Solar (China)
-
Canadian Solar (Canada)
-
Dow Corning (USA)
-
Jinko Solar (China)
Recent Development:
-
On July 22, 2024, First Solar has opened the Jim Nolan Center for Solar Innovation in Ohio, focusing on thin film and tandem PV module development with an efficiency of 23.1% for cadmium telluride cells. This is part of a USD 500 million investment in R&D to maintain U.S. leadership in solar technology.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 7.15 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 28.33 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 16.53% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Material (Cadmium telluride (CDTE), Amorphous silicon (A-SI), Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), Perovskite, Organic PV, Copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS), Quantum dot thin film solar cells, All-silicon tandem) • By Technology(Single-junction thin film, Multi-junction thin film, Flexible thin film, Transparent thin film) • By Installation Type(Ground-mounted, Rooftop, Floating solar, Building-integrated (BIPV)) • By Application(Utility-scale power generation, Building-integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV), Wearable devices, Others) • By End User (Agricultural, Automotive, Commercial & Industrial, Consumer electronics, Residential, Utility, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia-Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | First Solar (USA), Solar Frontier (Japan), Hanergy Thin Film Power Group (China), MiaSolé (USA), Ascent Solar Technologies (USA), Solibro GmbH (Germany), Global Solar Energy (USA), SunPower Corporation (USA), Tata Power Solar (India), Solexel (USA), Pristine Sun (USA), Nanosolar (USA), GCL-Poly Energy (China), SolarWorld (Germany), and Sharp Solar (Japan) are key players in the thin film photovoltaics market. |

