Microbiome Therapeutics Market Size Analysis:
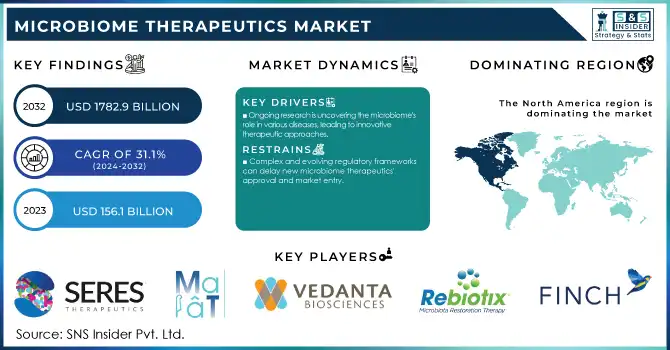
The Microbiome Therapeutics Market size was valued at USD 156.1 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 1782.9 million by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 31.1% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
To Get More Information on Microbiome Therapeutics Market - Request Sample Report
Growing research and development activities, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and rising awareness regarding the significance of gut health are some of the major factors impelling the microbiome therapeutics market growth. U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), which has spent more than $1.7 billion on the Human Microbiome Project alone since the initiative began in 2007. This project has significantly broadened knowledge of the human microbiome and its potential therapeutic application. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 3 million adults in the United States were diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in 2015, highlighting the growing need for effective treatments. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is also aware of the potential of microbiome-based therapies and in 2018 a new working group was established at EMA on microbiome-based medicinal products. Boosted by this regulatory backing, pharmaceutical companies have begun to invest in microbiome research, and the number of clinical trials sharing microbiome-based therapies has grown 70% from 2019 to 2023, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine. Interest in microbiome-based therapeutics has been accelerated even more by the COVID-19 pandemic where multiple studies have explored the role of the gut microbiome in severity and recovery from disease. Recently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has become more supportive of microbiome-targeted therapies as highlighted by the Breakthrough Therapy designation awarded to several candidates in recent years. It is this regulatory support, alongside progress in sequencing technologies and bioinformatics, that allows for the expanding detail with which researchers can now characterize the complex interplay between the microbiome and human health, which is beginning to offer a path for more precise and effective therapies.
The growth of the microbiome therapeutics market is fueled by supportive government programs and research and the wide acceptance of microbiome therapeutics as a viable treatment option for several diseases. Governments across the globe are heavily investing in the microbiome research sector to capitalize on its promise in the realm of human health. In 2023 the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) released a new strategic plan and investment of more than $200 million to accelerate microbiome research to understand how microbial communities over these diseases, diabetes, obesity, and autoimmune disorders among others. In addition, Horizon Europe, which is the EU's research and innovation program, is still funding microbiome-related research such as its €60 million funded Microbiome in Health and Disease initiative for therapeutic applications. Such developments highlight the growing impact of the microbiome on modern medicine.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Ongoing research is uncovering the microbiome's role in various diseases, leading to innovative therapeutic approaches.
-
A rise in gastrointestinal diseases is driving demand for microbiome-based treatments.
-
Advancements in microbiome sequencing and AI-driven technologies are enhancing the development of personalized therapies.
-
An increase in startups and small to medium-sized enterprises is fostering innovation and competition in the microbiome therapeutics sector.
Key factors driving the growth of the microbiome therapeutics market include advances in research related to microbiomes. In recent years, the understanding of the human microbiome's role in health and disease has grown exponentially. Research has indicated that the microbiome is essential for immune system regulation, digestive processes, and even the health of the brain. These findings unlocked remarkable prospects for drug development targeting the human microbiome directly. As noted in a 2024 report from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), more than 80% of diseases may have a microbial element, such as gastrointestinal disease, autoimmune disease, and neural disease. This increasing volume of work is one of the motivations for new microbiome-based treatments.
Companies such as Seres Therapeutics are developing microbiome-targeted therapies for conditions such as Clostridium difficile infection, which is known for causing debilitating gastrointestinal symptoms. With Phase 3 results for their lead product SER-109 indicating a potential breakthrough for microbiome-based therapies for complex diseases, there is a lot of excitement in the use of this technology to manufacture novel therapeutics. In addition, recent developments in microbiome sequencing technologies, particularly 16S rRNA gene sequencing, have enabled the identification of microbial consortia associated with diseases, which further fuel the development of microbiome therapeutics. These research advances are anticipated to continue translating into a robust pipeline of microbiome-based therapeutics, which will not only drive precision medicine but ultimately play a role in the overall healthcare ecosystem.
Restraints
-
The substantial investment required for developing and commercializing microbiome-based drugs poses a significant challenge.
-
Complex and evolving regulatory frameworks can delay new microbiome therapeutics' approval and market entry.
-
A lack of comprehensive knowledge about how microbiome alterations affect various diseases hinders the development of effective therapies.
The microbiome therapeutics market has a few restraints, one being the regulatory challenges. The development and commercialization of microbiome-based therapies face complex regulatory frameworks. While regulatory bodies have extensive guidance around the drug approval process, major authorities such as the FDA and EMA have very defined guidance around what constitutes a drug in those jurisdictions, leading to uncertainty over the microbiome therapeutics category in a relatively new and less defined category. Since these therapies are generally based on live microorganisms or complex biological systems, their safety and efficacy require detailed evaluations.
In addition, the regulatory pathways for microbiome-based products are still developing and are not necessarily consistent across regions. Some microbiome treatments may be fast-tracked in one country while another will never allow the same product on the market because of concerns about long-term safety and efficacy requirements. Such inconsistency can slow down the approval process, raise costs, and deter investment in the industry. And the absence of coherent and uniform regulatory guidance around the world makes the global deployment of such exciting therapies more complex.
Microbiome Therapeutics Market Segmentation Analysis
By Type
In 2023, fecal microbiota therapy (FMT) held the largest share of 91% of the microbiome therapeutics market. This large market share is due to the efficiency of FMT in treating repeated Clostridioides difficile infections (rCDI) and its applications in other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. This advancement has historically led to clinical adoption and research of FMT, recognized as an investigational new drug by the U.S. FDA for rCDI treatment. The CDC estimates C. difficile causes 500,000 infections in the US annually, with roughly 15-30% of patients experiencing recurrent infection (the same infection returning), leading to the interest in using FMT to treat this infection. The success rate of FMT in treating rCDI is reported to be over 80%, significantly higher than traditional antibiotic therapies. Due to this high efficacy, it has been recommended in clinical guidelines as reported by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America 2021. Additionally, other studies are looking into the effectiveness of FMT for ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and even neurological disorders. The use of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is also substantiated by a plethora of clinical trials funded by NIAID exploring its use in multiple indications which have bolstered the position of this therapy within the market. Additionally, the standardization of FMT procedures and the availability of encapsulated formulations have made it more accessible and acceptable among patients and healthcare providers, further driving its market share.
By Application
In 2023, the Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) segment held a significant share of the market. This has been driven by the increasing incidence of IBD globally as well as the awareness of the role of the gut microbiome in its pathogenesis. In the USA, the number of adults with IBD appeared to rise from 2 million in 1999 to 3 million in 2015 according to CDC, which is a 50% increase. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) represents an economic burden, with annual direct healthcare costs exceeding $6.3 billion in the US alone. To unravel this complex disease and develop new treatments, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) spends more than $300 million each year on IBD research. Previous studies demonstrated that gut microbiota compositions in IBD patients were different from healthy controls, which suggested a target for the treatment. Several microbiome-based therapies have been approved by the FDA for IBD, notably probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation for some indications. The promising results from clinical trials exploring microbiome-based neutral and supplementary therapies for IBD, including up to 30% of adults and children in some studies entering remission after receiving native microbiome therapy for ulcerative colitis show a new potential for the treatment of function and inflammatory-associated disorders. Microbiome-based therapies have also been included in the European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) treatment guidelines for the management of IBD.
Regional Analysis
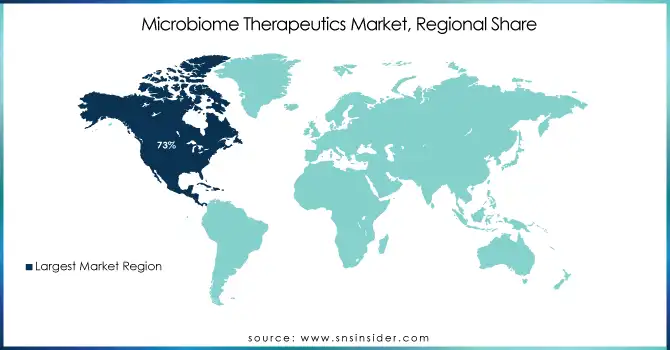
In 2023, North America held the largest share of the microbiome therapeutics market, accounting for around 73% of the global share of the microbiome therapeutics market. The region's market leadership is the product of a well-established healthcare infrastructure, significant research and development investments, and a favourable regulatory environment. In particular, the U.S. has led the development and commercialization of microbiomes. In 2007, the NIH established a foundation for microbiome research in the U.S. with the Human Microbiome Project. Publications originated from North American institutions increased exponentially from fewer than 100 in 2000 to greater than 5000 in 2023, according to the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The FDA has also played a crucial role in fostering innovation in this field, establishing a regulatory framework for microbiome-based therapies and granting fast-track designations to several promising candidates.
The Asia-Pacific region is estimated to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The reason for this quick growth is because of the increase in healthcare spending, increased knowledge about gut health, and the increase in research activities in nations such as China, Japan, and South Korea. Some of these include the China Microbiome project which was initiated by the Chinese government in 2019 with a funding of $400 million to study the microbiome of the Chinese population. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare has also been actively supporting microbiome research, allocating significant funding to projects exploring the relationship between the microbiome and various diseases
Do You Need any Customization Research on Microbiome Therapeutics Market - Enquire Now
Recent developments
-
In July of 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved SER-109, the first-ever microbiome-based therapy for the prevention of recurrent C. difficile infection. It should also open the doors to other therapies based on the microbiome in the future.
Key Microbiome Therapeutics Companies
-
Seres Therapeutics (Vowst, SER-109)
-
MaaT Pharma (MaaT013, MaaT033)
-
Vedanta Biosciences (VE303, VE202)
-
Rebiotix Inc. (RBX2660, RBX7455)
-
Finch Therapeutics (CP101, FIN-211)
-
Axial Biotherapeutics (AB-2004, AB-1001)
-
Enterome (EO2401, EO2463)
-
4D Pharma (MRx0518, Blautix)
-
Synlogic (SYNB1618, SYNB1934)
-
Evelo Biosciences (EDP1815, EDP1503)
-
Intralytix (EcoActive, ShigActive)
-
AOBiome (B244, Mother Dirt AO+ Mist)
-
Seed Health (DS-01, PDS-08)
-
OpenBiome (FMT preparations, Microbiome-derived therapies)
-
BiomeSense (GutProbe, Microbiome Monitoring Platform)
-
Freya Biosciences (Live Biotherapeutic Products, Microbiome Modulators)
-
Genetic Analysis (GA-map Dysbiosis Test, GA-map COVID-19 Fecal Test)
-
Siolta Therapeutics (STMC-103H, STMC-203H)
-
Biose Industrie (Bacilio®, Lactopia®)
-
Infant Bacterial Therapeutics (IBP-9414, IBP-1016)
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 156.1 Million |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 1782.9 Million |
| CAGR | CAGR of 31.1% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Type (FMT, Microbiome Drugs) • By Application (C. difficile, Crohn’s disease, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Diabetes, Others) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Seres Therapeutics, MaaT Pharma, Vedanta Biosciences, Rebiotix Inc., Finch Therapeutics, Axial Biotherapeutics, Enterome, 4D Pharma, Synlogic, Evelo Biosciences, Intralytix, AOBiome, Seed Health, OpenBiome, BiomeSense, Freya Biosciences, Genetic Analysis, Siolta Therapeutics, Biose Industrie, Infant Bacterial Therapeutics |
| Key Drivers | • Ongoing research is uncovering the microbiome's role in various diseases, leading to innovative therapeutic approaches. • A rise in gastrointestinal diseases is driving demand for microbiome-based treatments. • Advancements in microbiome sequencing and AI-driven technologies are enhancing the development of personalized therapies. |
| Restraints | • The substantial investment required for developing and commercializing microbiome-based drugs poses a significant challenge. • Complex and evolving regulatory frameworks can delay new microbiome therapeutics' approval and market entry. |

