5G Satellite Communication Market Report Scope & Overview:
Get More Information on 5G Satellite Communication Market - Request Sample Report
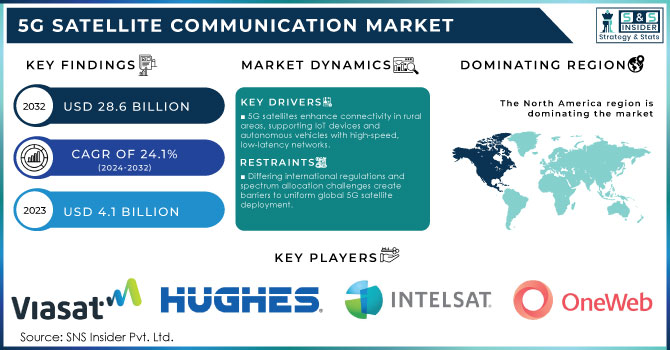
The 5G Satellite Communication Market Size was valued at USD 4.1 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 28.6 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 24.1% by 2024-2032.
The 5G satellite communication market is being driven by the rapid expansion of 5G networks, coupled with government efforts to bridge the digital divide and enhance communication infrastructure. The latest statistics published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) show that subscriptions to 5G technology around the world are projected to reach more than 2.7 billion in 2025. Further, different government bodies have considered 5G-capable satellite communication systems as one of the salient technologies in their deployment agenda. The ESA, for example, has made sizeable investments in its 5G satellite integration programs over USD 216.5 million in those projects in 2023 alone to help provide seamless connectivity within rural and remote areas. Traditional 5G infrastructure is challenging to deploy in hard-to-reach areas due to the high costs of fiber-optic networks. 5G satellite communication provides a viable solution, delivering high-speed internet without the need for extensive terrestrial infrastructure. This demand is particularly strong in regions like Africa and parts of Asia, where terrestrial broadband connectivity is limited.
In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has allocated USD 9 billion for the 5G Fund for Rural America, part of which is directed toward satellite-based solutions. The rise of new technological terrains like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and augmented reality requires ultra-low latency communication. Especially in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), 5G satellites are in the right place at the right time to fulfill these demands, offering truly real-time reliable communication for such contact-critical applications. This growing demand for next-generation technologies is accelerating the deployment of 5G satellite systems globally. Moreover, governments across Asia-Pacific, such as China, have launched ambitious projects to deploy 5G satellite constellations, with the country announcing in early 2024 its plan to launch over 10,000 5G-enabled satellites by 2030. These efforts are collectively enhancing the market potential for 5G satellite communication, which is projected to experience significant growth through the forecast period.
5G Satellite Communication Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
5G satellites offer widespread connectivity in rural and underserved regions, enhancing communication access. Increased reliance on IoT devices and autonomous vehicles requires high-speed, low-latency networks that 5G satellites provide.
-
5G satellites complement terrestrial infrastructure, ensuring seamless communication even in challenging environments. The allocation of higher spectrum bands (e.g., mmWave) for 5G satellite networks boosts data transmission speeds and network capacity.
One significant driver for the 5G satellite communication market is the global coverage for remote areas. Where traditional networks typically fail to fill essential coverage zones in rural, remote, or underserved regions, 5G satellite communication closes the gap and ensures wide-area seamless connectivity. This latter aspect is especially important for sectors including agriculture, mining, oil and gas, and even emergency services where they are often mobile operating in environments with little or no cellular infrastructure. An example would be to have satellite-enabled 5G networks maintain constant communications during precision farming operations in remote agricultural lands, thus increasing productivity and efficiency. In emergency response scenarios, first responders can rely on uninterrupted communication via 5G satellites in disaster-stricken areas where terrestrial infrastructure may be damaged or unavailable.
According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), nearly 37% of the global population still lacks access to reliable internet, especially those in rural areas. 5G satellite technology makes the possibility of linking these areas a reality, which further facilitates global economic expansion and digital accessibility. Additionally, partnerships between companies such as SpaceX’s Starlink and T-Mobile’s Project Genesis showcase efforts to integrate satellite communication with mobile services, targeting remote regions and enhancing global connectivity. The growing applications of 5G satellite communication These developments not only supply underserved regions with internet access but also open spaces for essential IoT-based services, such as autonomous drones, connected sensors, and remote monitoring systems in isolated locations, further fueling demand for 5G satellite communication.
Restraints
-
The cost of launching and maintaining satellite networks remains prohibitively expensive, limiting the entry of smaller players. Harmonizing satellite and terrestrial network technologies presents complex technical hurdles that delay widespread adoption.
-
Differing international regulations and spectrum allocation challenges create barriers to uniform global 5G satellite deployment.
The major factors restraining the growth of the 5G satellite communication market are regulatory and spectrum management issues. The allocation of spectrum for satellite communication varies significantly across countries, making global standardization difficult. The absence of unified standards has resulted in multifaceted challenges for the global deployment of 5G satellite services. National regulations vary widely and are often accompanied by complex licensing regimes and restrictions on spectrum use, posing additional challenges for satellite operators.
Moreover, the competition for spectrum between terrestrial and satellite operators may also slow down the regulatory process. Satellite communication needs certain dedicated frequency bands to operate properly for 5G networks, and these bands very often overlap with Earth-bound communications. Interference risks, which undermine the quality of service can increase in this context even more so since there are no clear and globally accepted guidelines for spectrum sharing. This regulatory complexity not only slows down the deployment of 5G satellite networks but also raises the cost of compliance for companies, creating further obstacles to market expansion.
5G Satellite Communication Market Segmentation Overview
By Satellite Solution Type
The backhaul and tower feed satellite solution type dominated the global 5G satellite communication market owing to its crucial role in enabling the growth of 5G networks in remote as well as unserved areas. Satellite backhaul solutions deliver the bandwidth and structural support needed to expand 5G coverage into regions where terrestrial infrastructure is insufficient or prohibitively expensive to build. The government push for rural broadband and backhaul solutions, particularly in the United States, where $65 billion from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law is allocated for nationwide broadband expansion, has significantly accelerated the demand for satellite-based backhaul solutions. This is especially relevant for nations such as India, where the government has launched its "Digital India" campaign that focuses on an initiative of connecting remote backhaul using satellite technologies. The backhaul solution’s ability to ensure high-speed data transmission and its scalability for 5G towers make it the most sought-after solution type, especially in regions lacking fiber-optic connectivity.
By Orbit
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites dominated the market as they are closer to the surface level, provide less latency, and can effectively transmit data faster. Low Earth Objects (LEOs) generally produce shorter communication connections as they orbit between 500 km to 2,000 km above the surface of the Earth, which are particularly necessary for providing 5G. There have been strong government initiatives to start supporting LEO satellites. The U.S. government identified space communication infrastructure as a critical need in 2023 through NASA's Artemis Accords with an emphasis on low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations. Likewise, the European Union Horizon Europe Program pledged USD 1.3 billion in 2023 for research and development in space-based communication with an emphasis on LEO satellite technologies. The low latency benefit from LEO satellites is crucial for providing high-quality 5G services, especially on the application side that needs real-time communication, including autonomous vehicles and smart cities. LEO satellite networks are likely to become a hotspot for investments over well-established conventional communication systems with high data transfer capacity and 5G network reliability.
By End-use
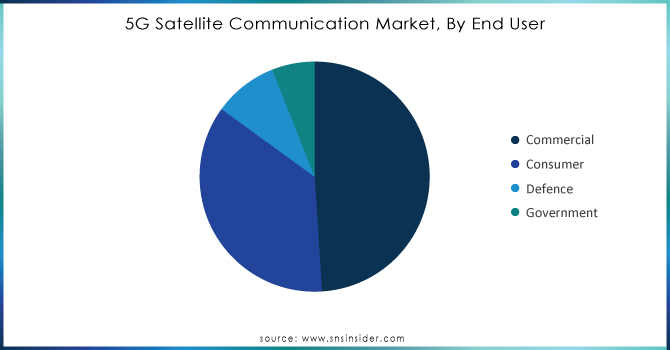
The commercial segment dominated the market with the highest revenue share 49% in 2023, due to growing demand from sectors such as transportation, media entertainment, and manufacturing among others. The commercial segment accounted for 45% of the market share. The increase in demand for 5G services delivered via satellites comes from industries looking to leverage the high-speed low-latency connectivity that 5G satellites enable. For instance, the global transportation industry has begun utilizing 5G satellite communication for fleet management and logistics tracking, especially in remote areas where terrestrial networks are absent. Another driving factor is the growing IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things), where manufacturers are supporting satellite communication for M2M (machine-to-machine) communication of things and remote monitoring.
Need Any Customization Research On 5G Satellite Communication Market - Inquiry Now
Regional Insights
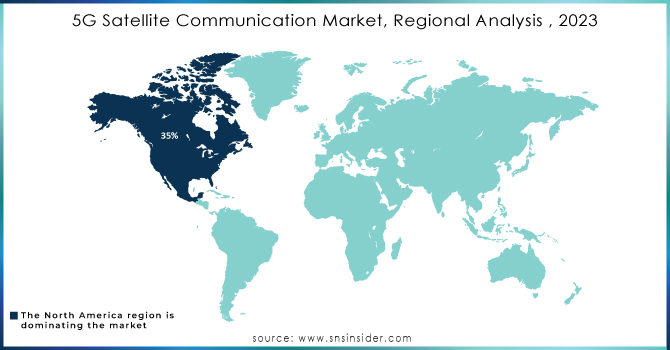
The North American region dominated the global 5G satellite communication market with a 35% market share in 2023, this is largely because of the large investments in satellite infrastructure and the rollout of 5G networks in both rural and urban areas of the USA and Canada. The U.S. government’s initiatives, such as the SpaceX Starlink program, which received approvals to expand its satellite constellation in early 2023, have further bolstered the region’s leadership in the market.
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest growth rate during the forecast period. The fast growth in the region is also driven by the expansion of its satellite communication infrastructure where coverage to remote areas is planned under the "Digital India" mission. This swift pace of investment in satellite technology places Asia-Pacific into a driving seat in 5G satellite communication globally.
Recent Developments
-
The European Space Agency (ESA) joined forces with SES S.A. in April 2024 to use its new SES-20 and SES-21 satellites for provisioning 5G backhaul services throughout Europe. The project will support satellite-enabled 5G networks and expand connectivity in unserved areas of Europe as part of ESA's Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems (ARTES) program.
-
In February 2023, SES, ThinKom, and Hughes successfully demonstrated a pioneering high-performance multi-orbit service, offering versatile solutions for government airborne missions.
Key Players
Service Providers / Manufacturers:
-
SES S.A. (O3b mPOWER, SES-17)
-
Viasat Inc. (ViaSat-3, ViaSat-2)
-
Intelsat (Intelsat 40e, EpicNG)
-
Hughes Network Systems (JUPITER System, HughesNet)
-
OneWeb (OneWeb Constellation, OneWeb Satellites)
-
SpaceX (Starlink, Falcon 9)
-
Thales Alenia Space (Space Inspire, Globalstar)
-
Lockheed Martin Corporation (AEHF-6, LM 2100)
-
Telesat (Telesat Lightspeed, Anik F3)
-
Eutelsat Communications (Eutelsat Quantum, KONNECT VHTS)
Users of 5G Satellite Services/Products:
-
Amazon
-
Microsoft
-
Google
-
Tesla
-
Vodafone Group
-
Boeing
-
Facebook
-
Apple
-
Airbus
-
Deutsche Telekom
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 4.1 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 28.6 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 24.1% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Orbit (Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), Lower Earth Orbit (LEO), Others) • By Frequency bands (S-band (2–4 GHz), C-band (4–8 GHz), Ku band and Ka band (12–18 GHz), Others) • By Solution Type (Trunking and Head-end Feed, Backhauling and Tower Feed, Communications on the Move, Hybrid Multiplay) • By End User (Commercial, Consumer, Defence, Government) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | SES S.A., Viasat Inc., Intelsat, Hughes Network Systems, OneWeb, SpaceX, Thales Alenia Space, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Telesat, Eutelsat Communications |
| Key Drivers | • 5G satellites offer widespread connectivity in rural and underserved regions, enhancing communication access. Increased reliance on IoT devices and autonomous vehicles requires high-speed, low-latency networks that 5G satellites provide. • 5G satellites complement terrestrial infrastructure, ensuring seamless communication even in challenging environments. The allocation of higher spectrum bands (e.g., mmWave) for 5G satellite networks boosts data transmission speeds and network capacity. |
| RESTRAINTS | • The cost of launching and maintaining satellite networks remains prohibitively expensive, limiting the entry of smaller players. Harmonizing satellite and terrestrial network technologies presents complex technical hurdles that delay widespread adoption. • Differing international regulations and spectrum allocation challenges create barriers to uniform global 5G satellite deployment. |

