GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market Size:
Get More Information on GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market - Request Sample Report
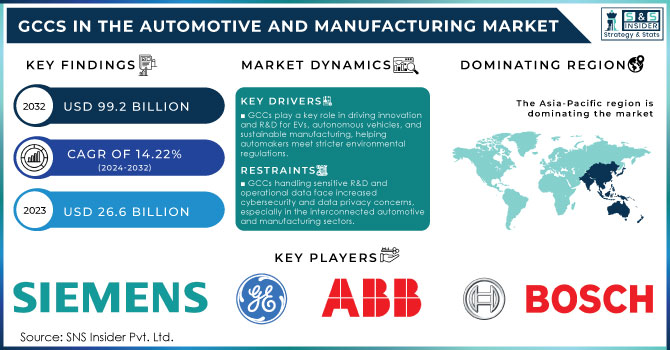
The GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market Size was valued at USD 26.6 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 99.2 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 14.22 % over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The growth of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in the automotive and manufacturing sectors is significantly driven by several factors, there is the rapid adoption of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things. These technologies help GCCs to streamline their operations, manage their supply chains, and optimize their production processes. AI will help to increase GCCs’ productivity while reducing downtime. There is the rapid implementation of digital transformation factors, coupled with the support of the central governments to bolster innovations within important sectors. As a result, automotive sector GCCs are playing a significant role in the global growth of the automotive market. According to SNS Insider, the global automotive industry will grow to reach USD 1.8 trillion by 2030, and play a critical role in enabling this growth. GCCs help multinational companies (MNCs) streamline operations, drive innovation, and reduce costs by leveraging global talent pools. Governments in emerging economies like India and Brazil have been actively encouraging the establishment of GCCs, offering tax incentives and infrastructure support. For instance, India’s Ministry of Commerce reported a 20% increase in the number of newly established GCCs in 2023, primarily in the automotive and manufacturing sectors.
Several factors support the growth of GCCs in the automotive and other manufacturing sectors in the European Union. As part of its Green Deal, the EU aims to reduce carbon emissions in manufacturing by 55% by 2030, creating significant opportunities for GCCs to drive sustainability initiatives. There is a high level of demand for electric vehicles and advanced automotive technologies, such as autonomous driving which require sophisticated global R&D capabilities. In response, several leading automotive manufacturers, including BMW, Ford, and Toyota, have expanded their GCC presence in key markets to tap into local expertise and accelerate product development cycles. These trends underscore the importance of GCCs in shaping the future of the automotive and manufacturing industries as global centers of innovation and efficiency.
GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market Dynamics
Drivers
-
GCCs are crucial in driving innovation and R&D for the rapid shift toward EVs, autonomous vehicles, and sustainable manufacturing processes, supporting global automakers’ efforts to meet stricter environmental regulations.
The most important driver for Global Capability Centers in the automotive industry deals with their expanded focus on electric vehicles and sustainable technologies. Automakers all over the world are currently investing significant resources in GCCs to enhance R&D, innovation, and engineering related to the transition, which is driven by a range of factors including regulatory environment and consumer demand. Therefore, according to the data, EV sales across the globe went up by 35% to 2023 with over 10 million units sold, which demonstrates the high demand for new zero-emission vehicles. Leading industry manufacturers, including Tesla, Volkswagen, and Ford, utilized their GCCs in India and Eastern Europe, which employed a cost-effective engineering workforce, to focus on battery technology, software development, and autonomous driving capabilities.
Moreover, government regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions are pushing manufacturers to invest in sustainable technologies like battery recycling and lightweight materials. In response, GCCs are being tasked with developing new solutions to improve EV range, charging infrastructure, and energy efficiency. For instance, BMW's R&D centers in China and India are focusing on EV battery optimization, while Toyota is working on hydrogen fuel cell technology, leveraging its global centers for innovation. In addition, the European Union has set its framework for banning the sales of new internal combustion engine passenger cars by 2035. GCCs would contribute to the industry’s success by helping it cut emissions to meet the expected stringency of the goal.
-
With the advent of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT, AI, and robotics, GCCs in the manufacturing sector are vital in integrating advanced digital capabilities like predictive maintenance, smart factories, and supply chain optimization.
Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in the manufacturing sector are playing a important role in the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics, driving significant advancements in automation and operational efficiency. These technologies are enabling manufacturers to embrace smart factories, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization, which are transforming traditional production models. For instance, by 2023, the adoption of industrial IoT solutions increased by over 28%, with more than 50 billion connected devices globally. GCCs are leveraging this trend by implementing IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics for predictive maintenance, reducing machine downtime by as much as 30%. Siemens' GCCs, for example, are focused on developing digital twins and AI algorithms for real-time equipment monitoring, significantly improving production line efficiency.
Additionally, smart factories equipped with robotics and automation tools are becoming more common, driven by GCCs' expertise in handling advanced robotic process automation (RPA) systems. Bosch has set up a network of GCCs to enhance its factories with AI and robotics, optimizing workflows and reducing manual intervention. Moreover, supply chain optimization through AI has become essential, with GCCs like those of Schneider Electric using AI to predict demand fluctuations and optimize logistics. These advancements enable manufacturers to respond faster to market changes while minimizing waste and improving productivity, showcasing the transformative impact of Industry 4.0 technologies in manufacturing.
Restraints:
-
As GCCs deal with sensitive R&D and operational data, there are heightened concerns around cybersecurity and data privacy, especially in highly interconnected automotive and manufacturing sectors.
Rising cybersecurity and data privacy concerns also remain a major Constraint for Global Capability Centers (GCCs), As GCCs handle sensitive information related to R&D, intellectual property, production processes, and supply chain operations, they become attractive targets for cyberattacks. The highly interconnected nature of the automotive and manufacturing industries, which increasingly rely on IoT, cloud computing, and data-driven decision-making, amplifies these risks.
GCCs have to comply with stringent data privacy regulations such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in the U.S. making their operations even more difficult. Even a small data breach or a cyberattack can cause great loss to the organization financially and reputationally, along with other legal penalties. This requires substantial investment in sophisticated, defensive cybersecurity systems at GCCs as well as training and compliance programs; ultimately driving up operational costs and adding complexity to their global operations.
GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market Segmentation Overview
By Functional Expertise
The digitalization and Tech Design segment held the largest share of the Global Capability Centers for GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market. The tremendous demand for Industry 4.0 technologies triggers the need for digitalization. Manufacturing companies are trying to enhance efficiency, cut costs, and drive time-to-market. They aim to automate numerous manufacturing processes, ensuring predictive maintenance, and boosting production quality with the help of digitalization. According to a report by the World Economic Forum, the manufacturing sector contributes to almost 16% of the global GDP. It means that this contribution is about to increase thanks to digitalization because digitalized companies are more productive and efficient. It can be achieved through the integration of IoT, digital twins, and cloud computing into their manufacturing ecosystems. These technologies enable the automation of processes in the automotive sector as well. Moreover, the shift towards electric vehicles and autonomous driving fosters the demand for various innovative software and equipment designs within the making of smart features in vehicles. Thereby, the need for digitalization is the most remarkable among the functional expertise segments, which is why it is expected to be the most demanded in the future.
The Product Design and Development segment is growing with explosive growth in the coming years. The current trend towards electric vehicles and the increasing need for smart vehicle technologies contribute to the surge of this segment. As a fact, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics expects that the employment of industrial engineers, who often handle product design, will grow by 7% from 2020 to 2030. The increase is mainly due to the substantial advancements in the automotive sector. The shift towards EVs urges companies to invest in the development of new technologies and materials for engineering. Besides, smart vehicles are designed to be connected to other hardware either within the vehicle or outside it, with the help of increasingly popular features, including Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems and automation. All these trends imply the need for sophisticated vehicle designs in terms of electronics. Companies also focus on making machinery as effective as possible to optimize production processes and cut operation costs, which implies a need for innovations. The role of GCCs is invaluable since they provide the necessary R&D, talented workforce, and technologies supporting rapid iteration design and prototyping thanks to their distributed teams. The approach facilitates the time-to-market, which is critical in the contemporary fast-developing world with high competition, enabling automotive and manufacturing companies to remain successful and innovative.
By Industry Application
The Global Capability Centers (GCCs) landscape is dominated by the Automotive OEMs segment, owing to the increasing demand existence for innovative technologies including electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving systems, and advanced connectivity features; pushing automotive manufacturers to considerably strengthen their research and development capabilities. GCCs are a key enabler of this transformation, offering dedicated domain expertise and resources to drive product development and improve supply chain efficiencies. In addition, the automotive sector needs to comply with high legislative demands related to emissions and safety standards that require continuing innovation. With companies moving towards sustainable practices in a digital-first world, GCCs provide the strategic advantage of rapid prototyping, data analytics, and ease of technological integration. Consequently, the focus on electric mobility, coupled with the increasing complexity of modern vehicles, underscores the automotive OEMs segment as the leading sector in leveraging GCCs to achieve competitive advantages and meet evolving market demands.
By Innovation and Emerging Technologies
Connected Vehicles & IoT segment held a significant share in the automotive market because as consumer expectations evolve, there is growing demand for vehicles with improved connectivity that allow easy integration to smartphones, smart home devices, and many online services. This connectivity not only enables real-time navigation and entertainment options but also strengthens advanced safety features like collision avoidance systems and adaptive cruise control, contributing to an enhanced driving experience. The connected vehicle technology has the potential to reduce the number of all motor vehicle crashes by as much as 80%, according to the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT), making IoT devices for cars significant in improving vehicle safety. To advance the use of connected vehicle technology as a means to enhance safety and mobility, the DOT has been working on its integration into the transportation infrastructure.
Smart infrastructure, including traffic management systems and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, is essential for a more efficient and safer transportation ecosystem. In this process, Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have a significant role in utilizing IoT tools to collect and analyze large volumes of data generated by connected vehicles that provide insights such as enhancing performance, predicting maintenance needs, and improving fleet management. As automakers and tech companies collaborate to deliver smarter and more responsive vehicles, the Connected Vehicles & IoT segment is set to maintain its dominance, driving forward innovations that cater to the future of mobility.
GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market Regional Analysis
Owing to favorable government policies, strong availability of skilled manpower and major investment in infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region held the largest share of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in the automotive and manufacturing market. In 2023, India and China have seen substantial growth in their manufacturing sectors, with India's manufacturing output projected at USD 1 trillion by 2025 (World Bank). Make in India and "Made In China 2025" are the two government Initiatives to improve the manufacturing capability of each region while encouraging foreign investments. Additionally, the Asian Development Bank also indicated that infrastructure investment in the region is expected to be more than USD 1.7 trillion each year by 2030, facilitating the expansion of GCCs. This combination of supportive policies, skilled labour availability, and infrastructure development makes the Asia-Pacific region a prime hub for automotive and manufacturing GCCs, reinforcing its leading position in the global market.
Additionally, India is home to several prominent automotive Global Capability Centers (GCCs), with major companies such as Bosch, Ford, Hyundai, Stellantis, Volvo, Mercedes Benz, BMW, and Continental operating in the country. The majority of these GCCs are concentrated in Pune, Bengaluru, and Chennai, with Pune and Bengaluru alone accounting for more than 52% of the total automotive GCC units in India. Together, these three cities also house over 85% of the skilled talent available in the automotive GCC sector. Since 2021, several new automotive GCCs have established their centers in India, including Daimler Trucks, Switch, and Webasto. Additionally, companies like ZF, Hella, and BorgWarner have expanded their presence in the Indian market during the same period. Notably, approximately 50% of the automotive GCCs in India are headquartered in the United States and Germany.
Recent News and Developments
-
Caterpillar (2024) - Caterpillar has expanded its GCC in India, focusing on enhancing its capabilities in product development and digital technologies. This expansion aims to leverage local talent and boost operational efficiency, aligning with global trends in automation and digital transformation.
Key Players in GCCs in the Automotive and Manufacturing Market
Key Service Providers / Manufacturers
-
Siemens AG (Siemens Digital Industries Software, Siemens Teamcenter)
-
General Electric (GE) (GE Digital Wind Farm, Predix Platform)
-
ABB Ltd. (ABB Ability, RobotStudio)
-
Bosch Group (Bosch IoT Suite, Bosch Connected Industry)
-
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) (TCS DigiFleet, TCS Smart Manufacturing)
-
Capgemini (Capgemini Manufacturing Cloud, Smart Industry)
-
Cognizant (Cognizant Smart Factory, Intelligent Manufacturing)
-
Infosys (Infosys Manufacturing Edge, Infosys Cloud)
-
Wipro Limited (Wipro Holmes, Wipro Digital Operations)
-
Accenture (Accenture Industry X.0, Accenture Connected Asset)
Key Users of Services and Products
-
Toyota Motor Corporation
-
Volkswagen AG
-
Ford Motor Company
-
General Motors (GM)
-
Nissan Motor Corporation
-
Boeing
-
Honeywell International Inc.
-
Lockheed Martin
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 26.6 Billion |
| Market Size by 2032 | USD 99.2 Billion |
| CAGR | CAGR of 14.22% From 2024 to 2032 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Historical Data | 2020-2022 |
| Report Scope & Coverage | Market Size, Segments Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Regional Analysis, DROC & SWOT Analysis, Forecast Outlook |
| Key Segments | • By Functional Expertise (Digitalization and tech design, AI and ML, Product design and development, Embedded systems, Quality Control & Testing) • By Service (End-to-End Support, Specialized/Niche Services, Consulting and Strategy Services, Managed Services for IT/Engineering, Shared Services) • By Innovation and Emerging Technologies (Connected Vehicles & IoT, Electrification & Electric Vehicles (EVs), Autonomous Driving, Additive Manufacturing & 3D Printing, Predictive Maintenance & AI-driven Insights, Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR) for Design & Training) • By Industry Application (Automotive OEMs, Heavy Machinery Manufacturing, Precision Engineering Firms, Industrial Equipment Manufacturers) |
| Regional Analysis/Coverage | North America (US, Canada, Mexico), Europe (Eastern Europe [Poland, Romania, Hungary, Turkey, Rest of Eastern Europe] Western Europe [Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, Rest of Western Europe]), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Australia, Rest of Asia Pacific), Middle East & Africa (Middle East [UAE, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Rest of Middle East], Africa [Nigeria, South Africa, Rest of Africa], Latin America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America) |
| Company Profiles | Siemens AG, General Electric (GE), ABB Ltd., Bosch Group, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Capgemini, Cognizant, Infosys, Wipro Limited, Accenture |
| Key Drivers | • GCCs are crucial in driving innovation and R&D for the rapid shift toward EVs, autonomous vehicles, and sustainable manufacturing processes, supporting global automakers’ efforts to meet stricter environmental regulations. |
| RESTRAINTS | • As GCCs deal with sensitive R&D and operational data, there are heightened concerns around cybersecurity and data privacy, especially in highly interconnected automotive and manufacturing sectors. |

