Healthcare Biometrics Market Size & Report Overview:
Get more information on Healthcare Biometrics Market - Request Sample Report
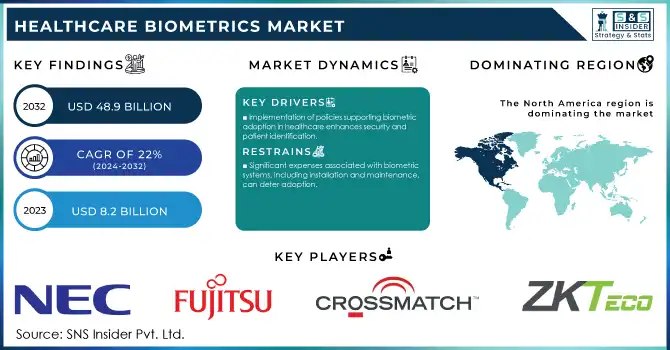
The Healthcare Biometrics Market size was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 48.9 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 22% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Increasing concerns about patient data security, growing incidences of healthcare fraud, and the requirement for attention in the patient identification process are some of the forces that are driving the healthcare biometrics market, and developing markets in the Asia-Pacific region are also expected to create growth opportunities. Growing government initiatives across the globe also represent a significant market-driving factor. As an example, HHS reported that healthcare data breaches in 2020 had increased by 55% in comparison to 2019 which underscores the need for strong security. To meet this challenge, the HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has ramped up its enforcement attention on institutions that are not in compliance with HIPAA and imposed fines of more than $13 million for data breaches in 2022. On another hand, the fine for non-compliance with the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was €1.6 billion in 2022 which has triggered the uptake of Biometric technologies in healthcare.
The pandemic of COVID-19 has accelerated the shift towards biometric solutions in healthcare even more, in 2020 the World Health Organisation (WHO), announced a global increase of 63% of telemedicine services. With the shift has come an increased need for secure remote patient identification. In addition, U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have introduced new rules for healthcare providers to access electronic health records using multi-factor authentication, which in turn propels the biometric solutions demand. Facial recognition still has some way to go, but technological progress is also helping out, with the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reporting a 20x boost in accuracy over facial recognition test databases between 2014 and 2023.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
Implementation of policies supporting biometric adoption in healthcare enhances security and patient identification.
-
Increasing incidents of data breaches and medical identity theft necessitate advanced biometric solutions for protection.
Government projects have been some of the initiatives facilitating the adoption of biometric technologies within the healthcare sector, aimed to enhance information safety, patient identification, and healthcare services. For instance, the South African Social Security Agency (SASSA) implemented a biometric enrollment system to authenticate beneficiaries, effectively reducing fraud in social grant distributions. In India, more and more healthcare institutions have begun to implement biometric attendance services over the past years. The system seems to be very productive in terms of staff punctuality and, as a result, hospital care. Recent studies demonstrate that biological attendance has been integrated into 96% of district hospitals, 99% of sub-district hospitals, and over 62% of satellite hospitals. At the same time, 96% of district hospitals, 100% of sub-district hospitals, and over 62% of satellite hospitals use CCTV cameras to control timely staff arrivals. In this way, the integration of biometrics within the healthcare sector seems productive for patient care and overall hospital performance. The examples prove that government initiatives are efficient in fostering the implementation of biometric systems. When governments focus on establishing biometric systems, they can target a range of problems like fraud, healthcare delivery inefficiency, or information safety. In turn, more effective hospitals and improved patient care will be achieved.
Restraints:
-
Significant expenses associated with biometric systems, including installation and maintenance, can deter adoption.
-
Issues like false positives/negatives in recognition technologies may impact accuracy and reliability.
The use of biometric systems in the healthcare system is often limited by high purchase, installation, and maintenance costs for hardware and software. However, advanced biometric technologies, such as fingerprint scanners, facial recognition systems, and iris scanners, can be relatively costly to implement, which may pose a barrier to entry for smaller to medium-sized healthcare providers due to the high up-front costs of technology adoption. The need for specialized skills to integrate these systems with current healthcare IT is noticeable to increase costs.
Operational costs such as frequent software updates, periodic system calibration, and personnel training into the cost equation. Such costs can be prohibitive to adoption, especially in geographies without deep healthcare budgets or healthcare systems working in low-margin environments. Despite their potential to enhance security and patient management, the financial implications of biometric systems pose a significant barrier, slowing down their widespread deployment and limiting their accessibility to resource-constrained organizations.
Healthcare Biometrics Market Segmentation Analysis
By Type
In 2023, the single-factor authentication segment accounted for the highest market share of 63%. This dominance is driven by the widespread adoption, affordability, and availability of nucleic acid testing in the healthcare environment. This level of authentication primarily uses fingerprints or facial recognition to help ensure that patient data is accessed only by the right people, while reducing the burden of providing multiple passwords or logins, thus falling in the middle ground between security and usability, which is why many healthcare providers prefer to opt for this. A 2023 survey conducted by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) found that 78% of healthcare organizations have adopted a biometric authenticator in some form, although the most deployed systems are single-factor in nature. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), single-factor biometric systems can achieve up to a 99.7% accuracy rate in a controlled environment, which is good enough for various use case scenarios of the healthcare system.
In addition, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) implemented a requirement for at least single-factor authentication to access electronic health records, fostering significant usage. One of the leading reasons is the cost-effectiveness of single-factor systems, as the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) estimates implementing multi-factor authentication can cost as much as 3.5 times compared to a single-factor solution. This cost differential is especially relevant to smaller healthcare providers and rural hospitals that operate on thin profit margins. Moreover, the relative ease of use of single-factor systems fits well with the current demand to process patients rapidly and efficiently for better patient accommodation in high-volume healthcare environments (AHA; 2023).
By Technology
In 2023, the fingerprint recognition segment dominated the Global Biometric Systems Market with a revenue share of 38%. This leadership position can be attributed to the technology's maturity, widespread acceptance, and proven reliability in healthcare settings. Fingerprint recognition, due to its unique combination of accuracy, usability, and cost has made it the top selection for many healthcare providers. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in tests, has found that, in controlled environments, fingerprint recognition systems can achieve accuracy rates as high as 99.9%, outperforming numerous other biometric modalities. Many fingerprint-based systems have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the healthcare sector as they are reliable and non-invasive.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has also endorsed fingerprint biometrics as a hygiene-friendly option when implemented with proper sanitization protocols, especially important in healthcare settings. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) revealed that 65% of healthcare data breaches in 2022 were preventable with better authentication solutions, which certainly shows the need for reliable biometric solutions such as fingerprint technology. The range of use cases for the versatile technology is seen in its widespread adoption in healthcare from patient identification to safe access to electronic health records (EHRs). The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) has reported that 72% of hospitals using biometric authentication in 2023 employed fingerprint recognition systems, underscoring its dominance in the healthcare sector.
By Application
In 2023, the patient identification & tracking segment dominated the market, accounting for 34% of the global share. The critical need for accurate patient identification to prevent medical errors, improve patient safety, and enhance care quality in healthcare settings has been attributed to this dominance. The World Health Organization (WHO) notes that the misidentification of patients is one of the top contributors to medical errors and leads to 400,000 deaths a year globally. a National Patient Safety Goal that focuses on accurate patient identification in healthcare delivery within the United States by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO). According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), patient identification errors result in more than $6 billion in annual costs to the healthcare industry annually, which illustrates the financial impact that this problem has. These concerns have been met with great efficacy by identifying patients with biometric patient identification systems.
Research performed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) showed that medical errors were 35% lower and patient satisfaction scores were 22% higher after using biometric patient identification. CMS also sees the value in biometric patient identification and has made it a recommended practice for reducing hospital readmissions. Information Technology (ONC) said that in 2023, among healthcare providers that had deployed the use of biometrics, 68% used biometrics for patient identification and tracking. This widespread adoption is driven by the technology's ability to prevent duplicate medical records, reduce fraud, and ensure continuity of care across different healthcare settings.
By End Use
The hospitals & clinics segment was the largest in the market in 2023 and accounted for 49% of the overall revenue share. The largest share of the patient verification market can be attributed to a large volume of patient interactions, a high need for reliable patient identification, and complex security requirements in hospital and clinic settings. As of 2022, there were more than 36 million hospital admissions in the USA, highlighting how many patients experience these appointments and stay in these buildings, according to the American Hospital Association (AHA). In the same year, there were more than 883 million outpatient clinic visits in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The healthcare sector is considered to be a significant adopter of biometric technologies and is mainly driven by the requirement of stringent regulatory adherence in hospitals and clinics.
In a 2022 report by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR), hospitals and clinics were cited in 60% of healthcare data breaches, further supporting the need for up-to-date security. As a result, the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) has added biometrics as a best practice in their patient safety goals. As per the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), biometric systems operated in a healthcare setting can attain accuracy rates of as high as 99.8%, thus ensuring the best patient identification and access control in the healthcare systems. Furthermore, a study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that implementing biometric patient identification in hospitals reduced medical errors by 25% and improved patient throughput times by 15%, demonstrating the tangible benefits of these technologies in hospital operations.
Regional Insights
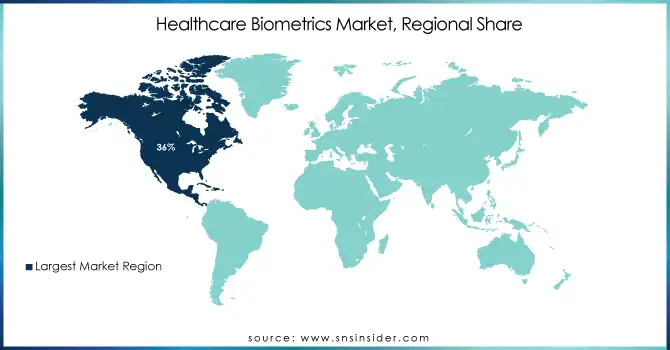
North America held the largest share of 36% in the healthcare biometrics market. The region's mature healthcare system, stringent regulatory environment, and favorable early adoption of leading-edge technologies have all contributed to this leadership position. Biometric implementations in healthcare are especially growing in the United States. By 2023, more than 75% of hospitals in the country will use some cool kind of biometric technology, mainly inpatient identifications and staff authentications (HHS). The region's dominance is further reinforced by substantial government investments in healthcare IT infrastructure. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) reported that federal spending on healthcare IT reached $8.5 billion in 2023, with a significant portion allocated to enhancing data security and patient identification systems.
On the contrary, the Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing region and is expected to register an exceptional CAGR during the forecast period 2024–2032. The increasing healthcare expenditure, the growing awareness towards patient safety, and initiatives taken by governments to modernize healthcare systems are leading to faster expansion. Asia-Pacific had a share of the global healthcare biometrics market in 2023. China and India are the main growth drivers in this area. China devotes massive money to healthcare digitization (biometric technologies particularly) through its so-called Healthy China 2030 plan. The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) in India is focused on developing an integrated digital health infrastructure with biometric authentication for accessing health records. A testament to the overwhelming scale of biometric adoption in the region with over 300 million Indian citizens enrolled as of 2023. This is surging owing to the region's population base, along with the rising chronic diseases that need robust, cost-effective, and secure healthcare systems to manage them.
Need any customization research on Healthcare Biometrics Market - Enquiry Now
Recent Developments
-
Imprivata, Inc., a provider of patient identity solutions, announced Biometric Patient Identity, a facial recognition tool that helps healthcare institutions guarantee correct and secure patient identification in February 2024. This solution assists healthcare providers in reducing medical errors and improves patient safety.
Key Players
Key Service Providers/Manufacturers
-
NEC Corporation (NeoFace®, Bio-IDiom)
-
Fujitsu Limited (PalmSecure™, BioSec)
-
3M Cogent, Inc. (Cogent BioTrust™, Cogent BioKit)
-
Bio-Key International, Inc. (ID Director for Healthcare™, Biometric Service Platform)
-
Crossmatch Technologies (DigitalPersona®, Verifier Sentry)
-
M2SYS Technology (RightPatient®, CloudApper Biometric)
-
Safran Identity & Security (MorphoWave™, MorphoTablet)
-
Imprivata, Inc. (OneSign®, Confirm ID)
-
Integrated Biometrics, LLC (Watson Mini®, Kojak)
-
ZKTeco USA (BioTime®, ZPad Plus)
Key Users of Services and Products
-
Mayo Clinic
-
Cleveland Clinic
-
Kaiser Permanente
-
Mount Sinai Health System
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
-
Apollo Hospitals
-
Fortis Healthcare
-
NHS (National Health Service)
-
Singapore General Hospital
-
Medanta - The Medicity
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 8.2 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 48.9 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 22% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Type (Single Factor Authentication, Multi-Factor Authentication, Multimodal Authentication) • By Technology (Face Recognition, Fingerprint Recognition, Iris Recognition, Vein Recognition, Palm Geometry Recognition, Behavioral Recognition, Others) • By Application (Medical Record Security & Data Protection, Patient Identification & Tracking, Remote Patient Monitoring, Workforce Management, Pharmacy Dispensing, Others) • By End-use (Hospitals & Clinics, Healthcare Institutions, Research & Clinical Laboratories) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe] Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | NEC Corporation, Fujitsu Limited, 3M Cogent, Inc., Bio-Key International, Inc., Crossmatch Technologies, M2SYS Technology, Safran Identity & Security, Imprivata, Inc., Integrated Biometrics, LLC, ZKTeco USA |
| Key Drivers | • Implementation of policies supporting biometric adoption in healthcare enhances security and patient identification. • Increasing incidents of data breaches and medical identity theft necessitate advanced biometric solutions for protection. |
| Restraints | • Significant expenses associated with biometric systems, including installation and maintenance, can deter adoption. • Issues like false positives/negatives in recognition technologies may impact accuracy and reliability. |

